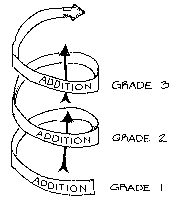
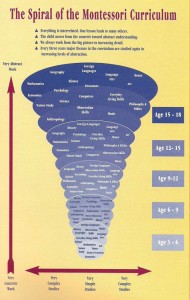
The spiral curriculum is an educational approach that emphasizes the repetition and reinforcement of concepts at increasingly complex levels. Rather than introducing new material in a linear fashion, the spiral curriculum gradually builds upon previously learned concepts, revisiting them multiple times throughout the educational process. This approach is based on the idea that students need to develop a deep understanding of fundamental concepts before they can effectively apply them to more complex tasks.
One of the key benefits of the spiral curriculum is that it allows students to gradually develop their understanding of a subject over time. By revisiting concepts multiple times, students are able to build a strong foundation of knowledge that they can then use to approach more advanced material. This can be particularly beneficial for students who may struggle with certain concepts at first, as it gives them the opportunity to revisit and reinforce their understanding as they progress through their education.
In addition to helping students build a strong foundation of knowledge, the spiral curriculum also allows for the integration of multiple subject areas. Because the spiral curriculum emphasizes the interconnectedness of different subjects, it can be used to encourage cross-curricular learning and the integration of different subject areas. For example, a math lesson might include elements of science and history, helping students to see how these subjects relate to each other and how they can be applied in real-world situations.
There are also some potential drawbacks to the spiral curriculum. Some critics argue that the emphasis on repetition can lead to boredom and a lack of motivation for students. Additionally, because the spiral curriculum involves a more complex and flexible approach to learning, it may be more difficult for teachers to plan and implement than more traditional, linear curricula.
Overall, the spiral curriculum is a valuable educational approach that emphasizes the importance of building a strong foundation of knowledge and the interconnectedness of different subject areas. While it may require more careful planning and implementation, the benefits of this approach can be significant for students as they develop a deeper understanding of the material and learn to apply their knowledge in a variety of contexts.
Spiral Curriculum Design & Learning Model
Our questioning requires students to make connections between topics, which teaches them the important study skill of elaboration Dunlosky, 2013. Then the students memorize the facts about numbers so that they no longer have to use number lines or count on fingers. A systemic approach is therefore required to analyse critical impediments and implement responsive interventions. The new information has a context to attach itself to, which was established in earlier grades. The spiral curriculum model indicates that courses do not include just a single lesson. In this way, they learned more about the subject by depending upon earlier simpler yet essential knowledge.
Spiral curriculum

And it seems to work. Lesson Summary A spiral curriculum can be defined as a course of study in which students will see the same topics throughout their school career, with each encounter increasing in complexity and reinforcing previous learning. New skills and notions are clearly related to previous learning, with the aim of progressively increasing competency Johnston, 2012; Harden, 1999. BMC Medical Education, 7 52 : doi:10. People confuse short-term performance with long-term learning and inaccurately predict that massed practice will lead to better long-term learning than spaced practice. Bruner, was an American psychologist who is best known for his contributions to cognitive and developmental psychology.
The Spiral: Why Everyday Mathematics Distributes Learning

Delegation, taking some time off, having some time to yourself? The teacher first demonstrates the process as the student watches. This is in Chapter 1 of textbooks, meaning that it is sometimes overlooked by teachers and students alike, and is considered too basic or boring. In sixth grade social studies, we introduce the agricultural revolution and the rise of civilizations and follow up in seventh grade with how those gave rise to patriarchy. Spiraling is effective with all learners, including struggling learners. This will help in learning new things with a reinforced foundation. Why does spacing work better than massing? When you return to the topic, the student may be at a developmentally appropriate level to understand the topic even more.
The Spiral Curriculum: A teacher's guide

Why is this a useful way of teaching? A spiral curriculum can be defined as a course of study in which students will see the same topics throughout their school career, with each encounter increasing in complexity and reinforcing previous learning. Last update:21 December, 2022 The spiral curriculum is about teaching a methodology proposed by the Singapore math method. They learn about laws, citizenship, and ethics. Spiral Curriculum Pros and Cons Anything good is bad. Spiraling also allows for more integration with other subject areas. In third grade, students will then learn about photosynthesis, which explains why plants need sunlight to grow.
Spiral Curriculum Model: Understand Its Pros and Cons

Educators would develop learning outcomes that have increasing levels of complexity. Mathematics Learning addition and subtraction with single digit numbers, then two-digit numbers. What is the research basis for spiraling? Instead of a linear progression, we now see the GCSE course as a web of linked ideas and we use a variety of techniques to emphasise this in our teaching. A better alternative may be mastery teaching, where a student does not move on until they have mastered the topic. As the ECE students progress through the integrated curriculum, they complete more complex robotics projects, and participate in courses that are tightly integrated with each other. Their education builds from a simple idea of communities to the analysis of major world conflicts. The ideas chosen were those important in securing understanding of the subject at GCSE and beyond, and those identified as poorly retained in mock examinations.
Teaching Using the Spiral Curriculum Approach
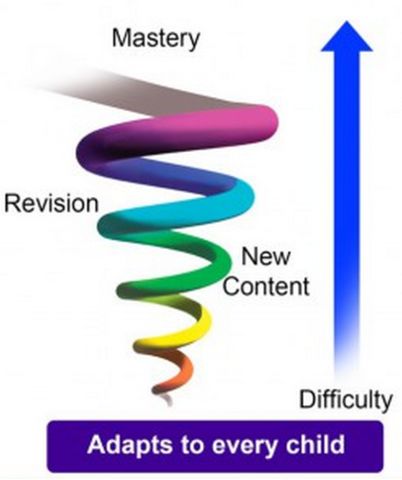
Key Principles of Spiral Curriculum The spiral curriculum has four key principles based on which effective education is achieved. Going from basic numbers to fractions would be a touchpoint. . Wilson F, Evans S and Old S 2015 Context led science courses: A review. When our first cohort sat their mock exams, we were disappointed in their answers on the knowledge recall questions and realised we needed to make changes to enhance long-term learning. If you have ever said to your students, ''Pay attention, this is something important that will come up again later in the year! Why does Everyday Mathematics spiral? What is a Spiral Curricula? Psychological Bulletin, 132, 354—380.