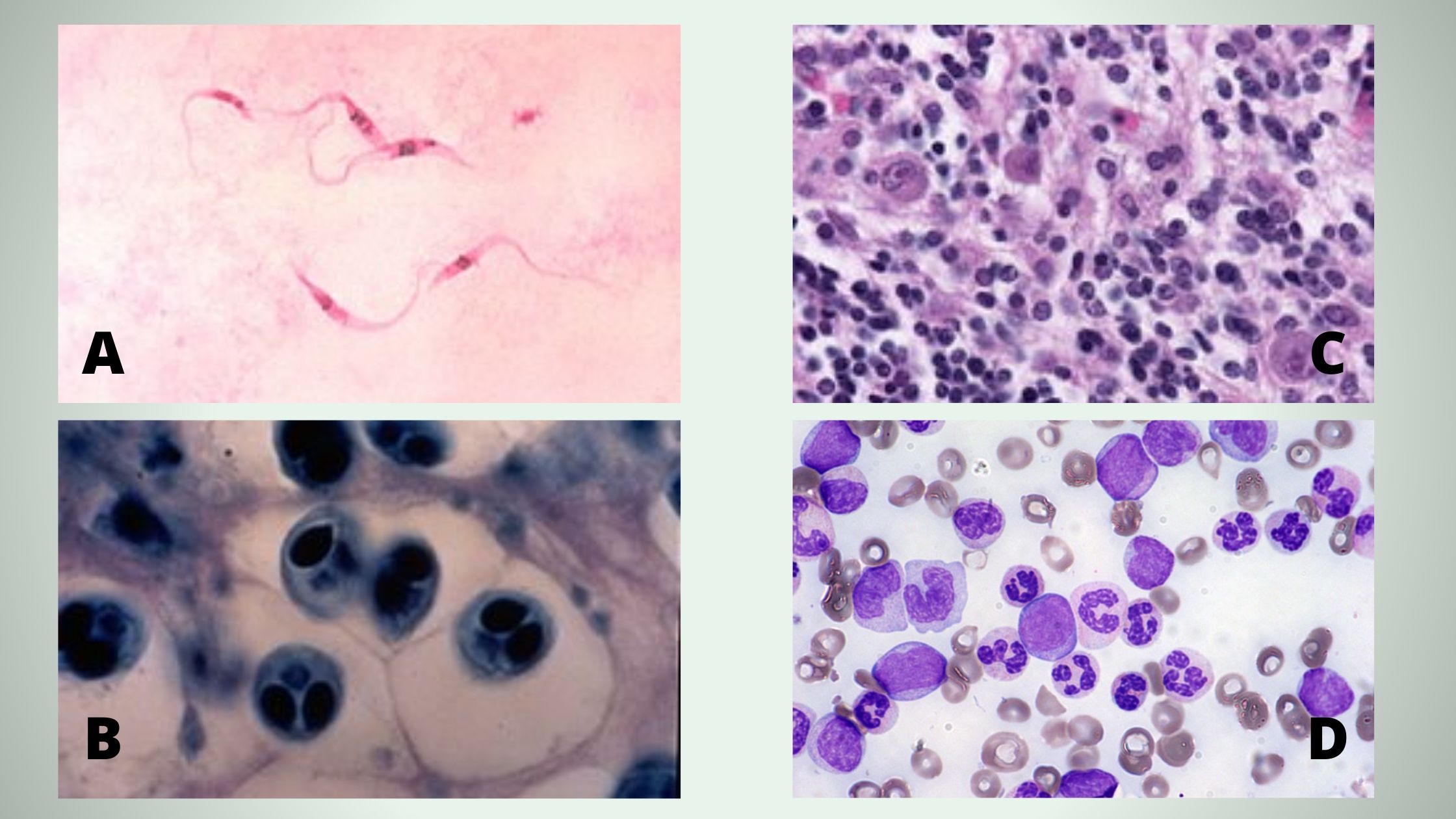
Methylene blue is a vital dye that is commonly used in the preparation of blood smears for microscopic analysis. It is used to stain the cells present in the blood sample, allowing for their identification and characterization under the microscope.
There are several functions of methylene blue solution in a blood smear. Firstly, it helps to improve the contrast and visibility of the cells present in the blood sample. Without the use of a dye, the cells in the blood smear may appear pale and difficult to distinguish from one another. Methylene blue solution helps to highlight the cells and make them more easily visible under the microscope.
Secondly, methylene blue solution is used to differentiate between different types of cells present in the blood sample. Different cell types have different morphologies, or shapes and sizes, and these morphologies can be used to identify and classify the cells. Methylene blue solution helps to highlight the morphological features of the cells, allowing for their accurate identification and classification.
Thirdly, methylene blue solution is used to identify abnormal cells in the blood sample. Abnormal cells, such as cancer cells or abnormal red blood cells, may have different morphologies compared to normal cells. By staining these cells with methylene blue solution, they can be easily identified and characterized under the microscope.
In conclusion, the function of methylene blue solution in a blood smear is to improve the contrast and visibility of the cells present in the sample, differentiate between different types of cells, and identify abnormal cells. It is an essential tool in the preparation of blood smears for microscopic analysis and is widely used in the field of hematology.
Methylene Blue as a Stain

This test is most useful in the diagnosis of haemoglobin H disease, where inclusions are usually found in 10—30% of red cells. If there is any doubt, Pappenheimer bodies can be identified by overstaining the film for iron by Perls reaction. What Is The Medical Definition Of A Microscope? What Happens If You Drink Methylene Blue? By this technique, late reticulocytes characterised by the presence of remnants of filaments or threads are readily distinguished from cells containing inclusion bodies. Haemoglobin H precipitates as multiple pale-staining greenish-blue, almost spherical, bodies of varying size Fig. They contain enzymes of the Embden—Meyerhof pathway and the pentose phosphate shunt and, unlike the mature red cells, can also derive energy aerobically via the Krebs cycle that operates in the mitochondria and oxidizes pyruvate to CO 2 and water.
New Methylene Blue

Interpretation and comments In α + thalassaemia trait, only a very occasional H body 1:1000 to 1:10000 is usually seen; they are more numerous in α 0 thalassaemia 1:100 to 1:10000 but the number of cells developing inclusions is not reliable in differentiating the various gene deletion patterns seen in α thalassaemia, and the absence of demonstrable inclusions does not preclude a diagnosis of α thalassaemia trait. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people think about worries that they just do not know about. The control specimens are treated in the same manner as the patient specimens. Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook. A correction factor is used, with the average normal hematocrit considered to be 45%.
LOEFFLER’s methylene blue solution, 500 ml, glass

As a result, when yeast cells are suspended in a dye-containing solution, the dye colours the dead cells blue while leaving the living cells uncoloured. It is also prone to technical errors that can falsely elevate or decrease the sedimentation rate. Since the surface of most bacterial cells is negatively charged, these positively charged stains adhere readily to the cell surface. The target is placed on the microscope objective, which is a clear lens that has been placed in front of the microscope. Follow the link to learn more… PROCEDURE OF LEISHMAN STAINING The Procedure of Leishman staining may vary as per the purpose of staining that means whether the staining is done for the examination of Blood cells Morphology, Toxic Granules in Leucocytes, Type of Anemia etc. Giemsa stain gives better results in parasitic studies.
What Is The Function Of The Methylene Blue Solution In The Experiment?

Gram staining is one of the most important staining methods in microbiology. Methylene blue is a colorful organic chloride salt compound used in medicine and by biologists as a dye to help them see under the microscope. The use of methylene blue is not restricted to the only chemical and medicinal field but has also been proved to be very useful in the field of aquaculture for the prevention of bacterial and fungal infections on the eggs of freshwater fish. For using counterstain you have to decolourize the primary stain using a decolorizing agent an acid-alcohol solution What does methylene blue stain One of the most popular uses of methylene blue today is in chemistry, biology, medicine and microbiology for staining or highlighting the sections specimens for the animal, bacterial, and blood tissues. Disclaimer The blog on chemicals. One of the traditional ways of demonstrating chemical kinetics in general chemistry is the blue bottle experiment.
Leishman Staining Technique

DNA analysis is then indicated see p. Methylene blue in simple staining gives up a hydroxide ion which leaves the stain positively charged. Step 5: The last phase in gram stain consists of using basic How to remove MB Stain Removal from Clothing Methylene blue is a tough stain to get out of clothing. Gram-positive organisms are organisms that preserve the primary colour and look purple-brown under a microscope. Methylene blue is soluble in water, chloroform, glacial acetic acid, glycerol, and ethanol, slightly soluble in pyridine, and insoluble in ethyl ether, oleic acid, and xylene. What Are the Chemical Properties of Methylene Blue? Staining Solution Dissolve 1. The abnormal hemoglobin cannot bind with oxygen, which results in oxygen deficiency.