The end of communism in Europe was a significant event in modern history that marked the end of a political and economic ideology that had dominated much of the region for much of the 20th century. The fall of communism was a complex and multifaceted process that involved various factors, including economic and social changes, political reforms, and international pressure.
The roots of communism in Europe can be traced back to the Russian Revolution of 1917, when the Bolshevik Party, led by Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Tsarist regime and established the first socialist state in the world. The success of the Bolshevik Revolution inspired other communist movements throughout Europe, and by the mid-20th century, communist parties had come to power in a number of countries in Eastern and Central Europe, including Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania.
For much of the Cold War, these countries were part of the Soviet-led communist bloc, which was in ideological and political opposition to the Western, capitalist democracies. The communist regimes in Eastern and Central Europe were characterized by one-party rule, censorship, and state control of the economy and society.
However, by the 1980s, the communist regimes in Europe were facing a number of internal and external challenges that would eventually lead to their downfall. One of the main factors was the economic stagnation and decline that had plagued many of the communist countries for years. The central planning and state control of the economy had resulted in inefficiencies and shortages, which had a negative impact on the standard of living of the population.
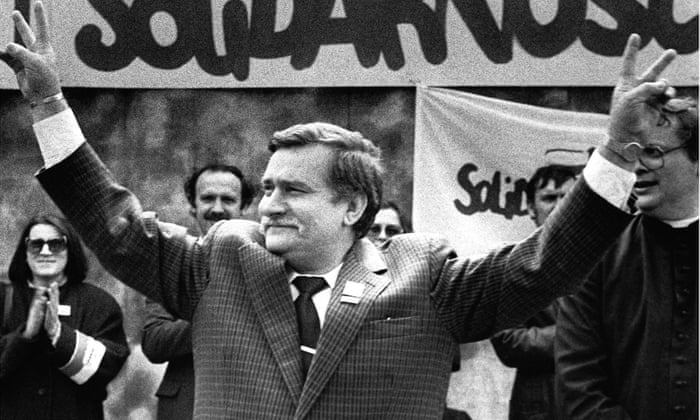
Another factor was the growing discontent and resistance to communist rule within the region. Many people in Eastern and Central Europe were disillusioned with the lack of political freedom and human rights under communist regimes, and they began to demand change. This was especially true in countries like Czechoslovakia, where the pro-democracy movement known as Charter 77 had emerged in the 1970s, and in Poland, where the Solidarity movement had gained significant support in the 1980s.
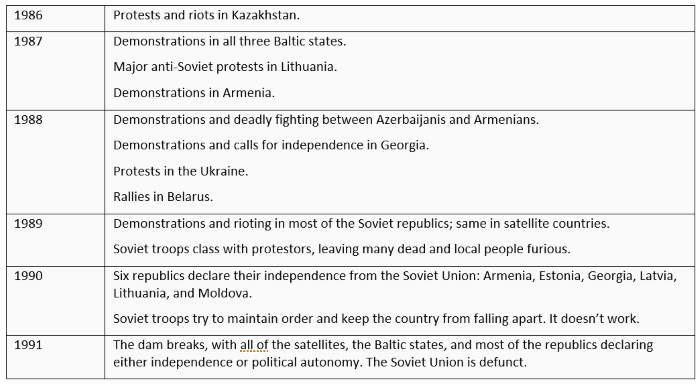
The collapse of communism in Europe was also influenced by international developments, such as the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, which had been the main ally and protector of the communist regimes in Eastern and Central Europe. The collapse of the Soviet Union weakened the Soviet influence in the region and provided an opportunity for the people of Eastern and Central Europe to pursue their own paths towards democracy and market economies.
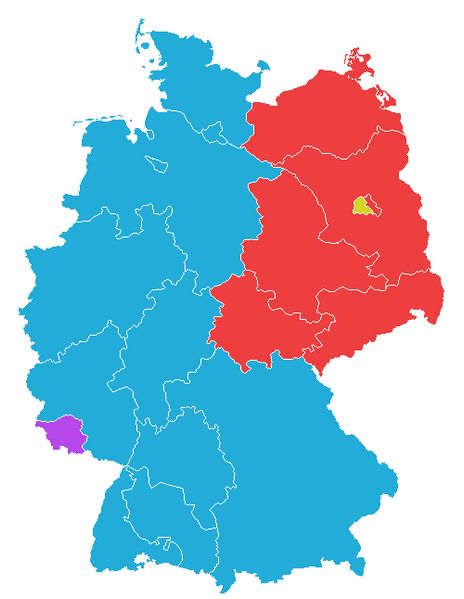
The end of communism in Europe was not a sudden or uniform process, and it took place at different times and in different ways in different countries. In some countries, like East Germany, the collapse of communism was relatively peaceful and occurred through negotiations and reforms, while in others, like Romania, it was marked by violent uprisings and civil war.
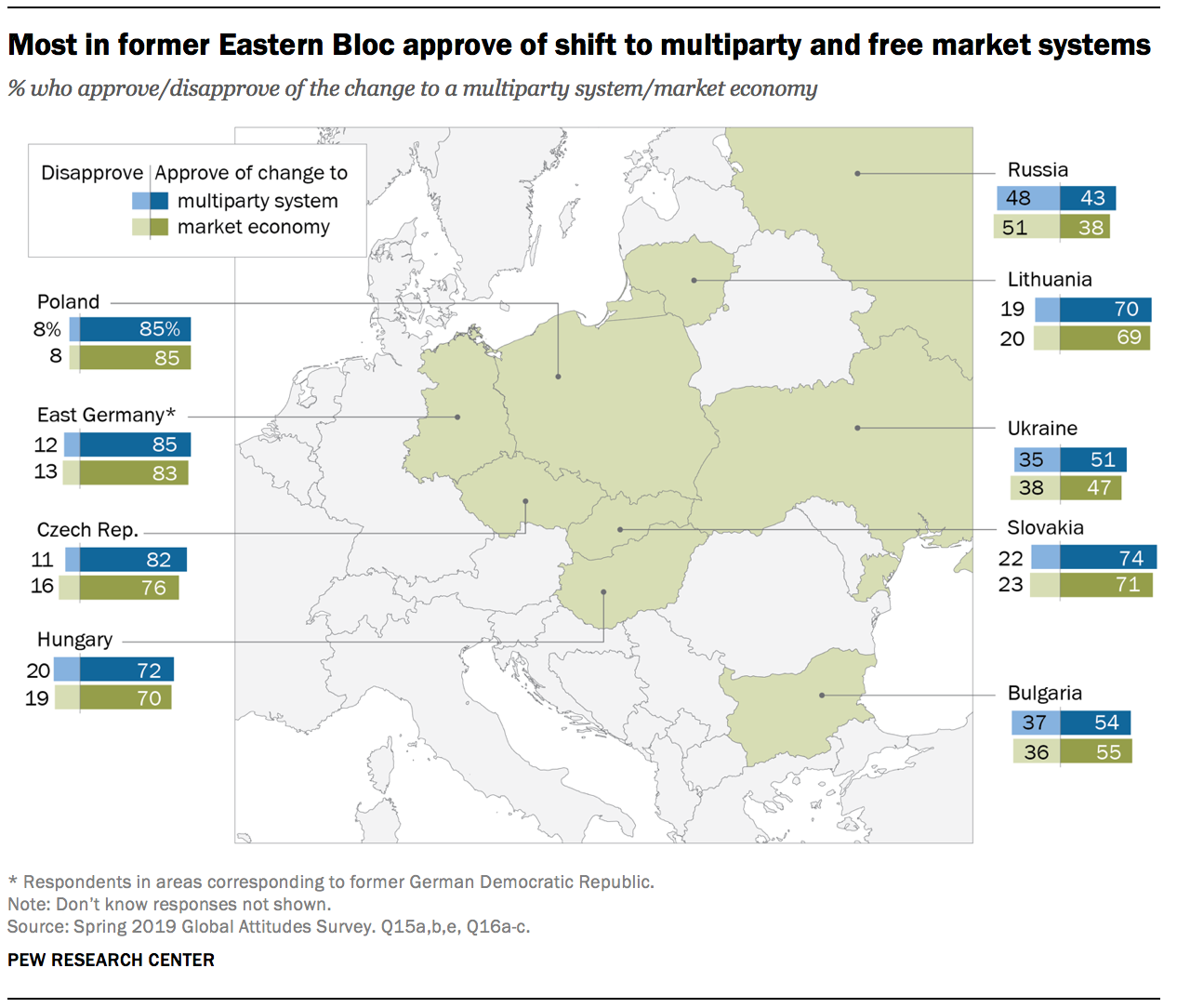
Overall, the end of communism in Europe represented a significant shift in the political and economic landscape of the region and had far-reaching consequences for the rest of the world. It was a major milestone in the process of democratization and integration of Eastern and Central Europe into the Western world, and it contributed to the end of the Cold War and the emergence of a more united and peaceful Europe.