Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and angles. Trigonometry has a long and rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Hindus.
The earliest known use of trigonometry can be traced back to the ancient Egyptians, who used it for surveying and construction purposes. The Greeks, including mathematician Hipparchus, made significant contributions to the development of trigonometry. Hipparchus is credited with the creation of the first trigonometric table, which listed the values of the trigonometric functions for various angles.
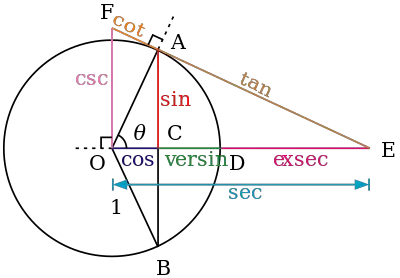
The Hindus also played a significant role in the development of trigonometry. Around the 5th century AD, Hindu mathematician and astronomer Aryabhata introduced the concept of sine, cosine, and tangent, which are now fundamental concepts in trigonometry. These functions were later used in the development of spherical trigonometry, which allows for the calculation of distances and angles on the surface of a sphere.
During the Middle Ages, trigonometry was mainly used in the study of astronomy and the calculation of the positions of celestial bodies. The Islamic mathematician Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, whose work was instrumental in the development of algebra, also made significant contributions to trigonometry.
In the 16th and 17th centuries, trigonometry saw further development with the work of mathematicians such as Galileo Galilei and René Descartes. In 1637, Descartes published his work "La Géométrie," which introduced the use of coordinates to represent points in space and laid the foundations for the development of analytic geometry.
Today, trigonometry is a vital field of mathematics that has applications in a wide range of fields, including physics, engineering, and computer science. It is used in the study of waves, oscillations, and vibrations, as well as in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures. Trigonometry is also an essential tool in the fields of navigation and satellite communication.
In conclusion, the history of trigonometry is a long and fascinating one that has seen significant contributions from many different cultures and civilizations. From its early beginnings in ancient Egypt and Greece, to its modern applications in a variety of fields, trigonometry has played a vital role in the development of mathematics and continues to be an important tool for understanding the world around us.