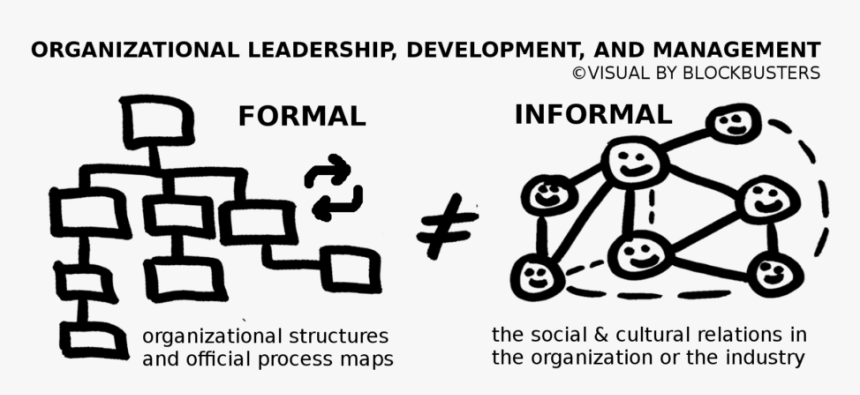
Formal and informal organizations are two different types of organizational structures that can exist within a company or other type of group. While both types of organizations have their own unique characteristics and functions, they can also work together to create a cohesive and effective work environment.
A formal organization is a type of organization that follows a predetermined set of rules, procedures, and hierarchies. It is characterized by a clear chain of command, with each level of the organization having a specific set of responsibilities and decision-making authority. Formal organizations tend to be more rigid and structured, with a clear division of labor and a focus on efficiency and productivity.
Examples of formal organizations include large corporations, government agencies, and military units. These types of organizations often have a well-defined hierarchy, with a CEO or other top executive at the top, followed by various levels of management and employees. Decision-making in a formal organization is typically centralized, with higher levels of the organization having more authority to make decisions that affect the entire organization.
In contrast, an informal organization is a type of organization that is not formally structured or governed by predetermined rules. It is characterized by a more flexible and adaptable approach to decision-making, with individuals taking on leadership roles based on their expertise and ability to contribute to the group. Informal organizations are often more collaborative, with a greater emphasis on teamwork and open communication.
Examples of informal organizations include small businesses, startups, and community organizations. These types of organizations may not have a clear hierarchy or a defined chain of command, and decision-making is often more decentralized and participatory. Informal organizations tend to be more agile and responsive to change, as they are able to quickly adapt and respond to new challenges or opportunities.
Both formal and informal organizations have their own strengths and weaknesses, and the best results can often be achieved when they work together. For example, a formal organization may provide the structure and resources needed to achieve long-term goals, while an informal organization can provide the flexibility and adaptability needed to respond to short-term challenges. By combining the strengths of both types of organizations, a company or group can create a dynamic and effective work environment that is able to meet the needs of its members and stakeholders.