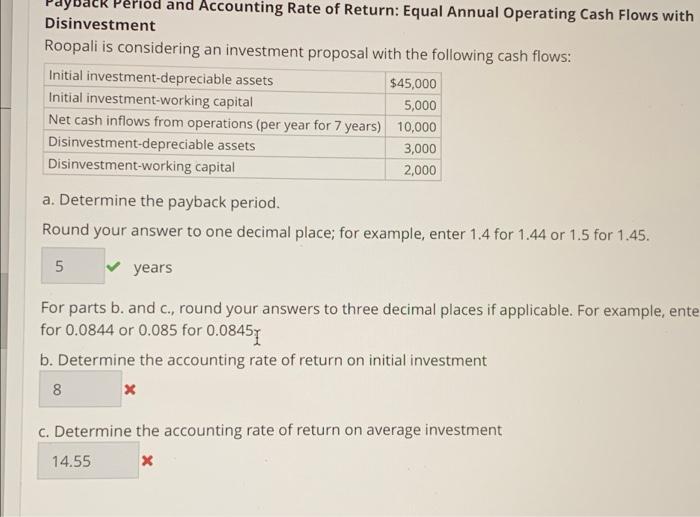
The accounting rate of return (ARR) is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of an investment. It is calculated by dividing the expected accounting profit of an investment by the initial investment cost. The resulting percentage is then used to evaluate the feasibility of an investment and compare the profitability of different investment opportunities.
An example of using the ARR to evaluate an investment can be seen in the following scenario:
A company is considering investing in a new piece of equipment that will cost $100,000. The company expects to generate $25,000 in annual profits from the use of this equipment. To calculate the ARR for this investment, we divide the expected annual profit by the initial investment cost:
ARR = ($25,000 / $100,000) x 100% = 25%
In this example, the ARR for the investment is 25%. This means that for every $1 invested in the new equipment, the company can expect to receive a return of $0.25.
One limitation of the ARR is that it does not take into account the time value of money. For example, if an investment generates a return of 25% over a period of 5 years, it may not be as attractive as an investment that generates a return of 15% over a period of 3 years. To account for this, some analysts may use the internal rate of return (IRR) or the net present value (NPV) to evaluate investments.
Overall, the ARR is a useful tool for evaluating the profitability of an investment. It provides a quick and easy way to compare the expected return on different investment opportunities, and can help a company make informed decisions about where to allocate its resources.
ARR

The internal rate of return IRR is a metric used in financial analysis to estimate the profitability of potential investments. It emphasizes accounting income, which is commonly used by investors and creditors in evaluating management performance. If ARR of a given project is 7%, the project is expected to earn 0. This number is based on accruals, not on cash, and it reflects the costs of amortization and depreciation. Example 3 J-phone is set to launch a new office in a foreign country and will now be assembling the products and sell in that country since they believe that the government has a good demand for its product J-phone. For example, if you are considering investing in a new piece of equipment for your business, you would want to compare the ROI of that equipment against other potential investments. How is RRR different from ARR? IRR is the rate at which the difference between the net present value of future cash flow ie NPV and the cash outflow is zero.
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR): Definition, How to Calculate, and Example

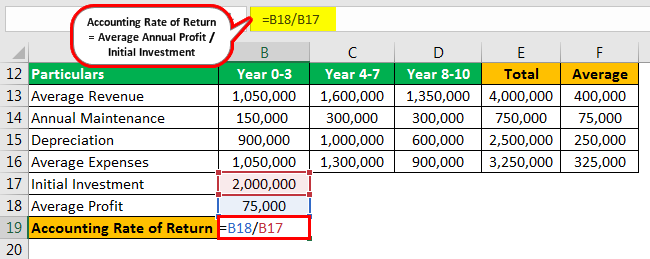
For example, if the minimum required return of a project is 12% and ARR is 9%, a manager will know not to proceed with the project. Also, the accounting rate of return can be used for ranking investments according to expected return or set a minimum benchmark return for selection. Finally, divide the Average Net annual Profit from the investment by the initial investment to arrive at the Accounting Rate of Return. When calculating the rate of return, you are determining the percentage change from the beginning of the period until the end. The denominator in the formula is the amount of investment initially required to purchase the asset. Expressed as It is expressed in the form of a percentage % It is expressed in the form of the ratio Discount Rate Finding a suitable discount rate is not a challenge for ARR. What would be the Accounting Rate of Return for the year? Example of Average Accounting Rate of Return Now, we will show how to apply ARR using MS Excel.
Accounting rate of return (ARR) method

IRR is a discount rate that makes the net present value NPV of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis. ARR is the annual percentage of profit or returns received from the initial investment, whereas RRR is the required rate of return that the investor wants. In view of this, recognizing revenues earlier and deferring expenses for later periods could lead to distortion of ARR results. Depreciation is a helpful accounting convention whereby the cost of a fixed asset is spread out, or expensed, annually during the useful life of the asset. Rely on accounting profit The accounting profit is very subjective, the management will be able to influence the final figure. Difference between ARR and IRR ARR versus IRR Basis of Difference Accounting Rate of Return A. While expected rates of return can be helpful in making decisions about where to invest, it is important to remember that they are only estimates.