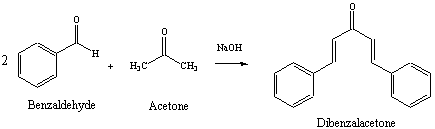
Dibenzalacetone, also known as 2,4-diphenyl-3-buten-2-one, is a chemical compound that is commonly used in the synthesis of various chemicals and materials. It is an important intermediate in the manufacture of plastics, rubber, and dyes, among other things.
The formation of dibenzalacetone involves the condensation reaction of an aldehyde and a ketone. In this reaction, an aldehyde and a ketone react with each other to form a new compound, which is characterized by the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond and a new carbon-carbon single bond.
One of the most commonly used methods for the synthesis of dibenzalacetone is the Knoevenagel condensation. In this reaction, an aldehyde is treated with an excess of a ketone in the presence of a basic catalyst, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The reaction proceeds via the formation of an enolate ion, which then reacts with the aldehyde to form the desired dibenzalacetone compound.
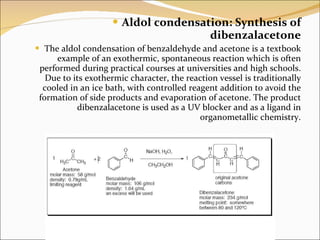
An alternate method for the synthesis of dibenzalacetone is the Aldol condensation. In this reaction, an aldehyde is treated with a ketone in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. The reaction proceeds via the formation of an enol, which then reacts with the aldehyde to form the dibenzalacetone compound.
Both the Knoevenagel condensation and the Aldol condensation are widely used in the synthesis of dibenzalacetone. These reactions are highly efficient and allow for the production of high yields of dibenzalacetone in a relatively short period of time.
In conclusion, the formation of dibenzalacetone involves the condensation reaction of an aldehyde and a ketone. The most commonly used methods for the synthesis of dibenzalacetone are the Knoevenagel condensation and the Aldol condensation, which are highly efficient and allow for the production of high yields of dibenzalacetone.
(E,Z)
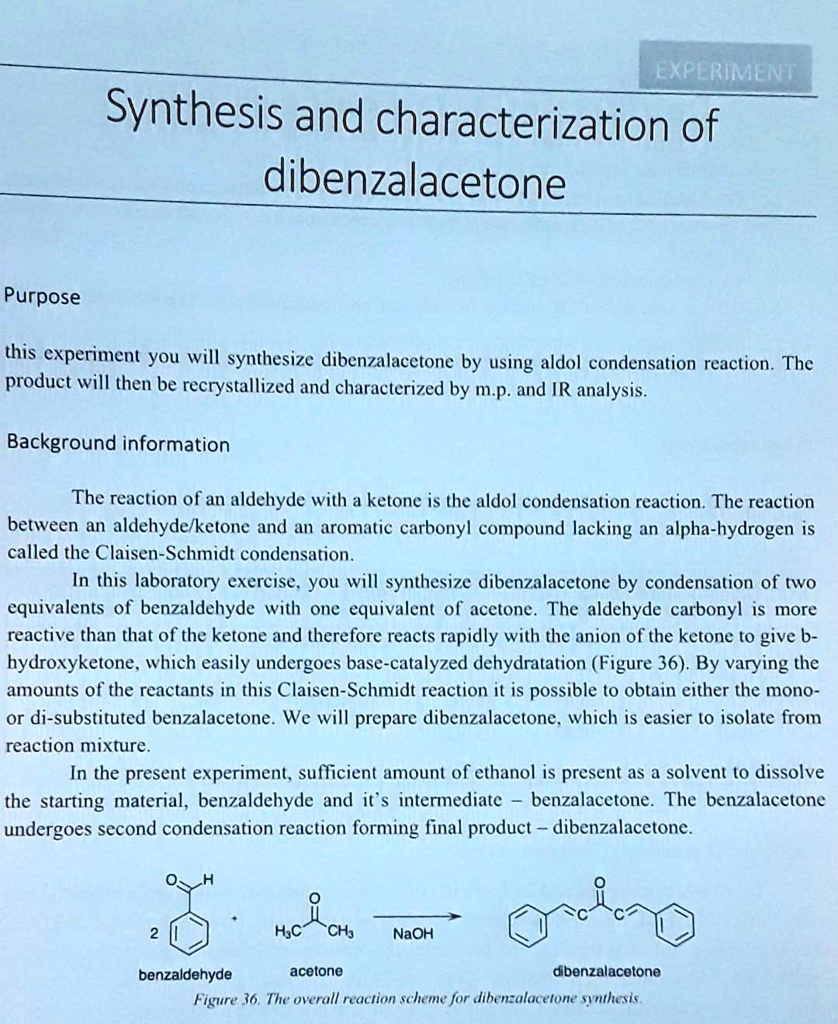
In this condensation an enol or enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxyketone or β-hydroxyaldehyde which is then followed by dehydration. Reagents : commonly a base such as NaOH or KOH is added to the aldehyde. An aldol reaction is comprised of two parts: an aldol addition and dehydration. Calculations for the percent yield of dibenzalacetone are as follows: Theoretical Yield: The melting point of recrystallized product differed from found literature value, indicating presence of impurities. What is the mass of 1 mole of dibenzalacetone? Then, it was placed in an ice bath for five minutes, after cooling to for a bit, allowing for the yellow precipitate to form. Introduction In an aldol condensation, two molecules of aldehyde or ketone are joined together along with the loss of water. Source: Stephanb Likewise, a basic ethanol-water medium is used to solubilize the reagents and, at the same time, promote the final precipitation of dibenzalacetone, a hydrophobic and insoluble compound.
How do you make dibenzalacetone?
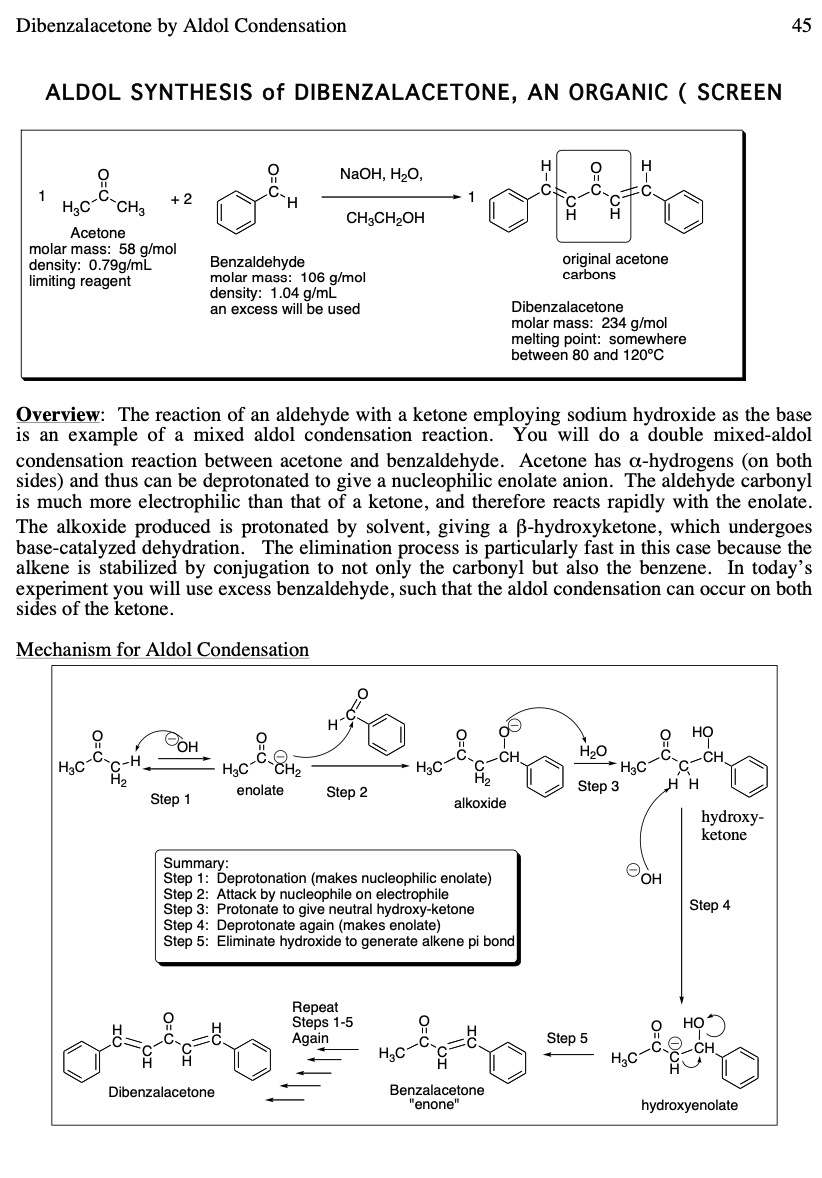
So far, it is not known what negative effects dibenzalacetone can have on the body or the environment, other than being an irritant. Use minimum amount of water for transferring and washing of the precipitate. Since dibezalacetone is an aromatic compound and consists of a conjugated pi system that absorbs light in the visible region, so it absorbs by maximum up to 380nm and thus gives off yellow, hence it appears to be yellow in color. Thus and finally, dibenzalacetone is produced. The students are also asked to check the purity of the product synthesized using TLC technique. Process In a large beaker, mix the ethanol with the benzaldehyde.
Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone by Aldol Condensation
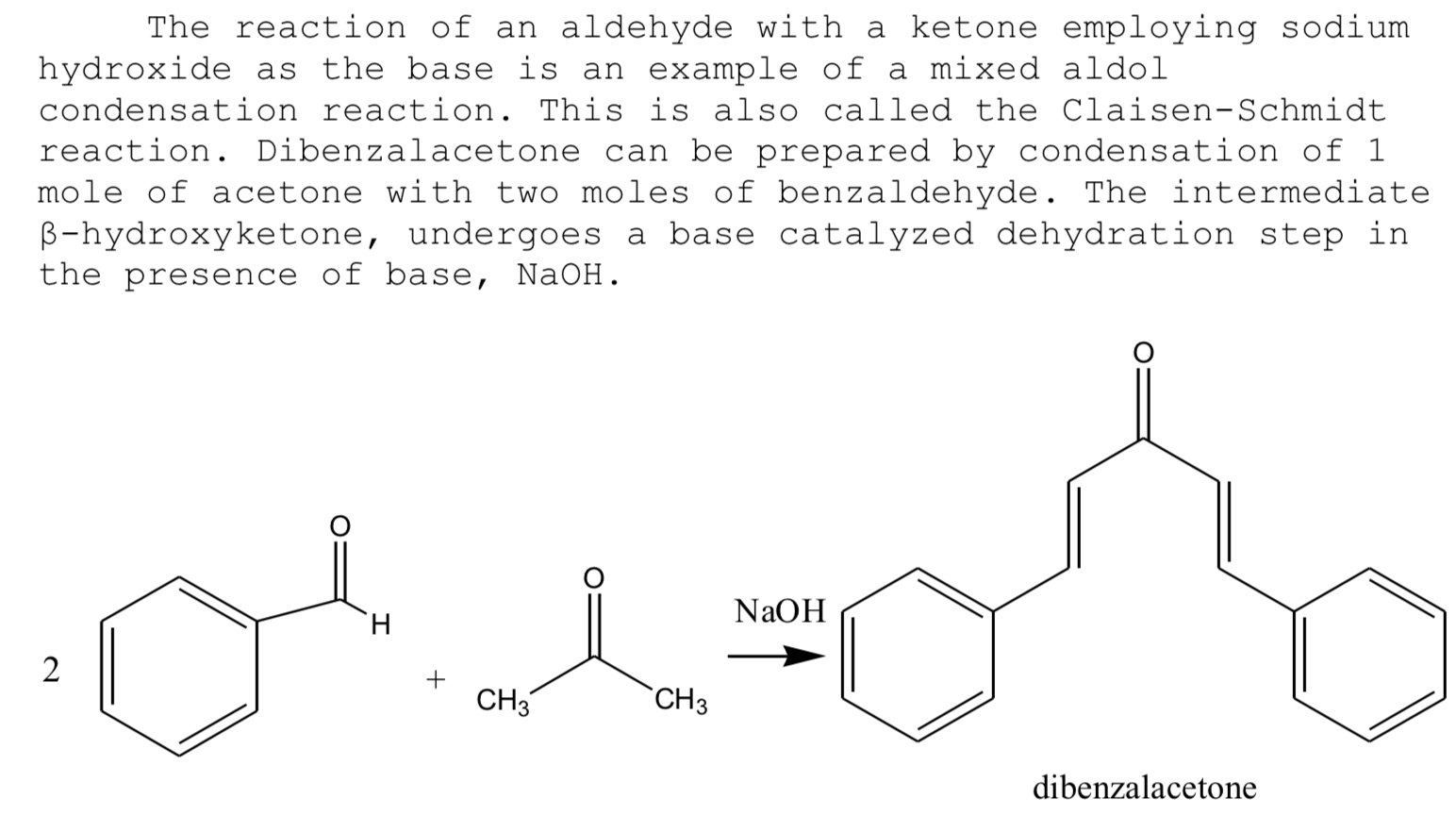
The liquid solution was attempted to be carefully extracted using a Pasteur pipette but proved to not be successful. This is a particular example of Claisen Reaction as Claisen showed that aldehyde under the influence of sodium hydroxide condenses with i another aldehyde, or ii a ketone, with the elimination of water. Aim To prepare Dibenzal acetone organic compound from benzaldehyde and acetone in the presence of sodium hydroxide. Due to its ability to absorb ultraviolet light, it is used in the formulation of sunscreens, or any other product that seeks to mitigate the incidence of UV rays, be it coatings or paints. It is widely used in the production of fine organic compounds, processing of perfumes, production of vegetable oil and biodiesel, etc. Recrystallization A recrystallized sample of dibenzalacetone should glow similar to the crystals in this image.