Apple Inc is a multinational technology company that designs and develops consumer electronics, computer software, and online services. It was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, and it is headquartered in Cupertino, California. Apple is known for its innovative products, such as the iPhone, iPad, Mac, iPod, and Apple Watch, as well as its services, including the App Store, Apple Music, and iCloud.
The corporate structure of Apple Inc consists of a board of directors, executive team, and various divisions and departments. The board of directors is responsible for the overall governance of the company and includes a mix of internal and external members. The executive team, which is led by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO), is responsible for the day-to-day management and operation of the company.
One of the key divisions within Apple is the hardware engineering division, which is responsible for the design and development of the company's hardware products, such as the iPhone, iPad, and Mac. Another division is the software engineering division, which is responsible for the development of the operating systems, applications, and other software products that run on the company's hardware.
In addition to these core divisions, Apple also has a number of other departments and functions, including marketing, sales, finance, human resources, and legal. These departments support the company's operations and help to ensure that it runs smoothly and efficiently.
One of the key characteristics of Apple's corporate structure is its strong focus on innovation and creativity. The company is known for its ability to constantly come up with new and innovative products and services, and it places a strong emphasis on research and development. This focus on innovation has helped Apple to become one of the most successful and respected technology companies in the world.
In conclusion, the corporate structure of Apple Inc is characterized by a strong focus on innovation and a clear division of responsibilities between the board of directors, executive team, and various divisions and departments. This structure has helped the company to become a leader in the technology industry and to consistently deliver high-quality products and services to its customers.
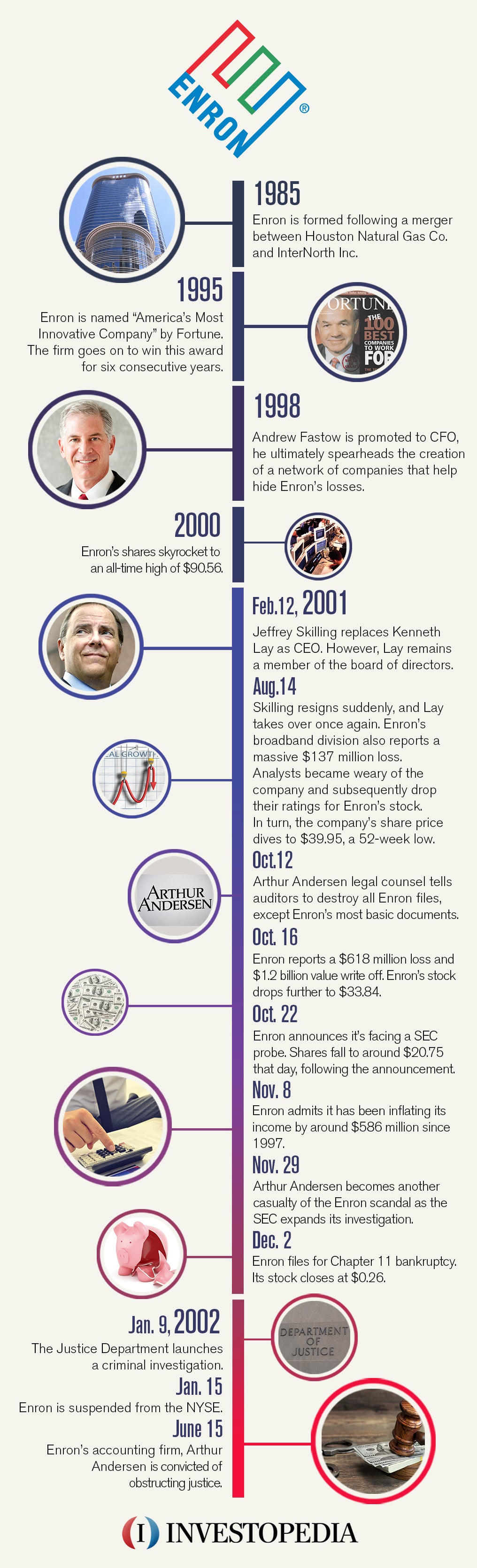
Enron was once a highly successful and innovative energy company, but it ultimately became synonymous with corporate corruption and unethical behavior. In the early 2000s, the company was at the center of one of the biggest corporate scandals in history, leading to the collapse of the company and the loss of thousands of jobs and billions of dollars for investors.
One of the main ethical issues at Enron was the company's use of accounting fraud to hide its financial problems and mislead investors and regulators. This included the use of special purpose entities (SPEs) to move debt off the company's balance sheet and manipulate financial statements. In addition, top executives, including CEO Jeffrey Skilling and CFO Andrew Fastow, sold off their own Enron stock while keeping this information from the public, resulting in insider trading.
Another major ethical issue at Enron was the company's culture of greed and pressure to meet performance targets at all costs. This led to unethical practices such as the manipulation of energy prices in California during the state's energy crisis, which resulted in rolling blackouts and led to widespread public outrage. Enron employees also engaged in activities such as shredding documents and deleting emails in an attempt to cover up their wrongdoing.
The Enron scandal had far-reaching consequences, leading to the downfall of the company, the loss of thousands of jobs, and the loss of billions of dollars for investors. It also had a significant impact on the public's trust in corporate America and led to the passage of stricter regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, designed to prevent similar corporate fraud in the future.
In conclusion, the ethical issues at Enron were widespread and included accounting fraud, insider trading, and a culture of greed that led to unethical practices. The scandal had a devastating impact on the company, its employees, and investors, and served as a wake-up call for the need for stronger corporate governance and ethical standards in the business world.