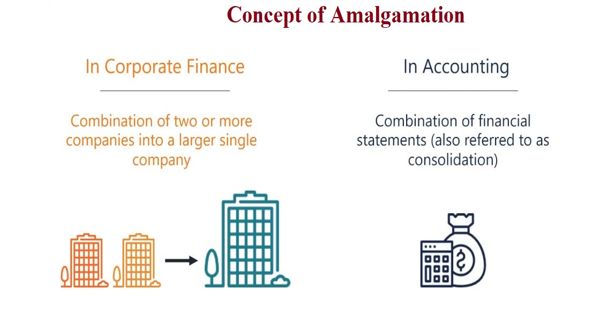
Amalgamation is the process of combining two or more companies into a single entity. This can take the form of a merger, where the companies involved maintain their separate legal identities but operate as a single business, or a consolidation, where the companies involved are merged into a new entity with a new legal identity. Amalgamation can be a complex process, involving the negotiation of terms and the transfer of assets, liabilities, and ownership interests between the companies involved.
There are several reasons why companies may choose to amalgamate. One of the primary reasons is to achieve economies of scale, which refers to the cost savings that can be achieved by producing goods or services on a larger scale. For example, a company that manufactures products may benefit from amalgamating with a company that supplies raw materials, as this would allow them to negotiate better prices for their inputs and increase their production capacity. Similarly, a company that provides a service may benefit from amalgamating with a company that has a similar business model, as this would allow them to combine their resources and offer a more comprehensive service to their customers.
Another reason for amalgamation is to increase market share or access to new markets. For example, two companies that operate in the same industry may amalgamate in order to gain a larger share of the market and better compete with their rivals. Alternatively, a company may amalgamate with a company that operates in a complementary industry in order to expand its product or service offerings and attract new customers.
In addition to the potential benefits of amalgamation, there are also risks and challenges that must be considered. One potential risk is the potential for cultural differences between the companies involved, which may lead to conflict or difficulties in integrating the businesses. Another risk is the potential for antitrust issues to arise, as the amalgamation of two large companies may create a dominant market player that could potentially engage in anticompetitive practices.
Despite these risks, amalgamation can be a useful tool for companies looking to grow and expand their operations. Some examples of successful amalgamations include the merger of Exxon and Mobil in 1999, which created the world's largest publicly traded oil and gas company, and the merger of Time Warner and AOL in 2000, which created a media and internet conglomerate.
In conclusion, amalgamation is the process of combining two or more companies into a single entity, and can be a useful tool for achieving economies of scale, increasing market share, and expanding into new markets. While there are risks and challenges involved in the process, successful amalgamations can result in significant benefits for the companies involved.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Amalgamation-fb7f6b585bf24159b5327fb8e3543cd4.jpg)