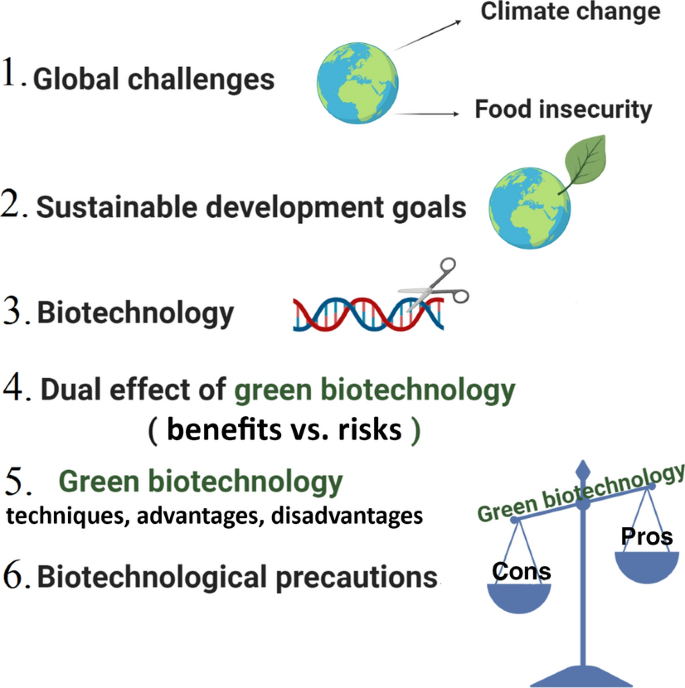
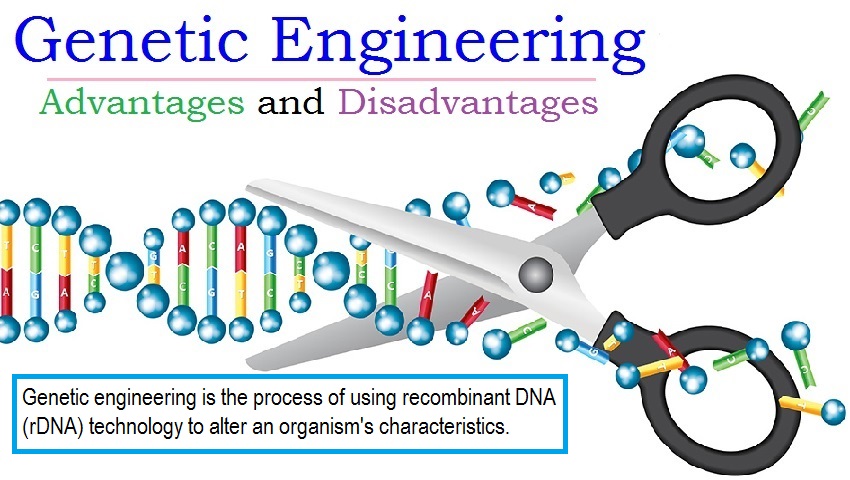
Genetic engineering, also known as gene editing, is a rapidly developing field that involves the modification of an organism's genes in order to produce a desired trait or characteristic. This technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including agriculture, medicine, and environmental conservation. However, as with any new technology, there are both advantages and disadvantages to genetic engineering that should be considered before it is widely adopted.
One major advantage of genetic engineering is the ability to produce crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, as well as more resilient to extreme weather conditions. For example, genetically modified crops such as corn, soybeans, and cotton have been developed with built-in resistance to pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and increasing crop yields. This can not only benefit farmers financially, but also reduce the environmental impact of agriculture by reducing the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
Another advantage of genetic engineering is the potential to develop new and improved pharmaceuticals, such as gene therapies that can treat or cure genetic diseases. These therapies have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of conditions such as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia, which are caused by inherited genetic mutations. In addition, genetically modified animals and plants can be used to produce proteins and other substances that can be used in the production of medications and vaccines.
However, there are also potential disadvantages to genetic engineering. One concern is the potential for unintended consequences of gene editing, as the long-term effects of these modifications are not yet fully understood. There is also the possibility that genetically modified organisms (GMOs) could have negative impacts on the environment, such as by affecting the ecosystem or by cross-breeding with non-GMO organisms and spreading modified genes. In addition, there are concerns about the potential for genetically modified crops to negatively impact the livelihoods of small farmers, as well as the potential for these crops to be controlled by a few large corporations.
Another disadvantage of genetic engineering is the ethical concerns surrounding the modification of living organisms. Some argue that it is not ethical to tamper with the natural genetic makeup of an organism, and that doing so could have unintended consequences for future generations. There are also concerns about the potential for genetic engineering to be used to create "designer" babies or to enhance certain traits in humans, which could lead to a society where people are judged based on their genetic makeup rather than their character and abilities.
In conclusion, genetic engineering has the potential to bring about significant advancements in various industries and to improve the lives of people around the world. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential advantages and disadvantages before fully embracing this technology, as there are still many unknowns and ethical concerns to be addressed.