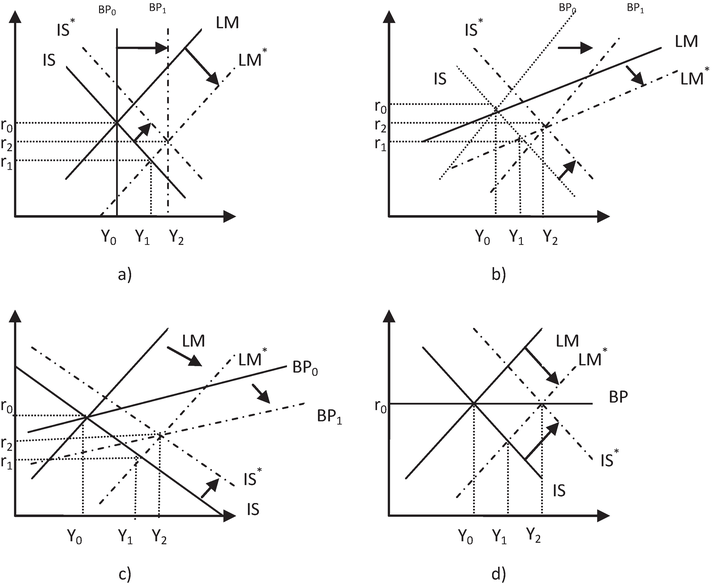
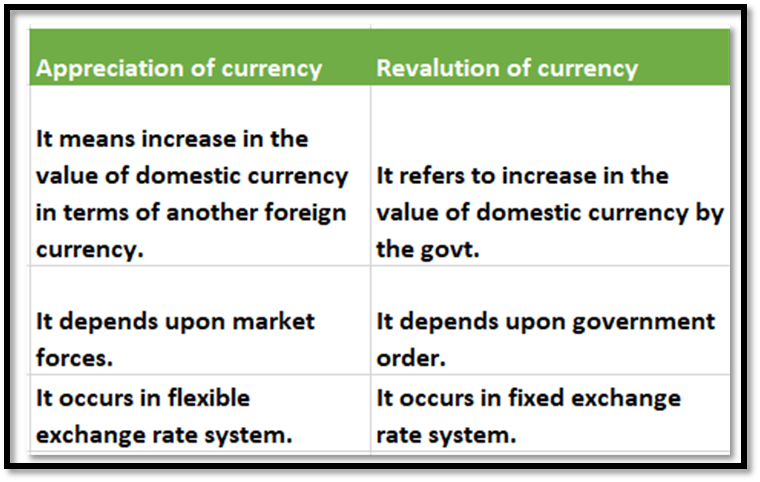
A flexible exchange rate system is a type of currency regime in which the value of a country's currency is determined by the market forces of supply and demand. This means that the value of the currency is not fixed, but rather it fluctuates based on the demand for it in the foreign exchange market.
There are several benefits to a flexible exchange rate system. One of the main advantages is that it allows a country to better adjust to external shocks and changes in economic conditions. For example, if a country experiences a sudden increase in inflation or a decline in competitiveness, a flexible exchange rate system allows the value of the currency to weaken, which can help to reduce the impact of these economic challenges.
Another benefit of a flexible exchange rate system is that it can help to reduce the risk of speculative attacks on a country's currency. In a fixed exchange rate system, speculators may try to take advantage of perceived weaknesses in the currency by selling large amounts of it, leading to further depreciation and potentially destabilizing the economy. A flexible exchange rate system, on the other hand, allows the market to determine the value of the currency, which can help to discourage speculative attacks.
A flexible exchange rate system also allows a country to pursue an independent monetary policy, as the central bank is not tied to maintaining a fixed exchange rate. This can be particularly beneficial in times of economic crisis, as the central bank has more flexibility to implement measures such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply in order to stimulate economic growth.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to a flexible exchange rate system. One potential disadvantage is that it can lead to greater exchange rate volatility, which can make it more difficult for businesses to plan for the future and make long-term investments. Additionally, a flexible exchange rate system can also expose a country to currency risk, as the value of the currency may fluctuate significantly over time.
In conclusion, a flexible exchange rate system offers a number of benefits, including the ability to adjust to external shocks and changes in economic conditions, reduce the risk of speculative attacks, and allow for independent monetary policy. However, it can also lead to exchange rate volatility and currency risk, and may not be suitable for all countries.