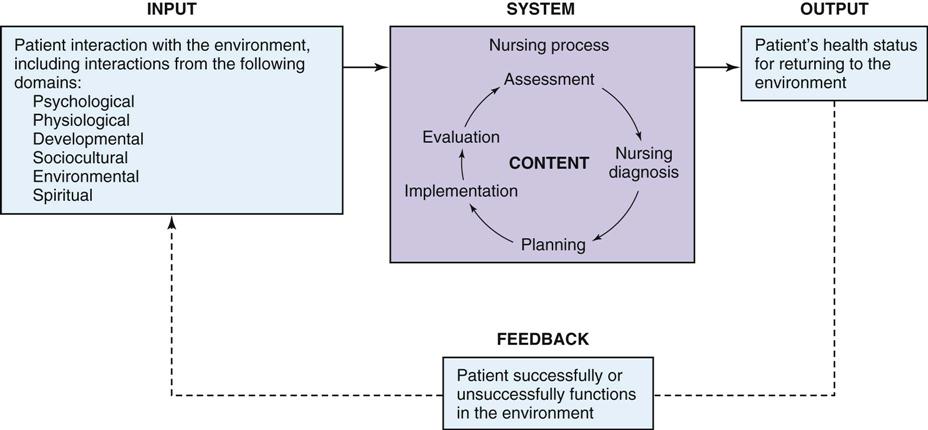
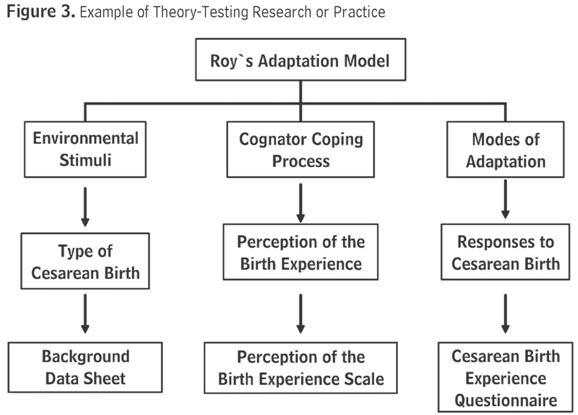
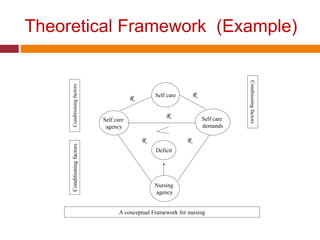
A theoretical framework is a set of ideas and concepts that provide a broad explanation of a particular phenomenon or issue. In nursing research, a theoretical framework serves as a foundation for the study, guiding the development of the research questions and hypotheses and informing the data collection and analysis. Theoretical frameworks can be drawn from a variety of disciplines, including sociology, psychology, and anthropology, and can provide valuable insights into the causes and consequences of health-related phenomena.
One example of a theoretical framework in nursing research is the Health Belief Model, which was developed in the 1950s to explain why some individuals engage in preventive health behaviors while others do not. The model suggests that people's health behaviors are influenced by their perceptions of the likelihood of contracting a particular illness, the severity of the illness, and the benefits and barriers to taking preventive action. For example, a person who believes that they are at high risk for developing a particular illness and that the illness will have serious consequences may be more likely to engage in preventive behaviors, such as getting vaccinated or exercising regularly.
Another example of a theoretical framework in nursing research is the Self-Determination Theory, which focuses on the psychological factors that influence individuals' health behaviors. According to this theory, people are more likely to engage in health behaviors when they feel autonomous and competent, and when their actions are aligned with their values and goals. This theory has been applied to a variety of health behaviors, including physical activity, healthy eating, and medication adherence, and has been found to be a useful predictor of health outcomes.
A third example of a theoretical framework in nursing research is the Social Cognitive Theory, which emphasizes the role of social and environmental factors in shaping health behaviors. According to this theory, people's health behaviors are influenced by their observations of others, their beliefs about the consequences of their actions, and the social and cultural norms that they encounter. This theory has been applied to a wide range of health behaviors, including smoking, alcohol consumption, and sexual risk-taking, and has helped researchers understand the complex factors that influence health behaviors.
In conclusion, theoretical frameworks are an important part of nursing research, providing a foundation for the development of research questions and hypotheses and informing the data collection and analysis process. The Health Belief Model, Self-Determination Theory, and Social Cognitive Theory are just a few examples of the many theoretical frameworks that have been applied to nursing research, and each has contributed valuable insights into the factors that influence health behaviors and outcomes.