Free fall acceleration due to gravity is a concept that is fundamental to the study of physics. It refers to the rate at which an object falls towards the Earth due to the force of gravity. In this lab report, we will explore the concept of free fall acceleration and how it can be measured using a simple experiment.
To begin, we need to understand the basic principles of free fall. According to Newton's law of motion, an object in free fall experiences a constant acceleration of 9.8 m/s^2, also known as the acceleration due to gravity. This means that the speed of an object in free fall increases by 9.8 m/s every second.
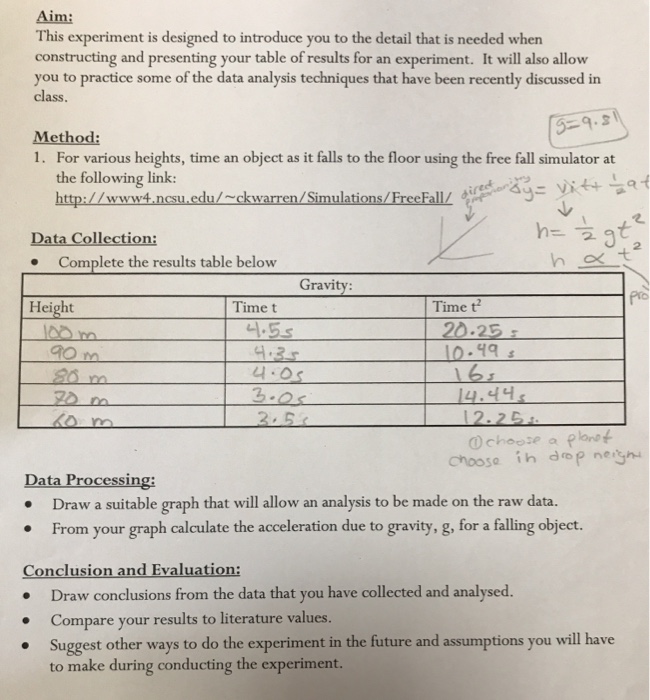
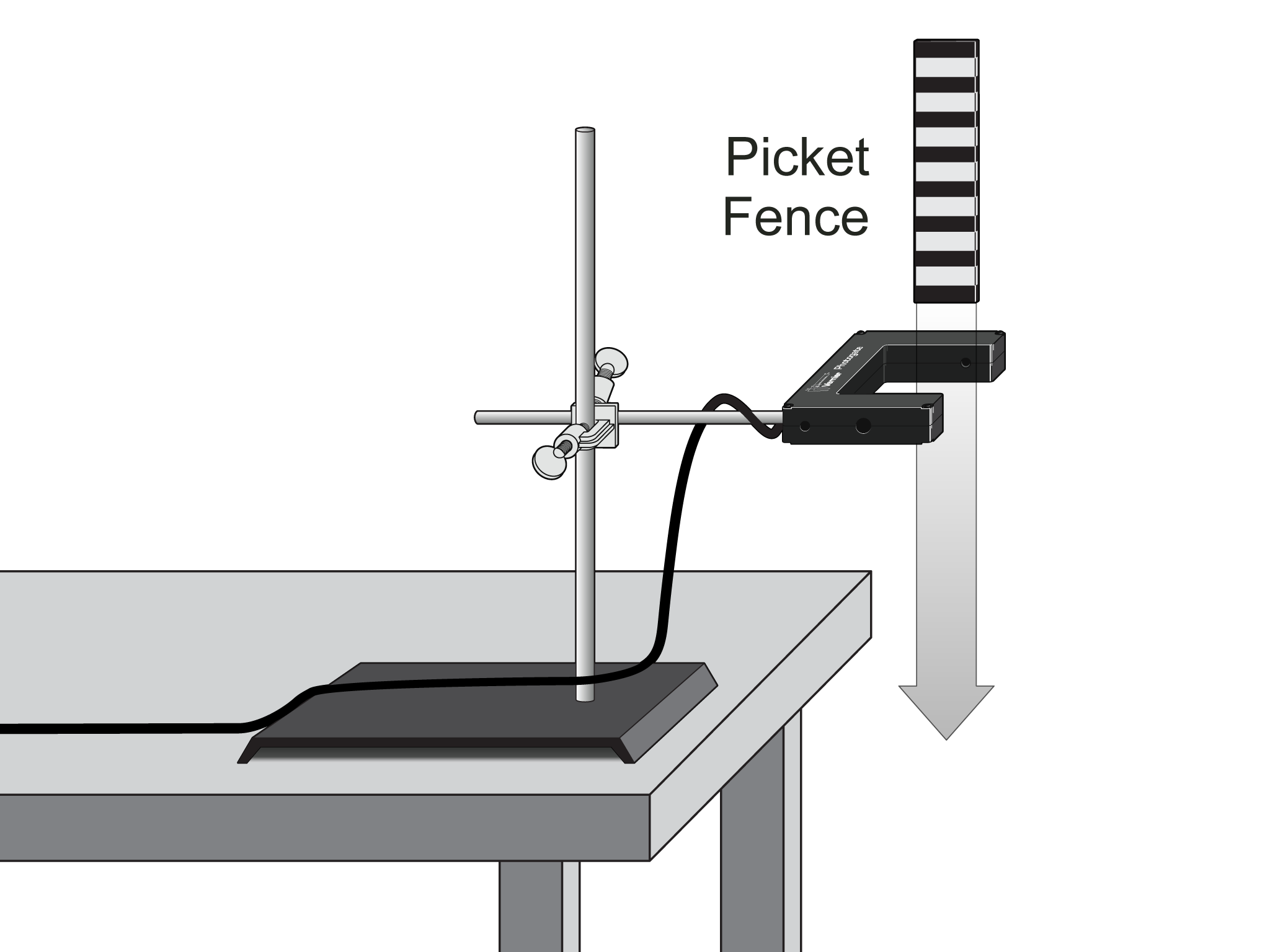
To measure the free fall acceleration of an object, we can set up a simple experiment using a timer and a ruler. First, we need to select an object to drop, such as a small ball or a pencil. Next, we need to set up a timer to measure the time it takes for the object to fall a certain distance. Finally, we can use a ruler to measure the distance the object falls.
To perform the experiment, we first need to mark a starting point and a stopping point on the ruler. We can then drop the object from the starting point and start the timer as it falls. When the object reaches the stopping point, we can stop the timer and record the time it took for the object to fall. We can then use this time, along with the distance the object fell, to calculate the free fall acceleration.
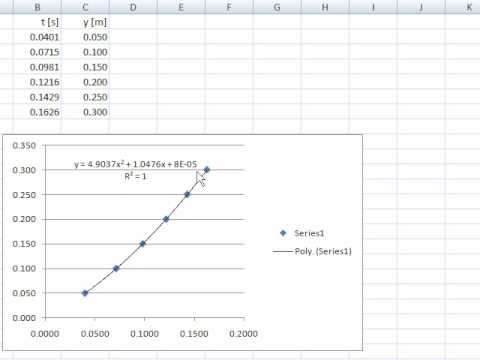
To calculate the free fall acceleration, we can use the equation: acceleration = distance / time^2. Using this equation, we can plug in the values for distance and time that we measured during the experiment to determine the free fall acceleration of the object.
Overall, the concept of free fall acceleration due to gravity is an important one in the study of physics. By performing a simple experiment, we can measure the free fall acceleration of an object and understand how it is affected by the force of gravity. This understanding can then be used to make predictions about the motion of objects in a variety of situations, such as the trajectory of a projectile or the landing of a parachute.