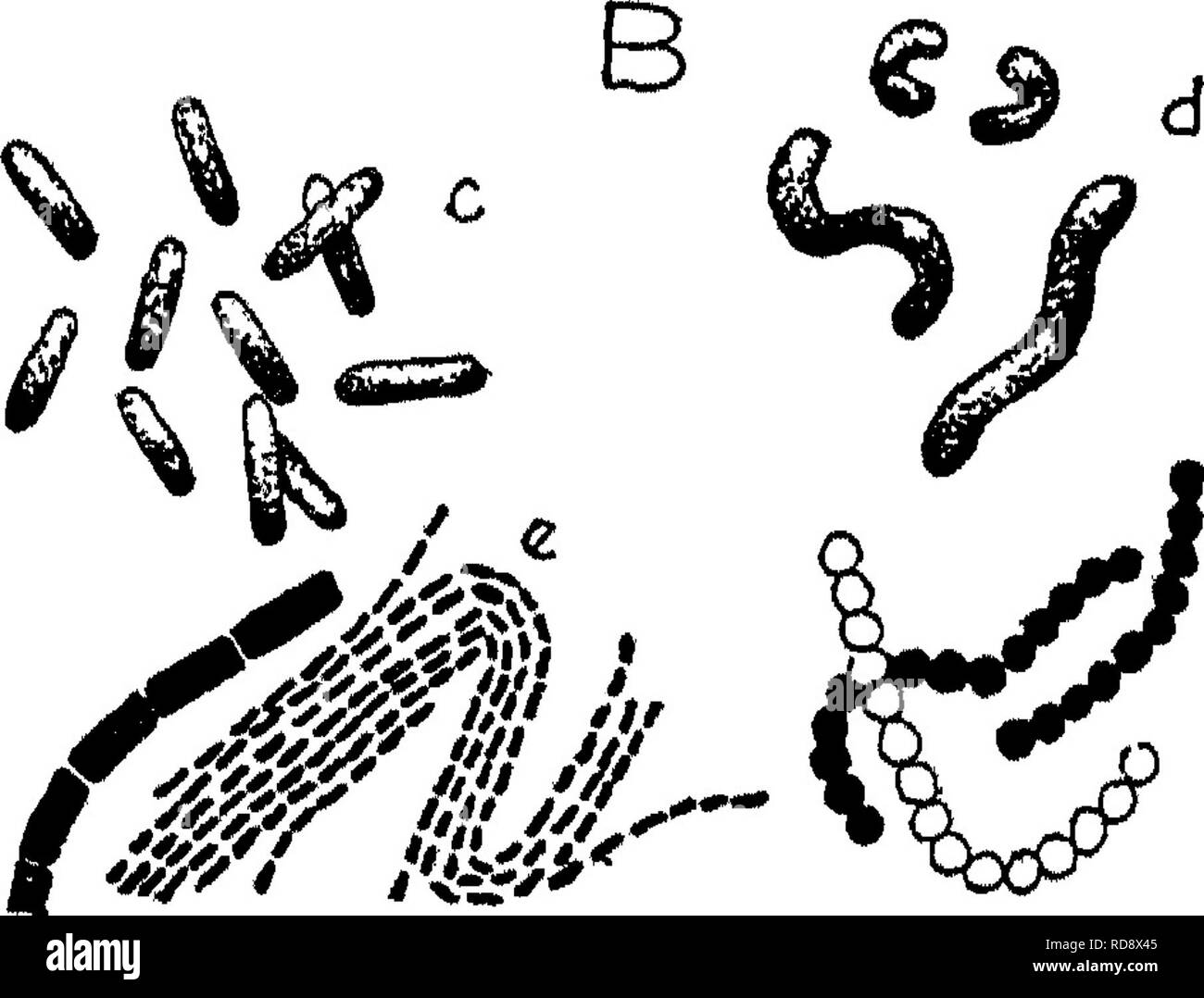
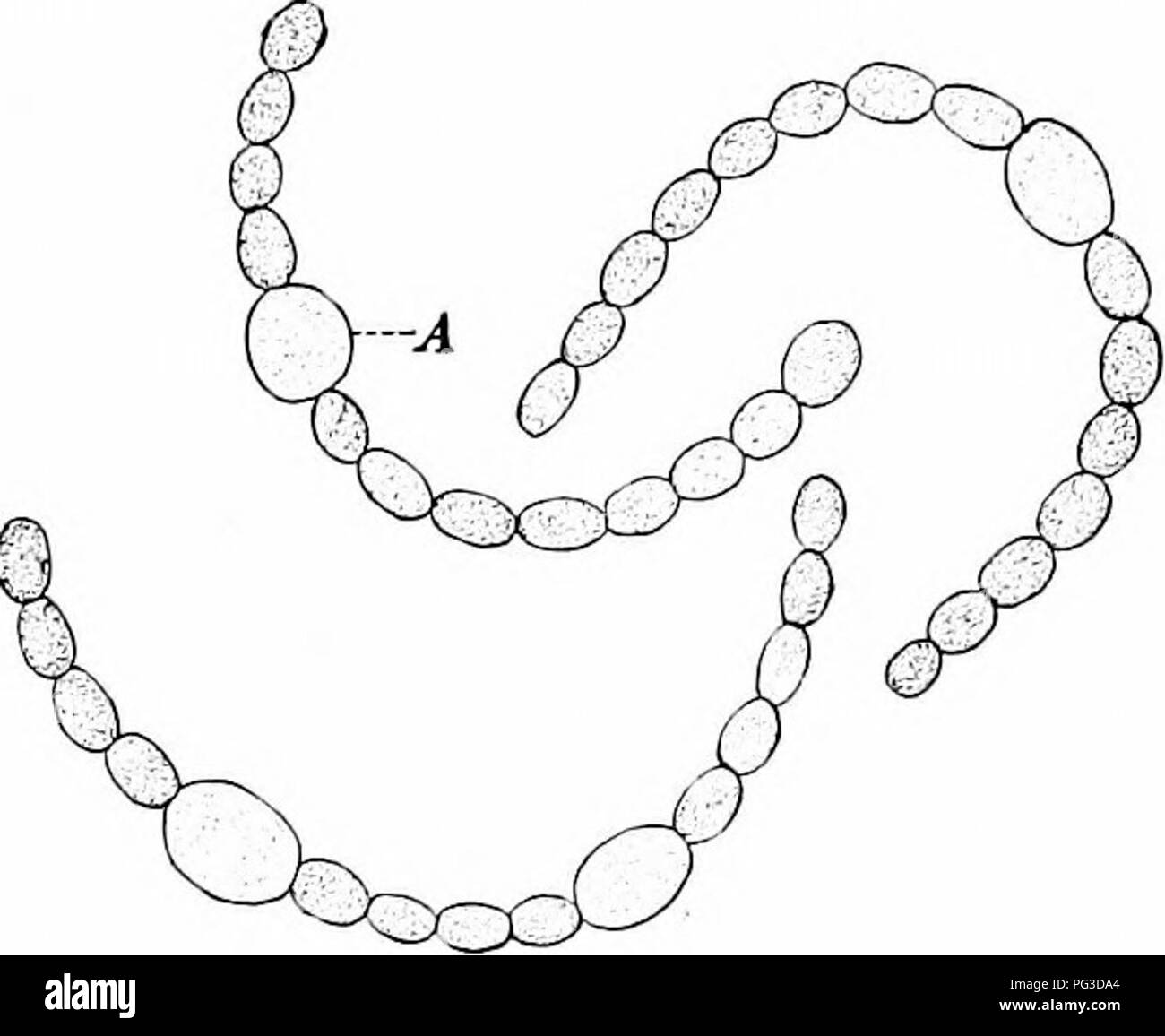
Nostoc cells and streptococcus cells are both types of bacteria, but they belong to different taxonomic groups and have a number of notable differences.
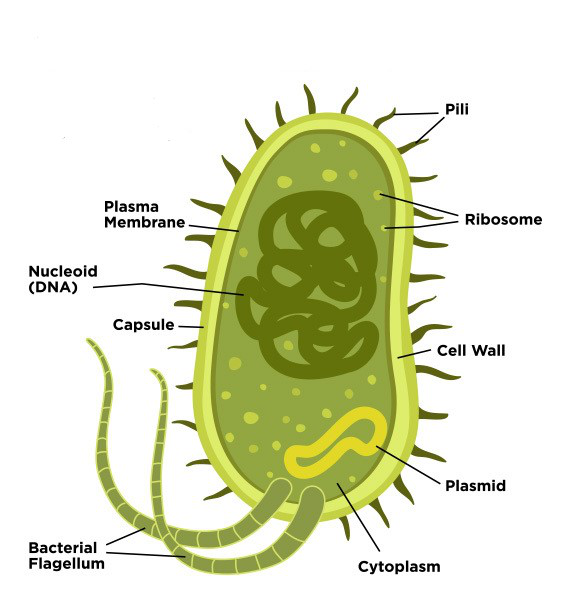
One of the main differences between nostoc cells and streptococcus cells is their shape. Nostoc cells are rod-shaped or spherical, while streptococcus cells are spherical or ovoid. This difference in shape is due to the presence of a cell wall, which provides structural support and protection to the cell. Nostoc cells have a thin, flexible cell wall made of peptidoglycan, while streptococcus cells have a thicker, more rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan and teichoic acids.
Another difference between nostoc cells and streptococcus cells is their mode of reproduction. Nostoc cells are capable of reproducing through a process called binary fission, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Streptococcus cells, on the other hand, can reproduce through binary fission as well as through a process called budding, where a small bud grows out of the parent cell and eventually separates to form a new cell.
In terms of their ecological role, nostoc cells and streptococcus cells also differ significantly. Nostoc cells are found in a variety of environments, including soil, water, and the surface of plants. They are important members of the nitrogen cycle, as they are able to fix nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and convert it into a form that plants can use. Streptococcus cells, on the other hand, are more commonly found in the intestinal tracts of animals and humans, where they can play a role in digestion. Some strains of streptococcus are also pathogenic, meaning they can cause disease in humans and animals.
Overall, nostoc cells and streptococcus cells are very different types of bacteria that have their own unique characteristics and ecological roles. While they may share some similarities as members of the bacterial kingdom, they are distinct in their shape, mode of reproduction, and ecological role.