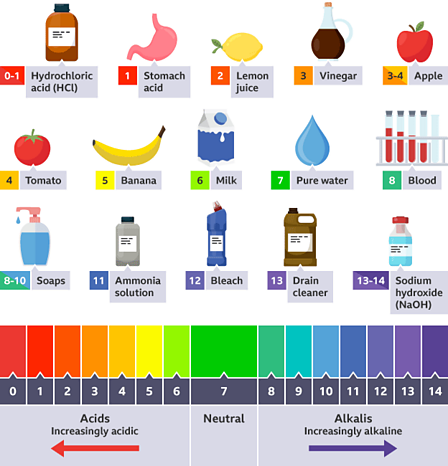
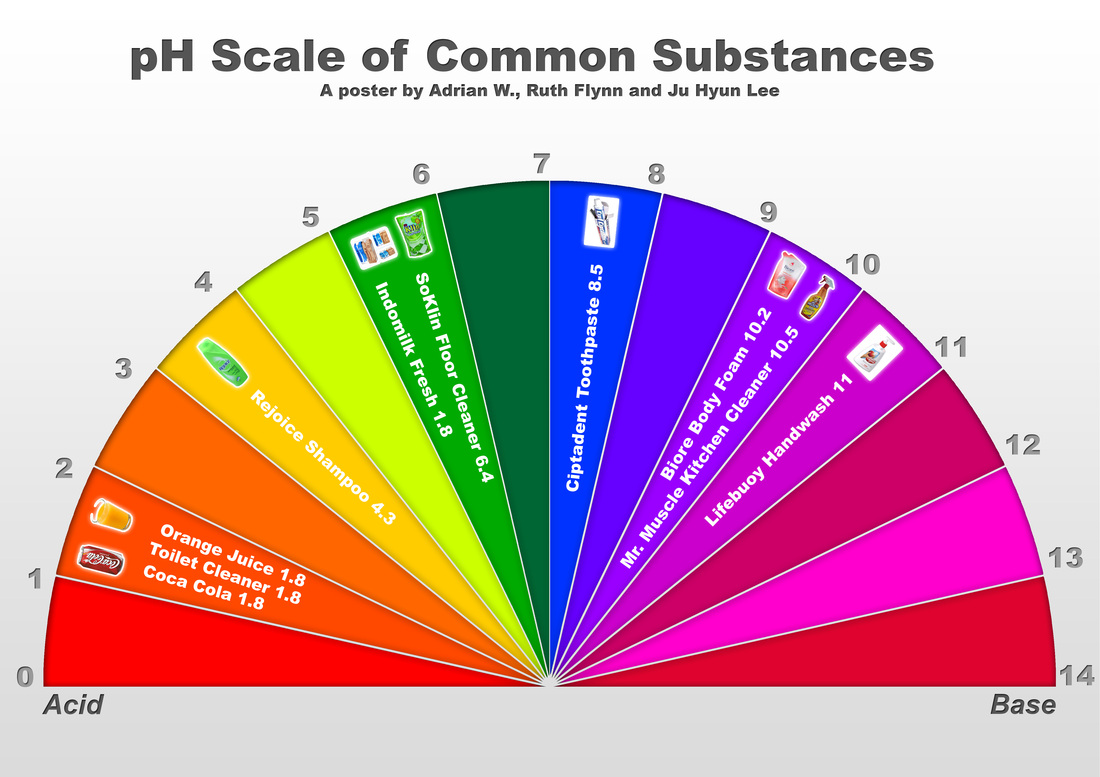
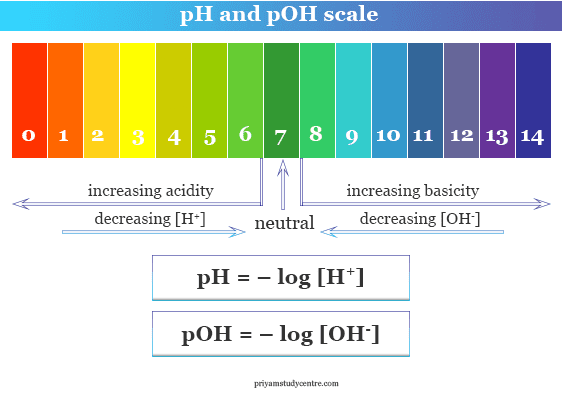
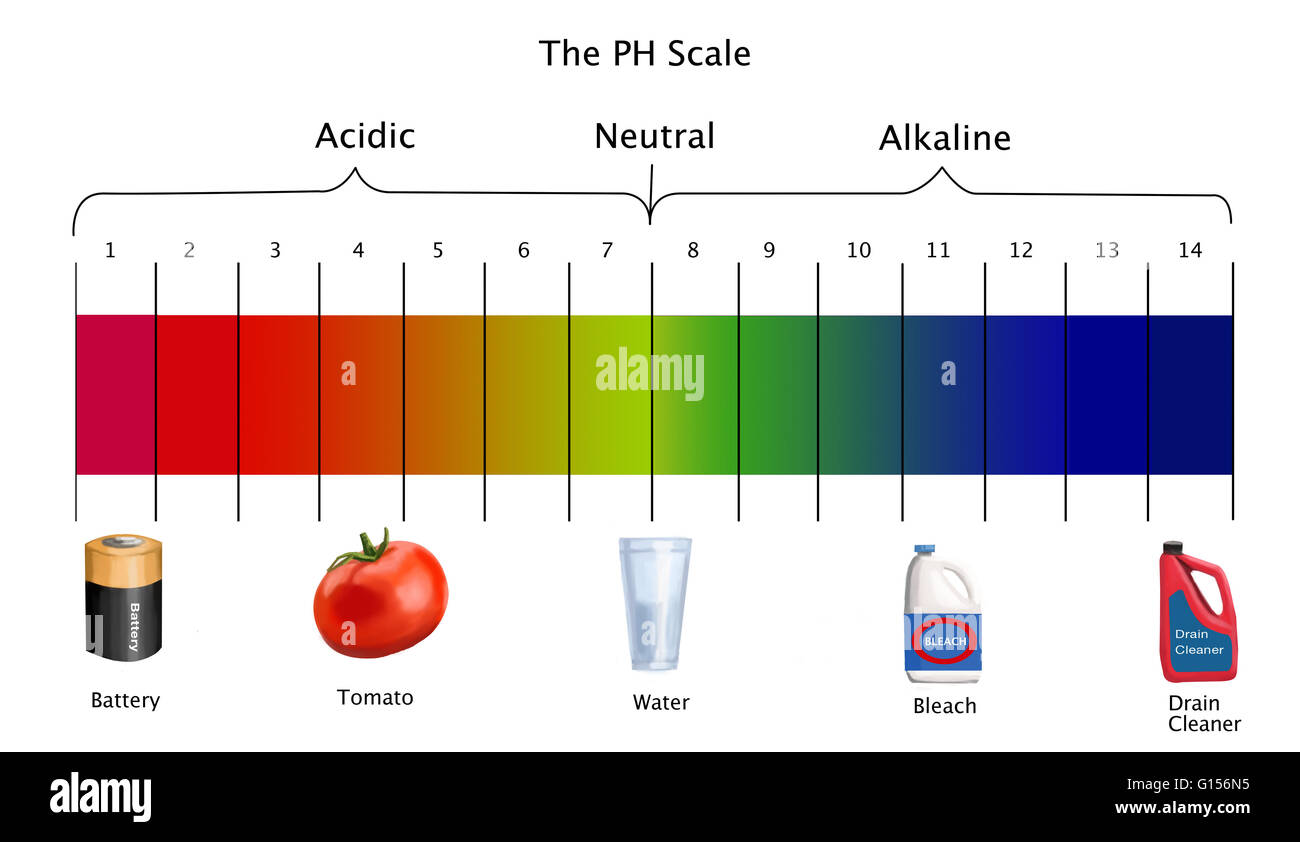
Acids and bases are important classes of chemicals that can be found throughout the world, and they are commonly measured on the pH scale. The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, with a range of 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, while a pH less than 7 is acidic and a pH greater than 7 is basic.
Examples of common acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and acetic acid (CH3COOH). These acids have a sour taste and can cause damage to living tissue if they come into contact with it. Hydrochloric acid, for instance, is found in the stomach and helps to digest food. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that is used in the production of fertilizers and detergents. Acetic acid, also known as vinegar, is a weak acid that is commonly used in cooking.
Examples of common bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2). These bases have a bitter taste and can also cause damage to living tissue if they come into contact with it. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base that is used in the production of soap and detergents. Potassium hydroxide is a strong base that is used in the production of fertilizers and soaps. Calcium hydroxide, also known as lime, is a weak base that is used in the production of cement and as a food additive.
The pH scale is important because it helps us to understand how acidic or basic a solution is. It is used in a variety of industries, including food production, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals. It is also important in biology, as the pH of bodily fluids such as blood and urine can impact the health of an individual.
In conclusion, acids and bases are important classes of chemicals that can be found throughout the world, and they are commonly measured on the pH scale. Examples of common acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and acetic acid, while examples of common bases include sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and calcium hydroxide. The pH scale is used in many industries and is important in understanding the acidity or basicity of a solution.