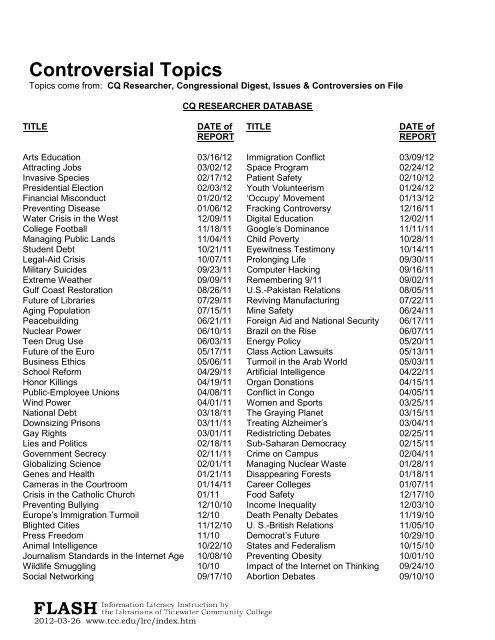
Controversial issues can be defined as topics or issues that are open to debate and likely to generate strong and often opposing views. These topics can range from social, political, and economic issues to scientific and ethical debates.
Good topics for controversial issues can be wide-ranging and varied, and may include:
Abortion: Abortion is a highly controversial and divisive issue, with people holding strong beliefs on both sides of the argument. Those who support abortion argue that it is a woman's right to choose what she does with her own body, while those who oppose abortion argue that it is the taking of a human life.
Climate change: Climate change is another controversial topic that has generated a lot of debate in recent years. While there is widespread scientific consensus that human activity is contributing to climate change, there are still those who deny that it is happening or that it is caused by human activity.
Gun control: Gun control is a highly controversial issue in the United States, with people holding strong views on both sides of the argument. Those who support gun control argue that it is necessary to reduce gun violence and protect public safety, while those who oppose gun control argue that it infringes on their right to bear arms.
Immigration: Immigration is another controversial issue that has garnered a lot of attention in recent years. Those who support immigration argue that it brings cultural diversity and economic benefits to a country, while those who oppose immigration argue that it can lead to job competition and cultural assimilation.
Euthanasia: Euthanasia, also known as assisted suicide, is the practice of intentionally ending a life in order to relieve suffering. Those who support euthanasia argue that it is a compassionate way to allow people to die with dignity, while those who oppose euthanasia argue that it is unethical and goes against the value of human life.
In conclusion, controversial issues can be found in many different areas and can be highly divisive. It is important for people to engage in respectful and open-minded dialogue when discussing these issues, and to recognize that there may be valid points of view on both sides of the argument.
World War II was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945 and involved the majority of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history, and directly involved more than 100 million people from more than 30 countries. In a state of "total war", the major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. Marked by mass deaths of civilians, including the Holocaust (in which approximately 11 million people were killed) and the strategic bombing of industrial and population centers (in which approximately one million people were killed), it resulted in 50 million to over 70 million fatalities.
The war in Europe began with the invasion of Poland by Germany and the Soviet Union, followed by the British and French declaration of war on Germany in September 1939. From late 1939 to early 1941, in a series of campaigns and treaties, Germany conquered or controlled much of continental Europe, and formed the Axis alliance with Italy and Japan. Under the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Germany and the Soviet Union partitioned and annexed territories of their European neighbours, including Poland, Finland, and the Baltic states.
In June 1941, Germany turned on the Soviets, opening the largest and the deadliest theatre of war in history. Nazi Germany acquired additional territories in eastern Europe, invaded the Soviet Union, and embarked on a massive campaign of extermination and enslavement, eventually committing the genocide of over 3 million Soviet and Polish Jews, as well as various Romani peoples, gay people, disabled people, priests, political opponents, and others deemed "unworthy of life" by the Nazi regime. In response, the Soviet Union, along with the United States, China, and the other Allies, eventually defeated the Axis powers and liberated Europe.
The drop of the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 marked the end of World War II, as the Japanese surrendered to the Allies. The United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union emerged as the world's three dominant powers, and the United Nations, formed in the aftermath of the war, and including many of the victorious powers, became the first international organization to address issues of global concern, including decolonization, and the prevention and mitigation of future conflicts. The Cold War, which began in 1947 and lasted until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, was largely a continuation of the Western and Eastern conflict and resulted in the emergence of the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc, with the United States and its allies, including the UK, facing off against the Soviet Union and its allies.
The war had a profound impact on the course of world history. The United Nations, formed in the aftermath of the war, and including many of the victorious powers, became the first international organization to address issues of global concern, including decolonization, and the prevention and mitigation of future conflicts. The legacy of the war and the ensuing Cold War shaped much of the second half of the 20th century, and continues to influence contemporary international relations.