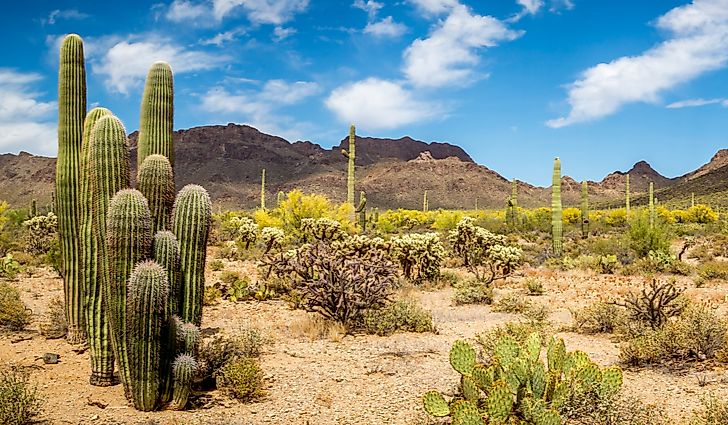
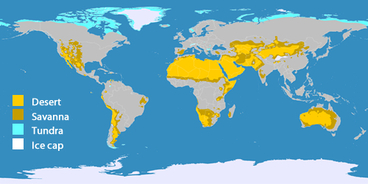
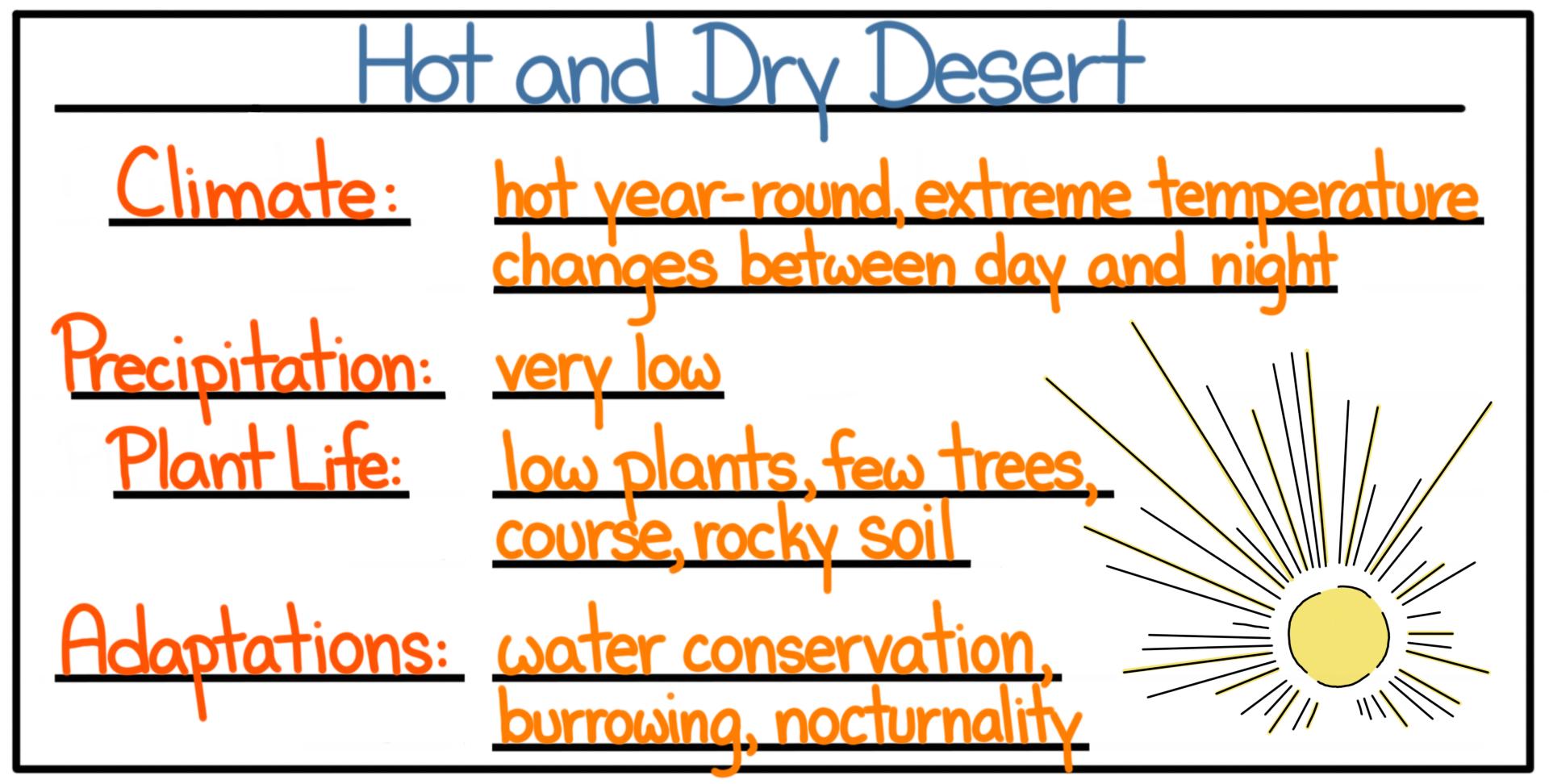
A hot desert biome is a terrestrial ecosystem characterized by extremely low precipitation, high temperatures, and sparse vegetation. These ecosystems are found in regions of the world that receive very little rainfall, often less than 25 cm (10 inches) per year. The lack of water limits the growth of plants and animals, resulting in a landscape that is largely barren and inhospitable to most forms of life.
Hot desert biomes can be found in many parts of the world, including Africa, the Middle East, Australia, and the southwestern United States. Some of the most famous hot desert biomes include the Sahara in Africa, the Mojave in the United States, and the Kalahari in southern Africa.
One of the most striking features of hot desert biomes is their extreme temperature fluctuations. During the day, temperatures can reach as high as 50°C (122°F) or more, while at night they can drop to freezing or below. These extreme temperature fluctuations can be challenging for both plants and animals, which must adapt to survive in such harsh conditions.
Despite the challenging conditions, hot desert biomes are home to a variety of unique and adapted plant and animal species. Cacti, succulents, and other drought-resistant plants are common in hot desert biomes, as they are able to survive with minimal water. Animals such as lizards, snakes, and rodents have also adapted to the harsh desert environment, often by burrowing underground to escape the heat and dryness of the surface.
Human settlements are also found in some hot desert biomes, although they are often limited in number due to the harsh living conditions. Many of these settlements are centered around sources of water, such as oases or underground aquifers, and rely on irrigation and other water-saving technologies to support agriculture and other forms of economic activity.
In conclusion, hot desert biomes are extreme and challenging environments that are characterized by low precipitation, high temperatures, and sparse vegetation. Despite the harsh conditions, these ecosystems are home to a variety of adapted plant and animal species, and are also home to some human settlements.
Hot Desert Climate: Location and Natural Vegetation
It has long stems, with the flowers placed right above a white layer of leaves, with disk-corollas that range from a dark yellow-orange hue, to a purplish one. Animals Despite the extreme environmental circumstances, numerous creatures exist in the desert habitat. Polar Deserts' Geographic Location Hot regions aren't the only regions that might have limited precipitation or harsh conditions. Polar deserts include examples such as Antarctica and Greenland. Its large ears help it to keep cool. Desert Biome Plants: The Cacti, Turpentine Bush, Brittlebush, Prickly Pears, Yuccas and Ocotillo.
The Desert Biome: Facts, Characteristics, Types Of Desert, Life In Deserts

Lizard After Emerging from Burrow The Great Basin spadefoot toad has adapted to deal with limited water and heat by burrowing into the ground and staying there until it rains. A common behavioral strategy for many desert organisms, from insects and reptiles to mammals, is to be nocturnal , or active at night. Now, what regions on Earth produce these circumstances? They are considered deserts because of the small amount of vegetation that grows there. The average temperature in this area ranges between 13-24°C, with the temperatures dropping to 5°C and below, during the winter. These plants are therophytes, which means that they spend most of their lives as seeds, only germinating when rain has fallen. Examples of coastal deserts include the Namib of southern Africa and the Atacama Desert of South America.
Desert Biome: A Definitive Guide to its Animals and Plants
By doing this, animals such as the Kangaroo Rat or the Fennec Fox, are able to burrow into the cooler earth during the day, avoiding the extreme heat and preventing wasted energy on keeping cool. Desert Geographic Distribution The latitudes that result in low precipitation circumstances due to direct sunlight or extreme lack of direct sunlight aren't the only circumstances that can create a desert. There are some differences between the different desert types but certain characteristics remain the same, allowing us to lump these 4 desert types into one biome. Their spines protect them from being eaten by animals and their waxy outer covering keeps moisture from escaping. Not solely do the burrows keep the animals cool, they are also a great place to store food. This means that each desert has its own set of plants and animals. These animals include badgers, jackrabbits, toads, lizards, nocturnal.







