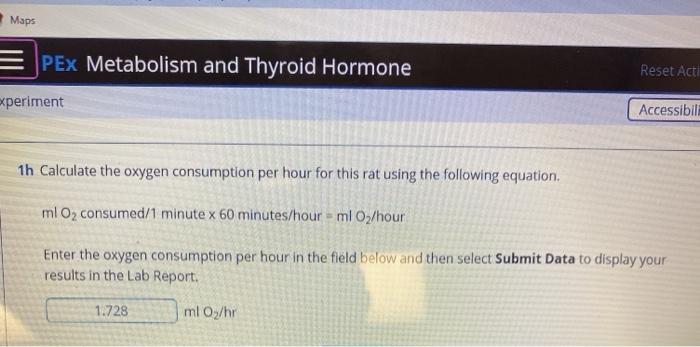
Oxygen consumption, or the rate at which oxygen is used by the body, is an important measure of physical fitness and can be used to assess the effectiveness of various training and exercise programs. In this essay, we will discuss how to calculate oxygen consumption per hour, and the factors that can affect oxygen consumption during exercise.
To calculate oxygen consumption per hour, it is necessary to measure the volume of oxygen consumed during a specific activity and the duration of that activity. This can be done using a device called an oxygen consumption meter, or an oxygen analyzer, which measures the concentration of oxygen in the air inhaled and exhaled by an individual.
To use an oxygen consumption meter, the individual being tested should wear a mask or mouthpiece that is connected to the oxygen analyzer. The oxygen analyzer will then measure the concentration of oxygen in the air inhaled and exhaled, as well as the volume of air inhaled and exhaled. The oxygen consumption per hour can then be calculated by dividing the volume of oxygen consumed by the duration of the activity.
There are several factors that can affect oxygen consumption during exercise, including the intensity and duration of the activity, the individual's age and fitness level, and the environmental conditions. For example, oxygen consumption will generally be higher during high-intensity activities, such as running or cycling, compared to lower-intensity activities, such as walking. Similarly, oxygen consumption will generally be higher in individuals who are less fit, as their bodies have to work harder to meet the demands of the activity. Finally, oxygen consumption may be affected by environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, which can affect an individual's ability to breathe and deliver oxygen to the muscles.
In conclusion, calculating oxygen consumption per hour is a useful way to assess physical fitness and the effectiveness of exercise programs. To do so, it is necessary to measure the volume of oxygen consumed during a specific activity using an oxygen consumption meter, and to take into account factors such as intensity, duration, fitness level, and environmental conditions.

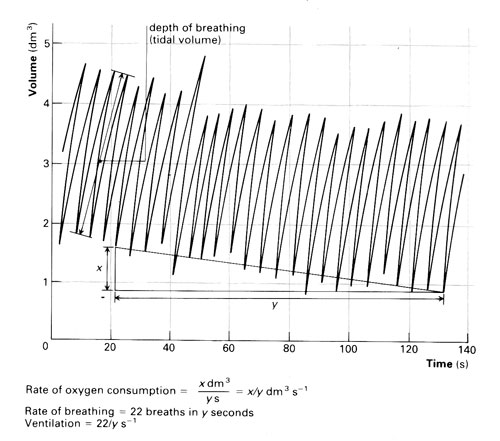

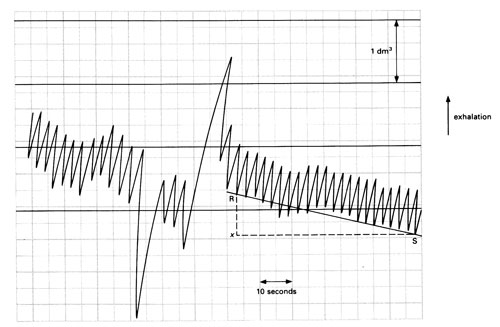
.jpg)