External respiration, also known as breathing, is the process by which oxygen is taken in from the environment and carbon dioxide is expelled. It is a vital physiological process that occurs in all animals, including humans.
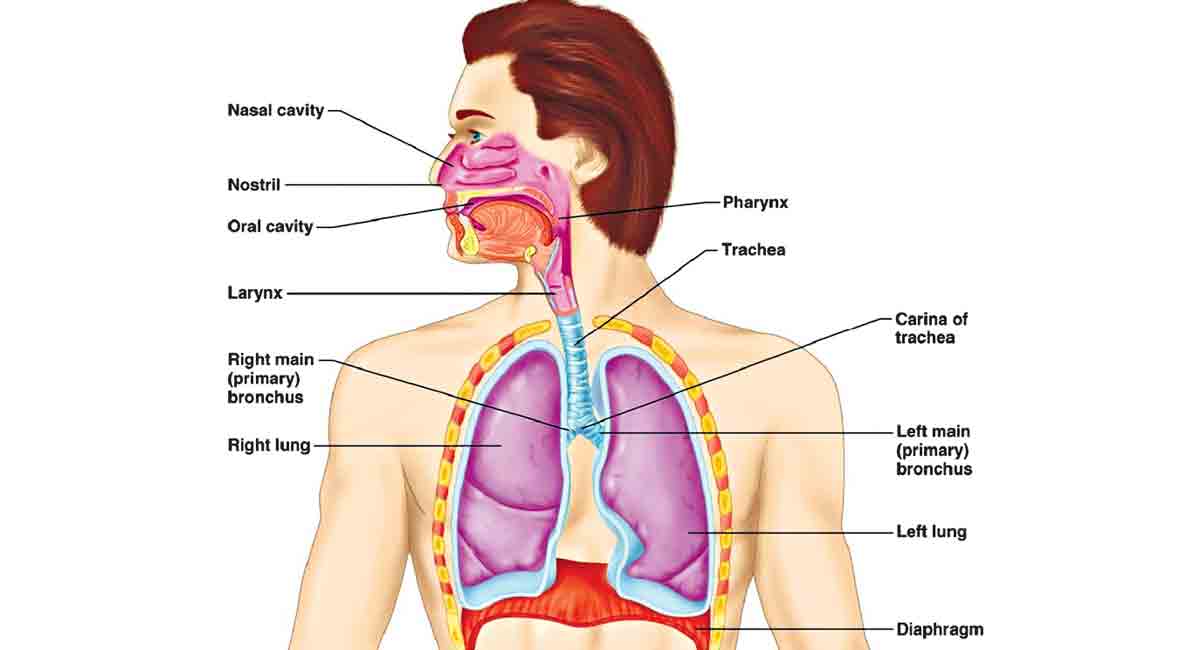
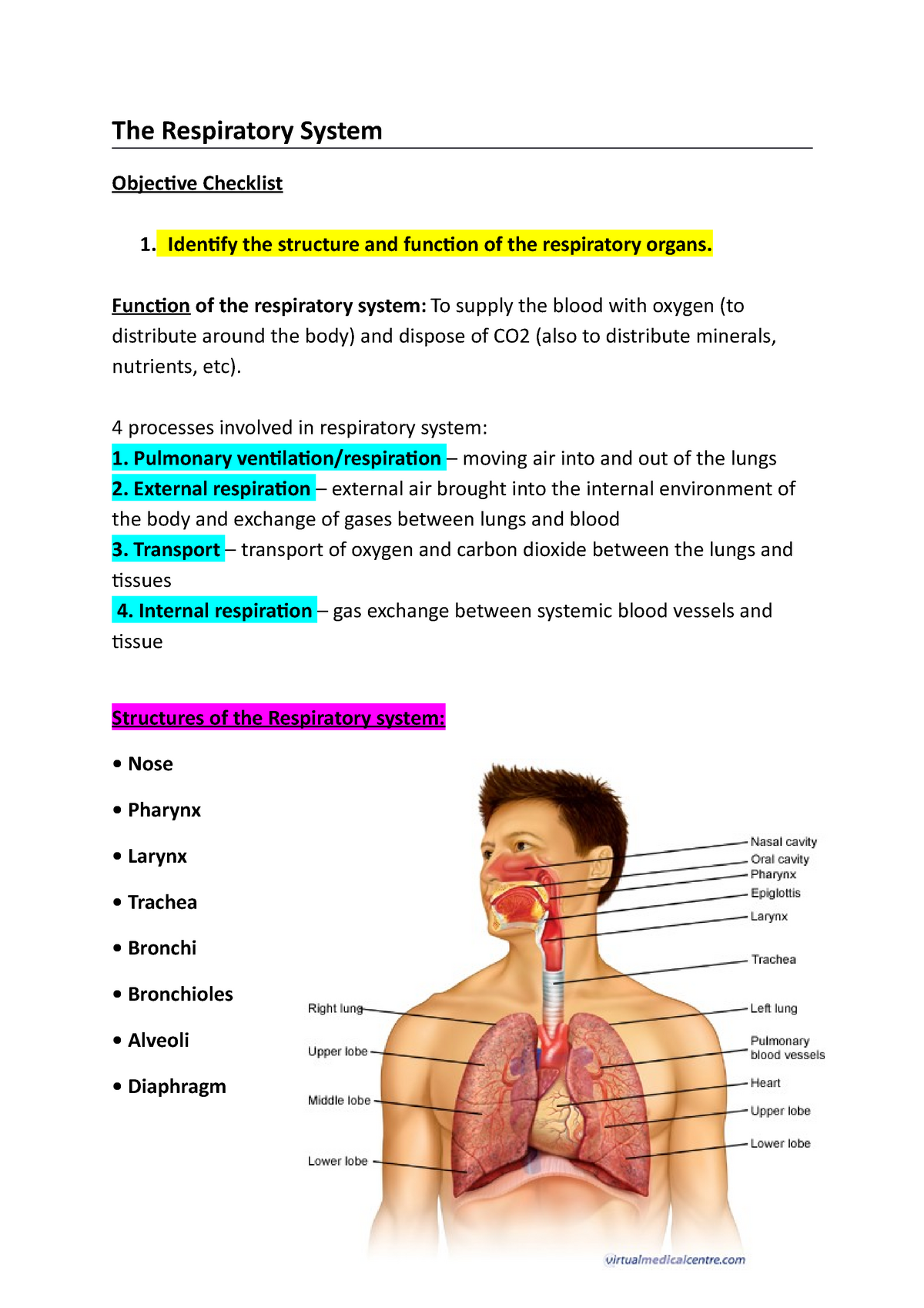
In humans, external respiration takes place in the lungs, which are located in the chest cavity. The lungs are made up of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are surrounded by a network of blood vessels called capillaries.
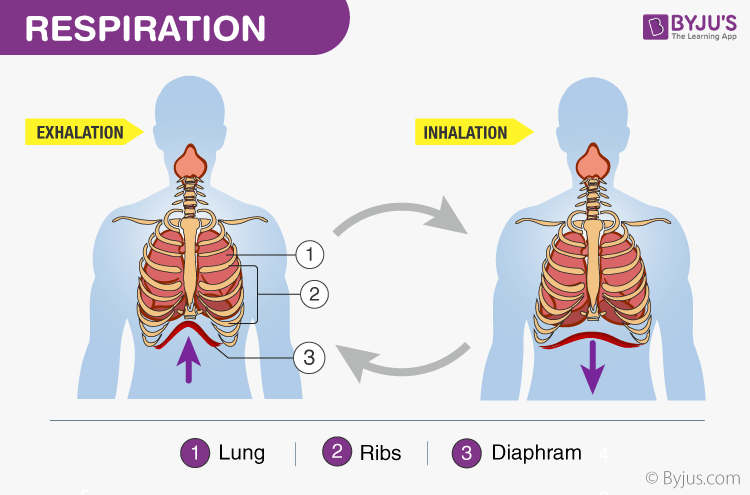
The process of external respiration begins when the muscles of the rib cage and diaphragm contract, causing the chest cavity to expand and the lungs to inflate. As the lungs expand, air is drawn in through the nose or mouth and into the trachea, or windpipe. The trachea then branches off into smaller tubes called bronchi, which lead to the individual alveoli.
Once the air reaches the alveoli, it is oxygenated by the process of diffusion. Oxygen from the air diffuses across the thin walls of the alveoli and into the capillaries, where it is picked up by the red blood cells and carried to the body's tissues and organs. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product produced by the body's cells during metabolism, diffuses out of the capillaries and into the alveoli, where it is exhaled out of the body.
External respiration is regulated by the respiratory center, a group of neurons located in the brainstem that controls the rate and depth of breathing. The respiratory center receives input from various sources, including the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, the pH of the blood, and the body's overall metabolic needs. It uses this information to adjust the rate and depth of breathing to ensure that the body is receiving enough oxygen and eliminating enough carbon dioxide.
In addition to its role in oxygenating the body's tissues and eliminating waste products, external respiration also plays a role in thermoregulation, the process by which the body maintains its internal temperature. When the body is too hot, the respiratory center increases the rate and depth of breathing to help dissipate heat through the process of evaporation. Conversely, when the body is too cold, the respiratory center slows down breathing to conserve heat.
Overall, external respiration is a vital physiological process that is essential for the health and well-being of all animals, including humans. Without it, the body's tissues and organs would not receive the oxygen they need to function properly, leading to serious health consequences.