The Great Depression and the Great Recession are two significant economic downturns that have had a lasting impact on the world economy. While both events were characterized by economic decline and high unemployment rates, there are also significant differences between the two.
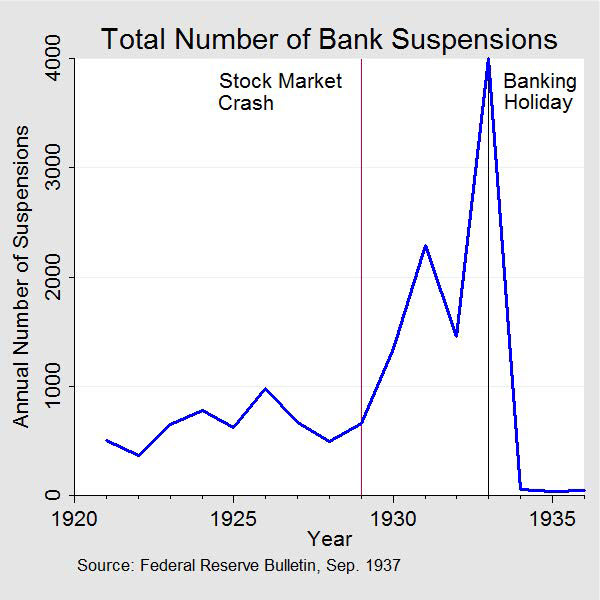
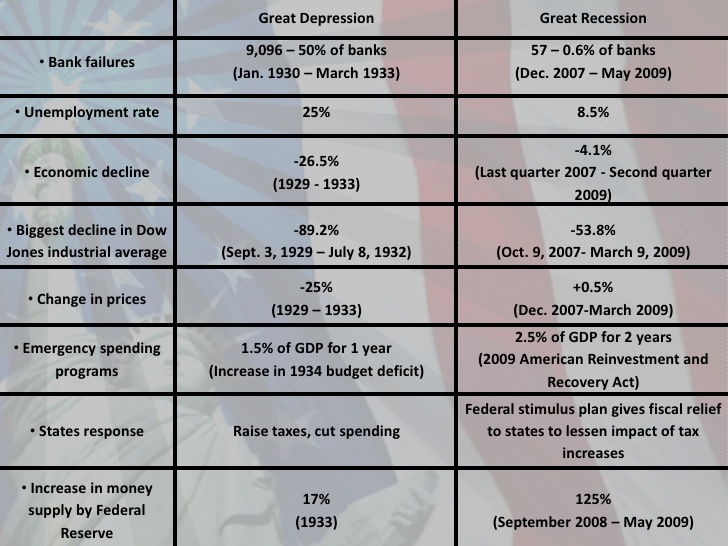
The Great Depression was a worldwide economic crisis that lasted from 1929 to 1939. It was triggered by the stock market crash of 1929, which was followed by a series of bank failures and a decline in industrial production. The Depression had a profound effect on countries around the world, with high unemployment rates, deflation, and a decline in international trade. The U.S. and Europe were particularly hard hit, with the U.S. experiencing a 25% decline in GDP and Europe suffering through a series of currency devaluations and political turmoil.
In contrast, the Great Recession was a global financial crisis that lasted from 2007 to 2009. It was triggered by the collapse of the U.S. housing market and the subsequent failure of a number of major financial institutions. The crisis spread quickly to other countries, with a decline in stock markets, a decrease in international trade, and high unemployment rates. The recession was particularly severe in the U.S., with a decline in GDP of 4.3%. However, the impact of the recession was felt around the world, with many countries experiencing economic decline and high unemployment rates.
One significant difference between the two events is the length of time they lasted. The Great Depression lasted for over a decade, while the Great Recession was relatively short-lived, lasting only a few years. This difference can be attributed to the fact that the Depression was a global economic crisis that affected nearly every aspect of the economy, while the recession was primarily a financial crisis that impacted specific sectors of the economy.
Another difference is the cause of the downturns. The Great Depression was triggered by a stock market crash, while the Great Recession was caused by the collapse of the housing market and the failure of financial institutions. This difference highlights the complexity of economic downturns and the many factors that can contribute to them.
In terms of the response to the downturns, both the Great Depression and the Great Recession saw governments taking a variety of measures to try and stimulate economic recovery. During the Depression, many countries implemented protectionist trade policies and increased government spending, while the Great Recession saw a variety of measures such as monetary and fiscal policy responses and bailouts of troubled financial institutions.
Overall, the Great Depression and the Great Recession are two significant economic downturns that have had a lasting impact on the world economy. While both events were characterized by economic decline and high unemployment rates, there are also significant differences between the two, including the length of time they lasted, their causes, and the response to the downturns.