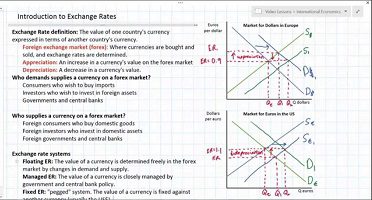
A fixed exchange rate system is a type of foreign exchange regime in which the value of a currency is pegged to the value of another currency or a basket of currencies. This means that the exchange rate between the two currencies is fixed and does not fluctuate in response to market forces.
The main purpose of a fixed exchange rate system is to stabilize the exchange rate between two currencies and reduce exchange rate volatility. This can be beneficial for countries that have a high dependence on international trade and need to have a stable currency to facilitate trade. A fixed exchange rate system can also help to reduce uncertainty in international transactions, as businesses and individuals can be more certain about the value of their currency when making financial decisions.
There are several ways in which a fixed exchange rate system can be implemented. One common method is through the use of a currency peg, in which a country's central bank sets the exchange rate between its currency and another currency at a specific level and intervenes in the foreign exchange market to maintain that rate. Another method is through the use of a currency board, in which a country's central bank issues its own currency but is required to hold a fixed amount of foreign currency reserves in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate.
Fixed exchange rate systems can be beneficial in certain circumstances, but they also have some drawbacks. One disadvantage is that a fixed exchange rate system may not allow a country's currency to adjust to changes in economic conditions. For example, if a country experiences inflation and its currency becomes overvalued, a fixed exchange rate system may prevent the currency from depreciating in value, which could have negative effects on the country's trade balance.
Another disadvantage of a fixed exchange rate system is that it requires a country to maintain large foreign exchange reserves in order to maintain the fixed exchange rate. This can be costly and may not be sustainable in the long term.
In summary, a fixed exchange rate system is a foreign exchange regime in which the value of a currency is pegged to the value of another currency or a basket of currencies. It is designed to stabilize exchange rates and reduce exchange rate volatility, but it can also have some drawbacks, such as not allowing for currency adjustment to economic changes and requiring large foreign exchange reserves to maintain the fixed exchange rate.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-123716978-b8f4b1e248a64dc4ab637256d7c61e3f.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-200147353-001-56a9a84f5f9b58b7d0fdb780.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-exchange-rates-3306083_FINAL-ad4aa801c7ff4b52810c734d345dc401.png)