John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker who made significant contributions to the fields of political philosophy and empiricism. He is best known for his ideas on the social contract, which form the basis for modern liberal democracy.
Locke was born in 1632 in Somerset, England. He studied at Oxford University and became a professor of Greek and Latin. However, he is best known for his philosophical work, which was heavily influenced by the scientific revolution of the time.
One of Locke's most important contributions to political philosophy is his concept of the social contract. In his view, individuals are naturally free and equal, and the role of government is to protect their natural rights. These rights include life, liberty, and property, and are inherent to all people. In order to protect these rights, individuals must agree to give up some of their freedom to a government in exchange for the protection of their rights. This idea forms the basis for modern liberal democracy, in which individuals are free to make their own choices as long as they do not harm others.
Locke also made significant contributions to empiricism, the belief that knowledge comes from sensory experience. In his Essay Concerning Human Understanding, Locke argued that the mind is a blank slate at birth and that all knowledge is gained through experience. This idea was influential in the development of modern psychology and the scientific method.
In addition to his work on the social contract and empiricism, Locke also made significant contributions to the field of education. He believed that education should be based on practical knowledge and that it should be available to all, not just the wealthy. He also argued that individuals have a natural right to freedom of religion and that the government should not interfere in matters of faith.
Overall, John Locke was an influential Enlightenment thinker who made significant contributions to the fields of political philosophy and empiricism. His ideas on the social contract and the importance of sensory experience continue to influence modern thought and shape the way we think about society and the role of government.
1.3: Enlightenment Thinkers and Democratic Government

Philosophers who had a great impact during the Enlightenment period included: John Locke, Voltaire and Montesquieu, Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Adam Smith. John Locke believed that people are born with natural rights, including life, liberty, and property. Locke coordinated the advice of several physicians and was probably instrumental in persuading Ashley to undergo surgery then life-threatening in itself to remove the cyst. He founded the modern theory of Liberalism and made an exceptional contribution to modern philosophical empiricism. They declared that governments get their power from the people and that people have the right to change or alter a government when it becomes destructive.
John Locke

How Did The Enlightenment Impact The American Revolution 543 Words 3 Pages During the Enlightenment there were lots of important and impacting philosophers. Gender, Class, and Freedom in Modern Political Theory. The english bill of rights influenced the U. He was also influential in the areas of theology, religious tolerance and educational theory. It maintains that all forms of knowledge can be reduced to only one origin and that is our sense perception. By his death in 1704, Locke had amassed a library of more than 3,000 books, a significant number in the seventeenth century. These intellectual and ethical values are not the exclusive preserve of the West, no matter how much white Europeans like to think so.
John Locke's Theory Of The Enlightenment: The Age Of...

How did Enlightenment philosophers influence the Founding Fathers of American government? The Enlightenment was also known as the Age of Reason or Age of Enlightenment. As the National Center for History in Schools 1992 noted: "The first great upheavals to be marked - though surely not 'caused' - by Enlightenment thought were the American and French revolutions, and they opened the modern era of world history" p. Jean Jacques Rousseau b. However, both philosophers did, in fact, have their personal views that helped them accomplish important achievements. Voltaire believed and fought for religious tolerance. This is a legacy of Montesquieu's political philosophy in practice today. H , the separation of powers Mont.
What Enlightenment thinkers influenced the Founding Fathers?

Although women did not have many rights and privileges, de Gouges used ideas from the Enlightenment to advocate for greater rights for women and enslaved Black people. John Locke proposed that everyone was born free and had certain unalienable rights. Questions Concerning the Law of Nature definitive Latin text , translated by R. Who was the most important Founding Father? Constitution they were attempting to create a Magna Carta for a new era. Two Treatises of Government 10th edition : Chapter II, Section 6. Indeed, until the late 1800s, the British Monarchy effectively ruled the nation with the help of the House of Lords and the House of Commons. She believed that women should be given greater education because of their importance in raising children and being not just wives but partners or "companions" with their husbands.
Enlightenment Thinkers blog.sigma-systems.com
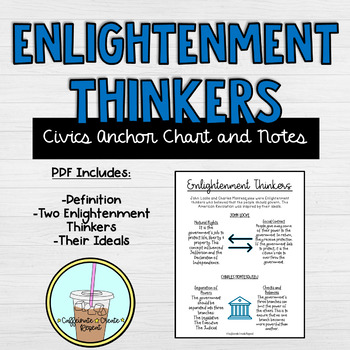
How did John Locke influence our government? To get any official new legislation passed into law, the U. John Locke was an Enlightenment thinker who proposed that as humans, we are entitled to basic rights and that when we are born we are blank canvases and are thereafter altered by our surroundings. All of Descartes, Locke, Berkeley, and Hume supposed that mathematics is a theory of our ideas, but none of them offered any argument for this conceptualist claim, and apparently took it to be uncontroversial. Arguing against both the all of our An Essay Concerning Human Understanding: This source of ideas every man has wholly within himself; and though it be not sense, as having nothing to do with external objects, yet it is very like it, and might properly enough be called 'internal sense. He explained the principle of checks and balances to limit government power. Ethics And the History of Philosophy. His 1762 work Rousseau believed that people could regain their lost freedom by creating a society where citizens choose to obey laws they themselves created, giving up some personal self gains in exchange for a wider common good.









