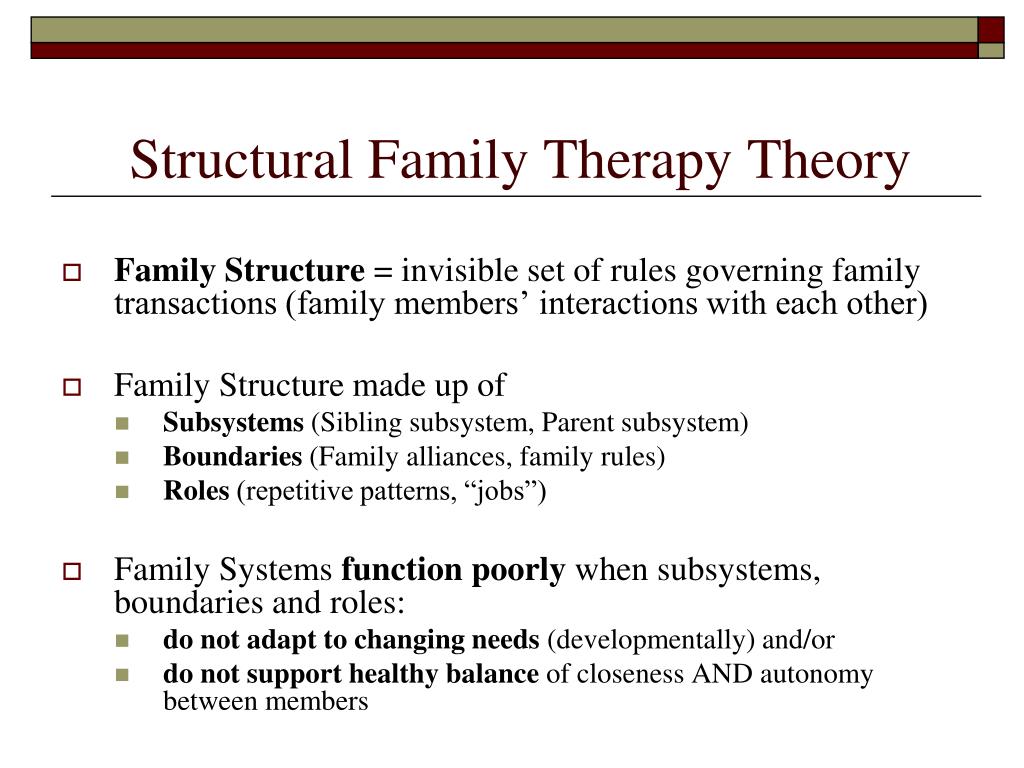
Family structural theory is a sociological perspective that examines the structure and functioning of families within the larger social context. It emphasizes the role of social and cultural factors in shaping family dynamics and interactions. According to this theory, the structure of a family is determined by the social and cultural context in which it exists, and the functioning of a family is influenced by the ways in which family members interact with one another and with the larger society.
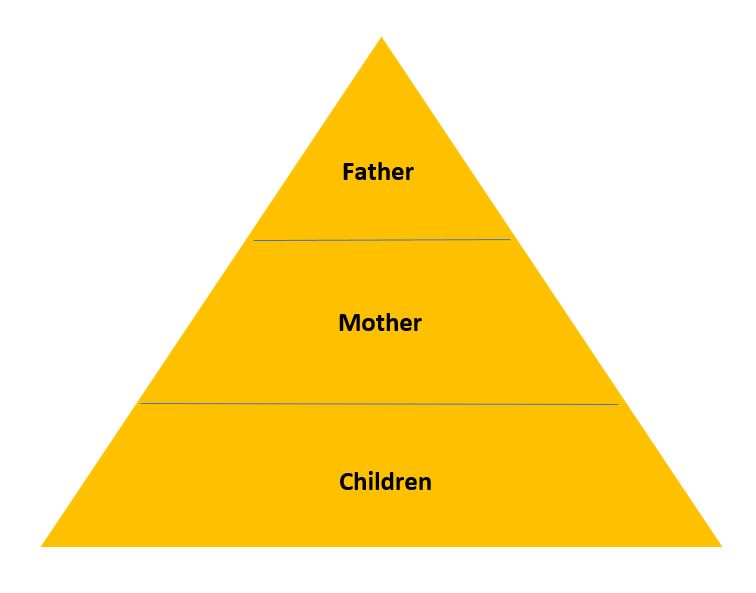
One key concept within family structural theory is the idea of family roles. Each family member is expected to fulfill certain roles within the family, such as provider, caregiver, or disciplinarian. These roles are shaped by the social and cultural norms of the society in which the family exists, and they can vary significantly from one culture to another. For example, in some societies, men are expected to be the primary breadwinners, while in others, women are expected to take on this role. Similarly, the role of caregiver may be expected to be fulfilled by the mother in some cultures, while in others it may be shared equally between both parents.
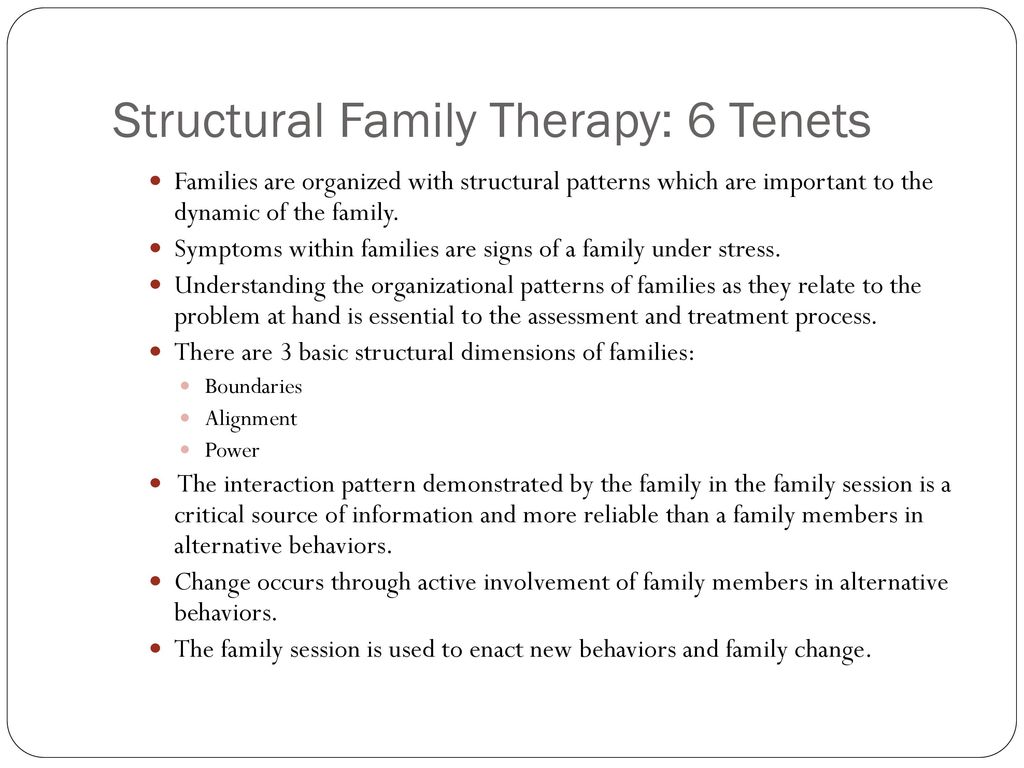
Another important concept within family structural theory is the idea of family power dynamics. Family power dynamics refer to the ways in which power is distributed and exercised within a family. This can be influenced by factors such as gender, age, and family roles. For example, in some families, the father may hold a position of power and authority, while in others, the mother may be the dominant figure. In addition, older family members may hold more power and influence than younger ones, and family roles such as provider or caregiver may also carry with them a certain degree of power and influence.
Family structural theory also emphasizes the role of social and cultural factors in shaping family dynamics. For example, the structure of a family may be influenced by the social and economic conditions in which it exists. In times of economic hardship, for instance, families may need to reorganize their roles and responsibilities in order to survive. Similarly, cultural values and beliefs can shape the way that families function, with some cultures placing a greater emphasis on collectivism and interdependence, while others may value individualism and autonomy.
In conclusion, family structural theory is a sociological perspective that emphasizes the role of social and cultural factors in shaping the structure and functioning of families. It highlights the importance of family roles and power dynamics, as well as the influence of larger social and cultural contexts on family dynamics. Understanding these factors can help us to better understand the complexities of family life and the ways in which families interact with the larger society.