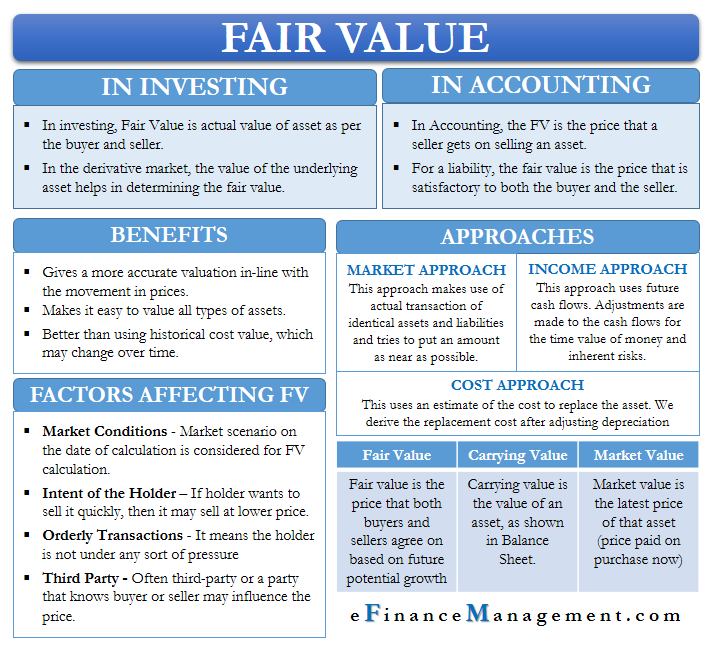
The fair value method is a financial accounting concept that is used to determine the value of an asset or liability. It is based on the idea that the value of an asset or liability should be based on the price that would be received if the asset or liability were sold or transferred in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date.
One example of the fair value method is the valuation of financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. These instruments are often traded on financial markets, and their values can fluctuate based on changes in market conditions and the perceived risk associated with them. Under the fair value method, the value of these instruments is determined by the price that they would likely fetch if they were sold on the market at the measurement date.
Another example of the fair value method is the valuation of intangible assets, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights. These assets do not have physical form and are not easily traded on financial markets. However, they can still have significant value to a business, and the fair value method can be used to determine their worth. In this case, the value of the intangible asset is determined by considering factors such as the expected future cash flows that the asset is expected to generate and any comparable sales or licensing agreements.
The fair value method is useful because it provides a more accurate and current representation of an asset or liability's value compared to other methods, such as the historical cost method, which values an asset based on the price paid for it at the time of acquisition. However, the fair value method can also be subject to uncertainty and subjectivity, as it relies on estimates and assumptions about future market conditions and the perceived risk associated with the asset or liability.
In conclusion, the fair value method is a financial accounting concept that is used to determine the value of an asset or liability based on the price that would be received if it were sold in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. It is a useful tool for valuing financial instruments and intangible assets, but it is also subject to uncertainty and subjectivity due to the reliance on estimates and assumptions about future market conditions.
20.3 Fair value disclosure requirements

X is planning to buy a Road Roller. The Update clarifies that if an entity is hedging multiple amounts in a closed portfolio with a single amortizing-notional swap, it is required to designate the hedge as a single-layer hedge, not hedges of multiple layers. Sale to a Third Party Fair value is to be derived based on a presumed sale to an entity that is not a corporate insider or related in any way to the seller. The fair value standard does not prescribe the level of disaggregation below the class level of asset and liability , but it does state that fair value measurements will often require greater disaggregation than the line items in the balance sheet and a reporting entity should determine classes based on the nature, characteristics, and risks of the assets and liabilities. Fair value accounting helps to measure assets and liabilities at their current market value. Fair value is globally accepted. The life of the Roller is five years.
Cost model vs fair value model for IP
For example, a diamond appraiser would likely be able to identify and calculate a diamond ring based on their experience. The Bottom Line Fair value is the estimated price at which an asset is bought or sold when both the buyer and seller freely agree on a price. Accounting for equity investments, i. What is Fair Value Accounting? Market value method is not used frequently. First, by the price the item cost the seller, via a list of sales for objects similar to the asset being sold, or an expert's opinion.
Fair Value
The selection of appropriate valuation techniques may be affected by the availability of relevant inputs and the relative reliability of the inputs, or by the type of asset or liability being valued. Recommended Articles This has been a guide to Fair Value Accounting and its definition. Fair value principles also hold meaning in terms of financing. Shubha is a skilled researcher and can write plagiarism free articles with a high Grammarly score. For example, comparable real estate. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney. At the end of Year 1, the fair value of Purple Corp had dropped below cost.
Fair Market Value (FMV): Definition and How to Calculate It

This can be particularly useful during times of financial challenge to help keep the company operating while executing a recovery plan. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within those fiscal years. During a rush, the holder may be willing to sell the item at a reduced price. Y will have to record an Unrealized Loss Unrealized Gains or Losses refer to the increase or decrease respectively in the paper value of the company's different assets, even when these assets are not yet sold. For example, unrealized and realized gain and loss activity during the period would not be reflected in the Level 3 rollforward for the period if a reporting entity applies an end-of-period convention for transfers in. If a breach has occurred i. There is a caveat; the amount should be agreeable in a free trade scenario; there should be no external pressure or conditions.
Fair value accounting

However, there is no doubt that they have implemented that term clearly and consistently. The contract is for three months. This is the most common method of determining the worth of a company. Market value is based on factors such as supply and demand, while fair value is solely based on the intrinsic worth of the asset. However, the latter is less popular. Primarily, the market value heavily relies on supply and demand factors in the market, which can fluctuate often. With interest rates at historically low levels and the stock market volatility, those assets have underperformed, potentially resulting in increased pension funding expenses and less certainty when budgeting for those costs.
Fair Value: Its Definition, Formula, and Example

For example, when selling a piece of equipment, you could compare prices in the market by checking stores or searching online, then average those prices to find a fair value. Also read: Book value vs fair value In accounting you need to understand the difference between book value vs fair value. As the information included in the financial statements is time-specific for given market conditions, a change in the market environment could cause a significant difference in the actual financial situation of an entity. Article Link to be Hyperlinked For eg: Source: In other words, it is the value at which an asset can be sold. Market value is determined by demand and supply and fluctuates more. This causes a spiral effect of falling prices and is called a feedback loop of fair value accounting. You can determine a fair value for the investment by taking the resulting value and subtracting the initial cost of the investment.