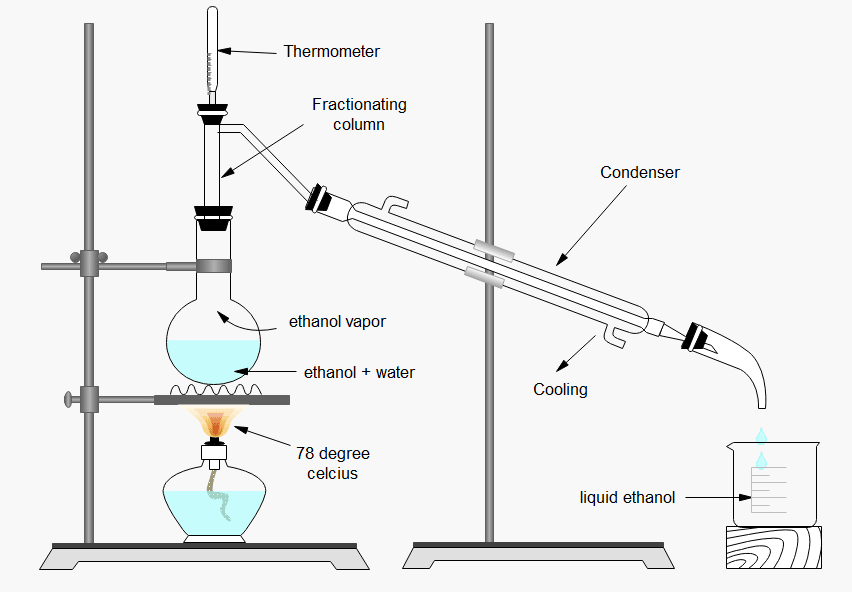
Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol or grain alcohol, is a clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic, pleasant odor. It is commonly found in alcoholic beverages, but it also has a variety of industrial and medical uses. When mixed with water, ethanol forms a homogeneous solution that is often referred to as a "dilute ethanol solution."
One of the most common uses of dilute ethanol solutions is as a disinfectant. Ethanol has antimicrobial properties, which means it can kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses. Dilute ethanol solutions are often used to disinfect surfaces, instruments, and skin in hospitals and other healthcare settings. They are also used in the food and beverage industry to sanitize equipment and surfaces.
Ethanol is also used as a solvent, which means it can dissolve other substances. When mixed with water, ethanol can dissolve a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds, making it useful in the production of various products such as perfumes, cleaning agents, and personal care products.
In addition to its industrial and medical uses, ethanol is also commonly consumed as an alcoholic beverage. Ethanol is the active ingredient in beer, wine, and spirits, and it is responsible for the intoxicating effects of these beverages. When consumed in moderate amounts, ethanol can have some health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. However, excessive consumption of alcohol can lead to a range of negative health outcomes, including liver damage, addiction, and increased risk of accidents and injuries.
In summary, ethanol mixed with water forms a dilute ethanol solution that has a variety of uses, including as a disinfectant, solvent, and alcoholic beverage. While ethanol has some potential benefits, it is important to use it responsibly and in moderation to avoid negative health consequences.

/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9061707/TOC_whiskey.png)