Example of axial skeleton. Axial Skeleton Worksheet 2022-12-18
Example of axial skeleton
Rating:
7,3/10
1464
reviews
The axial skeleton is a part of the human skeleton that includes the bones of the head, neck, and spine. These bones provide support for the body, protect the brain and spinal cord, and allow for movement and flexibility.
One example of a bone in the axial skeleton is the skull. The skull is made up of several bones that are fused together and form the structure of the head. It contains the brain, the eyes, the ears, and the nose, and is responsible for protecting these important organs.
Another example of a bone in the axial skeleton is the vertebral column, also known as the spine. The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. It provides support for the body and allows for movement, such as bending and twisting. The spine is also responsible for protecting the spinal cord, which is a bundle of nerves that runs through the center of the vertebral column.
Other bones in the axial skeleton include the ribcage, which protects the vital organs in the chest, and the pelvis, which supports the lower body and allows for movement in the hips and legs.
Overall, the axial skeleton plays a vital role in the structure and function of the human body. It provides support, protection, and movement, and is an essential part of the human anatomy.
Introduction to the Axial Skeleton

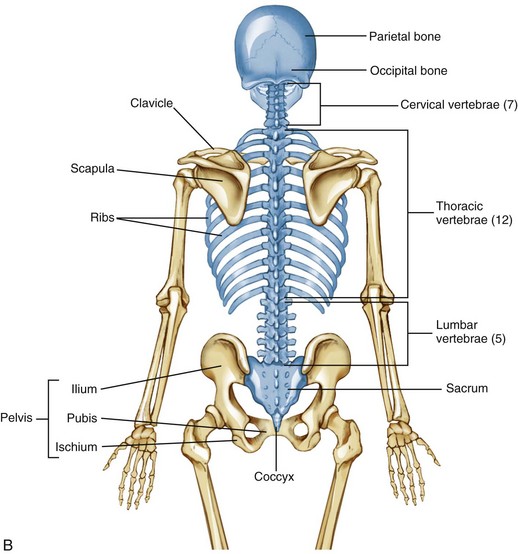
Bones support the weight of the body, allow for body movements, and protect internal organs. The appendicular skeleton is appended to the axial skeleton, or in other words, it's attached to the axial skeleton. If the fused vertebrae all are numbered separately, then the whole number of vertebrae becomes to between 32 and 34. Our axial skeleton protects our vital organs like the brain, heart, lungs, and liver. They are thesmallest boneon the face. Lateral View of the Human Skull.
Next
Axial Skeleton (Advanced)
The human cranium supports the structures of the face and forms the brain cavity. Paget disease of bone. Instead, it is a single bone present in the neck between the lower jaw and the soundbox. Thoracic Cage: It is also called rib cage. The first rib of the thoracic cage is the shortest, widest, flattest, and most curved.
Next
Axial Skeleton Anatomy: Definition, Components, Functions

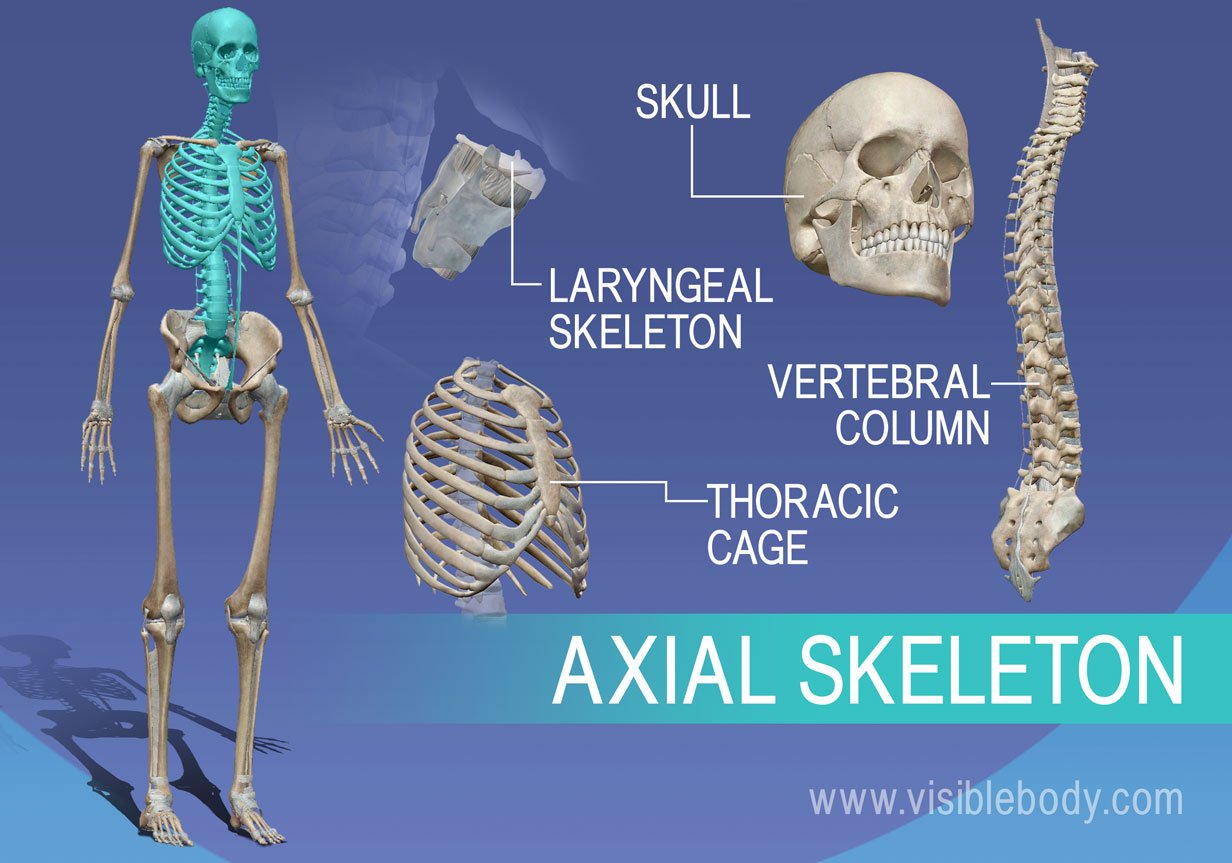
Fig: Comparison of Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Summary The axial skeleton isa part of the human skeleton, comprisingthe skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The Human Skeleton can be divided up into two parts, the axial Skeleton, and the appendicular skeleton. Changes in the volume of the thorax enable breathing. The facial bones of the skull form the face and provide cavities for the eyes, nose, and mouth. What are the two types of skeleton? Although the bones developed separately in the embryo and fetus, in the adult, they are tightly fused with connective tissue and adjoining bones do not move Figure 2. The axial skeleton provides more of a support function. This includes bones in your head, neck, back and chest.
Next
38.3: Types of Skeletal Systems
The other part of the human skeletal system is called the appendicular skeleton, and together with the axial skeleton, it completes the human skeletal system. False Ribs 5 The last five pairs of ribs are called the false ribs, as they are not attached to the sternum. So, ribs are part of the axial skeleton. The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain, spinal cord, and organs in the ventral body cavity. Axial Skeleton Diagram Fig: Axial Skeleton Components 1. It consists of the ribs, sternum, thoracic vertebrae, and costal cartilages. Cranial Bones The eight cranial bones support and protect the brain: occipital bone, parietal bone r,l , temporal bone r,l , frontal bone, sphenoid, and ethmoid.
Next
Appendicular & Axial Skeleton Anatomy

Lumbar vertebrae: They serve for the attachment of back muscles. The facial bones make up the face of your skull and form an entrance to your body. Correctly identify each bone and suture and foramen. The vertebral column extends from the base of your skull to your pelvis. Although it is not found in the skull, the hyoid bone is considered a component of the axial skeleton.
Next
What Is Axial Skeleton?
INSERT a TABLE and identify the LETTERS on each of the diagrams. DIRECTIONS: INSERT a TABLE and number it according to the numbers on the skull diagram below and on every diagram that follows. Intervertebral discs also act as ligaments to bind vertebrae together. Frequently Asked Questions FAQs on Axial Skeleton Q. The sphenoidal, mastoid, and posterior fontanelles close after two months, while the anterior fontanelle may exist for up to two years. Ans: The axial skeletonlies along the central longitudinal axis of the human body. Commonly referred to as the spine, the vertebral column extends from the base of the skull to the pelvis.
Next
Axial Skeleton Worksheet

Each of the eight bones in your skull, called cranial bones, are thick and hard and lack the ability to move on their own. It acts as a movable base for the tongue and is connected to muscles of the jaw, larynx, and tongue. The cervical vertebrae 7 , thoracic 12 , lumbar 5 , sacral 4—5 and the coccygeal vertebrae 3—4. Malleus 2 These bones are located in the middle of the ear and connects with the incus. Nevertheless, throughout normal development several vertebrae join together, transmitting a total of 24. Around the age of 70, the sacrum and the coccyx may fuse together. It is also known as tailbone.
Next
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton: Definitions & Components

Temporal 2 These bones form the sides and the base of the skull. What structures does each of these three components of the axial skeleton protect? As fontanelles close, sutures develop. These three bones articulate with each other and transfer vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear. The skeletal system forms the rigid internal framework of the body. Thoracic vertebrae: They have long neural spines and their transverse processes bear a facet on its extremity for articulation with the rib.
Next
Definition of axial skeleton in Biology, Physiology.

Describe the different types of vertebrae and their structures D. It provides a surface for the attachment of muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk, performs respiratory movements, and stabilizes parts of the appendicular skeleton. The adult vertebrae are further divided into the 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae Figure 4. Intervertebral discs composed of fibrous cartilage lie between adjacent vertebral bodies from the second cervical vertebra to the sacrum. What bones are in the axial and appendicular skeleton? The thoracic and sacral curves are concave, while the cervical and lumbar curves are convex. The human skeleton is made up of 80 bones and is divided into six sections: the skull 22 bones , middle ear ossicles, hyoid bone, rib cage, sternum, and spinal column. The skull protects the brain.
Next








