Exogenous theory is a branch of economics that focuses on external factors that influence the economy. It contrasts with endogenous theory, which focuses on internal factors within the economy.
According to exogenous theory, external forces such as technological innovations, natural disasters, and government policies play a significant role in shaping the economy. These forces can affect the economy through their impact on the supply and demand of goods and services, as well as on the production and distribution of wealth.
One key aspect of exogenous theory is the concept of exogenous shocks, which are sudden, unexpected events that can have significant impacts on the economy. For example, a natural disaster such as a hurricane or earthquake can disrupt the production and distribution of goods, leading to price changes and potentially causing a recession. Similarly, technological innovations can lead to changes in the demand for certain goods and services, resulting in shifts in the economy.
Government policies can also have exogenous effects on the economy. For example, changes in tax rates or regulations can affect the behavior of firms and individuals, leading to changes in economic activity.
Exogenous theory has important implications for economic policy and decision-making. By understanding the role of external factors in shaping the economy, policymakers can better anticipate and respond to economic shocks and make more informed decisions about how to address them.
Overall, exogenous theory highlights the importance of considering external factors when analyzing and understanding economic phenomena. It helps us to better understand the complex forces at play in the economy and how they can influence economic outcomes.
Exogenous and endogenous variables

Many fMRI studies have found that when participants were instructed to use a variety of cognitive techniques and methods to avoid negative emotional experiences, activity in the ventrolateral, dorsolateral, and dorsofrontomedial prefrontal cortices increased. The working paper below argues that money is not neutral in a modern economy and the quote below from nominal page 15 describes the disruptive power of the central bank: Oxygen is not responsible for fire, but the fire cannot exist without it. Besides their assistance in experiencing fear, the amygdala also facilitates humans in learning from fear-inducing circumstances. I know there are other tools such as open market operations that can be used to control the money supply in an Economy. This is because the money supply is not influenced by other economic factors or interest rates.
(PDF) The exogenous and endogenous approach to institutions: An overview

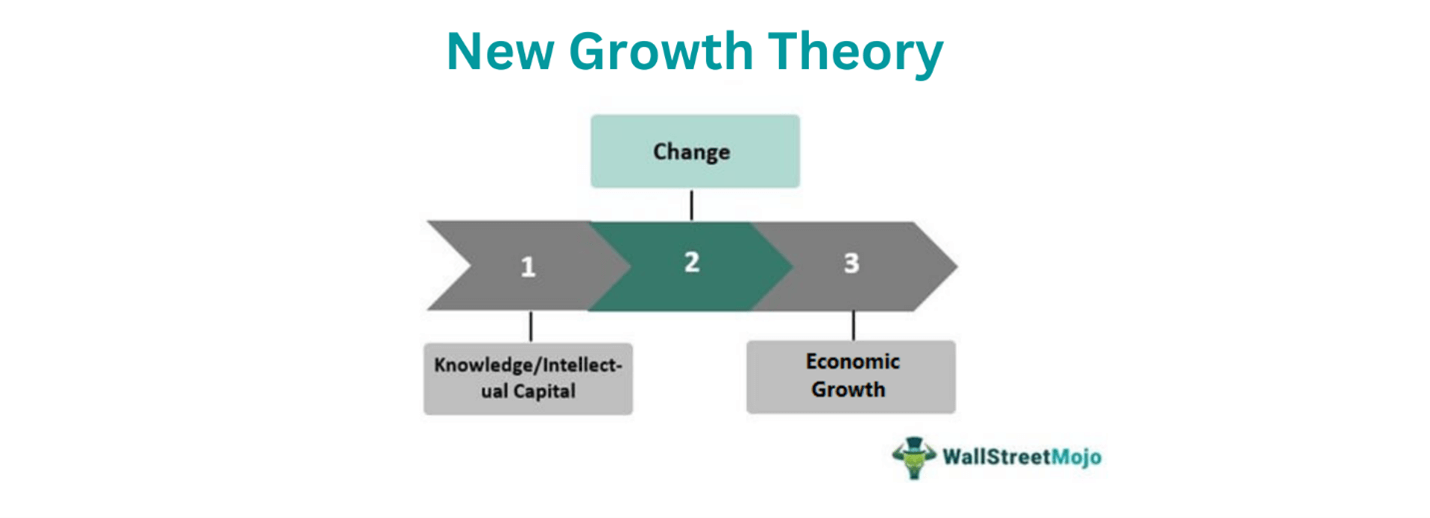
Although new growth theorists would easily identify higher growth potential in eighteenth-century Britain than in France, explaining the timing of the acceleration in growth remains elusive. Exogenous Theory Exogenous growth theory refers to its influence that will cause economic growth beyond the real money supply of a firm. Today, James Morley explains how the very concept of what economic growth means is being re-shaped by endogenous growth theory - the idea that rather than relying on building bridges and highways, growth can be determined by knowledge and population. If its existence and quantity are determined by the economy alone, money is considered endogenous. Smell interpretations and the emission of neurotransmitters associated with distress and aggressive behaviour are also sensations that are related to the functioning of the amygdala. For there to be sustained financial growth, there is need for an organization to keep on transforming. The Limbic System: The limbic system is the specific region of the brain that regulates feelings and the process of recollection otherwise known as memory Figure 1.
central banking
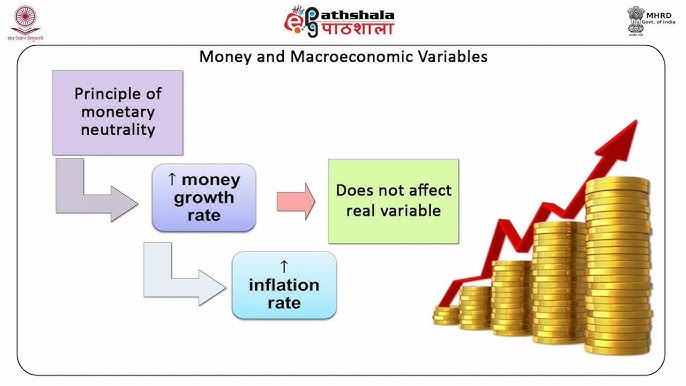
This convergence is nothing to fear. Under the classical model theory, money supply was not significan influenced by households and firms. This theory is one that maintains that economic growth is not affected by internal factors or influenced by the economy, rather by factors that are outside of the economy. Also, the central bank controlled the quantity of money supply. Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics, third edition, 1984.
Exogenous Growth: Definition, Economic Theory, Vs. Endogenous
They have at their disposal wide array of tools through which they can influence the interest rate although ultimately their goals are price stability and or full employment they only try to change the interest rate if they believe it will further one of those goals. This means that endogenous inhibition of emotions is possible. Rather than an easy path to prosperity, capital accumulation quickly becomes a lot like squeezing blood from a stone. Law argued that a credit currency of this kind would allow the market to determine the proper amount of money —when the economy was prospering and the demand for money was high, the bank would be able to expand the money supply and thus facilitate the growth of the economy. First, the prediction of higher economic growth for a larger population suggests that neoclassical growth theory, not to mention even more pessimistic economic theories of population going back to Thomas Malthus, got things completely wrong. No, central banks do not even have directly responsibility to adjust interest rate. Since alcohol affects the cerebellum, intoxicated people have a little more trouble walking linearly.
Exogenous Growth

But what drives this growth? Other key factors driving growth include An exogenous factor is one that is independent of factors within a specific economic system. Hence, while many writers opposed royal manipulations of the money stock, in particular debasements, this position was problematized by the conviction that an increase in the money supply would generate economic prosperity. The amygdala is mainly in charge of managing the conceptions of, and responses to, aggressive behaviour and the sensation of being afraid. The importance of this part of the brain can be understood by the fact that People who have cerebellar damage impacts their patients in a manner that they have trouble in walking, maintaining their balance, and attempting to keep their hands stable. I think there is some credence to this theory.
exogenous theory

The hippocampus is essential for the formation and storage of long-term memory. Uncertainty and Business Cycles: Exogenous Impulse or Endogenous Response? SEE ALSO Central Banks; Money; Money, Endogenous; Money, Supply of Desai, Meghnad. My question is that isn't the central bank only responsible for determining the interest rates? The Exogenous growth theory is an economic theory that states that economic growth occurs as a result of factors independent of the economy. Kühn, Haggard and Brass, 2009 Respondents were shown frightening images. The central bank induces "strains in the financial and industrial markets" that either reduce expected future profits or induce an actual loss for some units of the economy. Endogenous emotions: Emotions are typically considered as responses factors or stimuli that originate from the external surroundings. External factors greatly impact the equilibrium factor between demand and supply upon which basic ideology of economic growth puts the rest Kruglanski, A.
Endogenous vs. Exogenous

Brain activity is seen to be triggered in the dorsal frontomedial cortex dmPFC when contrasting endogenous inhibition to action experiments, but it could not be seen in the lateral prefrontal regions that are connected to exogenous inhibition. Figure 3: In experiments where participants successfully blocked their reaction, comparable lateral prefrontal brain regions, such as the inferior frontal cortex and middle frontal gyrus, were activated. A fully exogenous form of money had now developed. These new ideas make everyone else producing regular goods and services more productive - that is, ideas increase TFP. The person further adds that the money supply is independently determined by the central bank. Update Table of Contents What is Exogenous Growth? However, a large section of endogenous growth models have less stringent sense of perfect competition and such organizations enjoy a level of power monopoly. Money, Exogenous Money is considered exogenous or endogenous depending on its relationship to the economy.