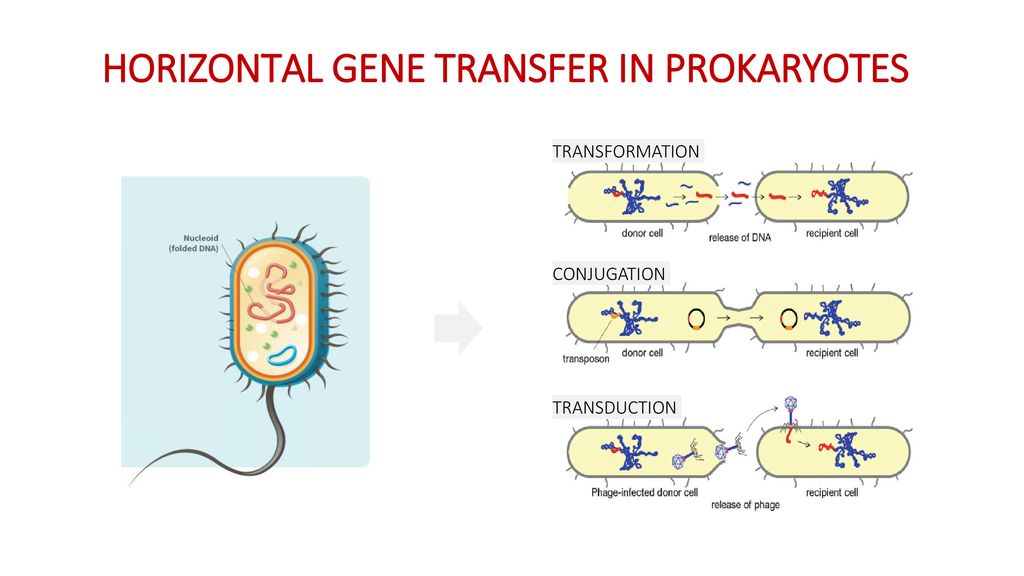
Gene transfer in prokaryotes refers to the movement of genetic material from one organism to another. This process plays a crucial role in the evolution and survival of prokaryotes, as it allows for the rapid acquisition of new genetic traits and the spread of beneficial mutations.
There are several mechanisms by which gene transfer can occur in prokaryotes. One of the most common is horizontal gene transfer, which occurs when genetic material is transferred directly from one organism to another. This can occur through various means, including the transfer of plasmids, transposons, or bacteriophages. Plasmids are small, circular pieces of DNA that can be transferred between bacterial cells and can carry a variety of genetic information, including genes for antibiotic resistance and the ability to metabolize certain substances. Transposons are also pieces of DNA that can move from one location in the genome to another, and can carry genes for antibiotic resistance and other traits. Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacterial cells and can transfer their genetic material to the host cell, leading to the expression of new traits.
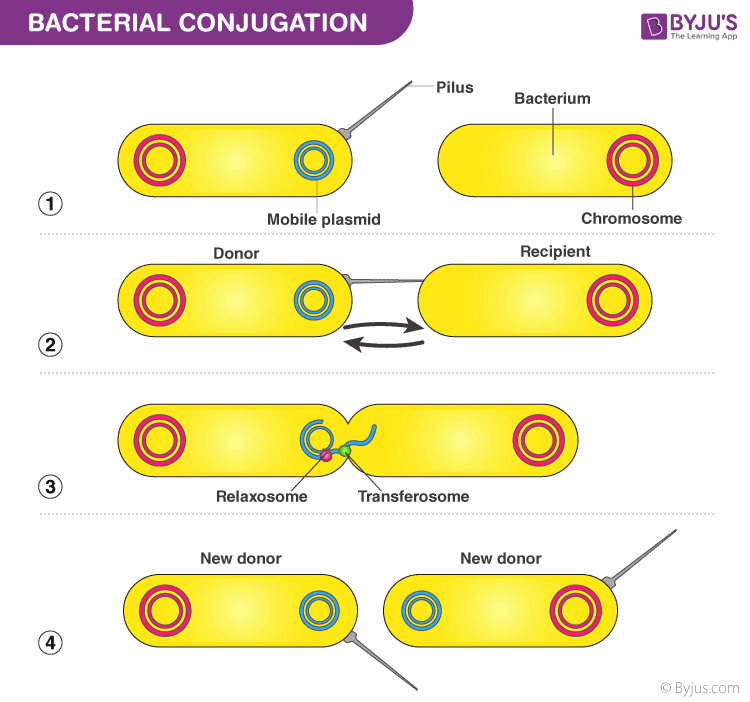
Another mechanism of gene transfer in prokaryotes is conjugation, which occurs when two bacterial cells come into physical contact and exchange genetic material through a pilus, or hair-like structure. This process is often mediated by plasmids, which contain the necessary genetic information for the transfer to occur.
Gene transfer in prokaryotes is also influenced by environmental factors, such as the presence of antibiotics or other selective pressures. For example, the widespread use of antibiotics has led to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria through the acquisition of new genetic traits through gene transfer. This has become a major public health concern, as these antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be difficult to treat and can cause serious illness.
Overall, gene transfer in prokaryotes plays a crucial role in the evolution and survival of these organisms. It allows for the rapid acquisition of new genetic traits and the spread of beneficial mutations, and is influenced by a variety of factors, including the presence of plasmids, transposons, and bacteriophages, as well as environmental pressures such as the use of antibiotics. Understanding the mechanisms and impacts of gene transfer in prokaryotes is important for understanding the evolution and behavior of these organisms, as well as for addressing public health concerns related to the spread of antibiotic resistance.