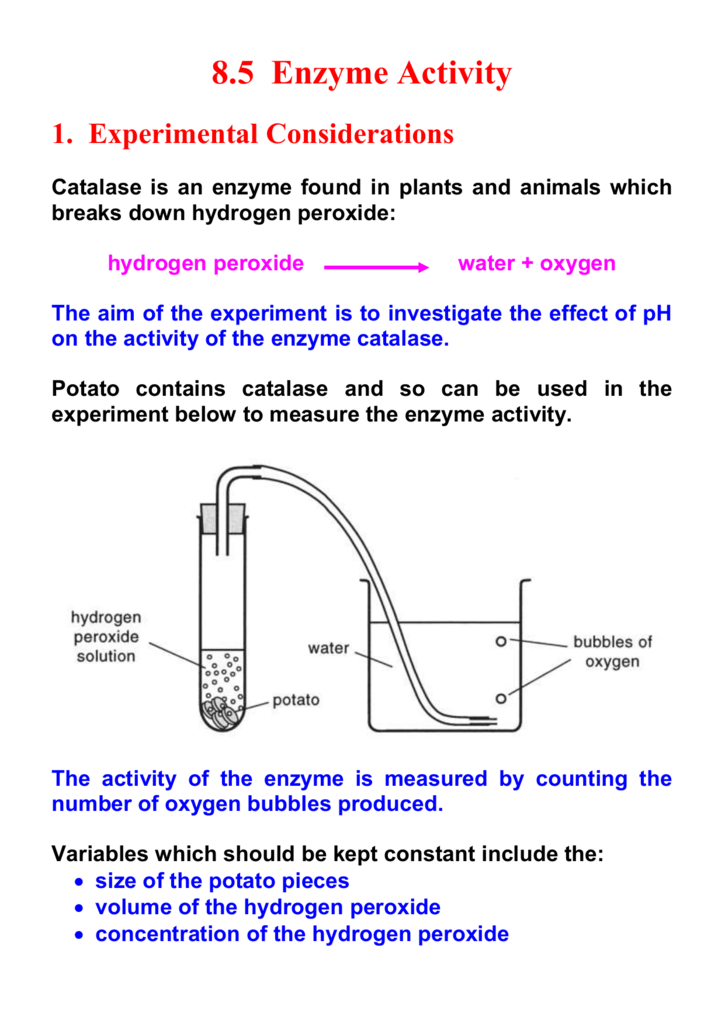
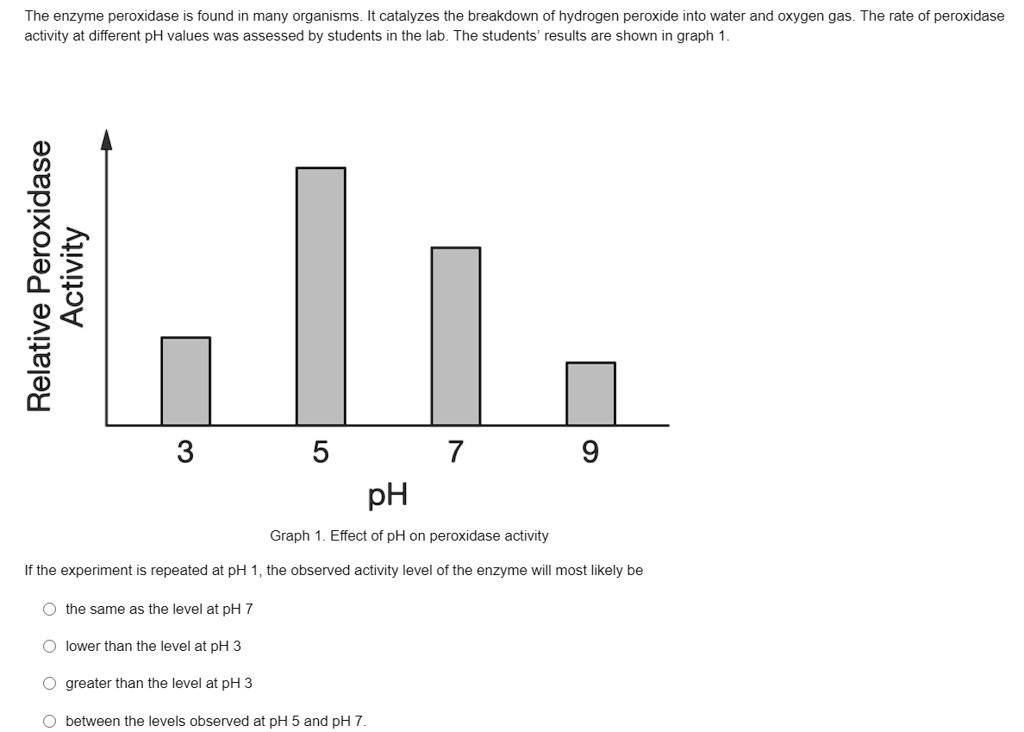
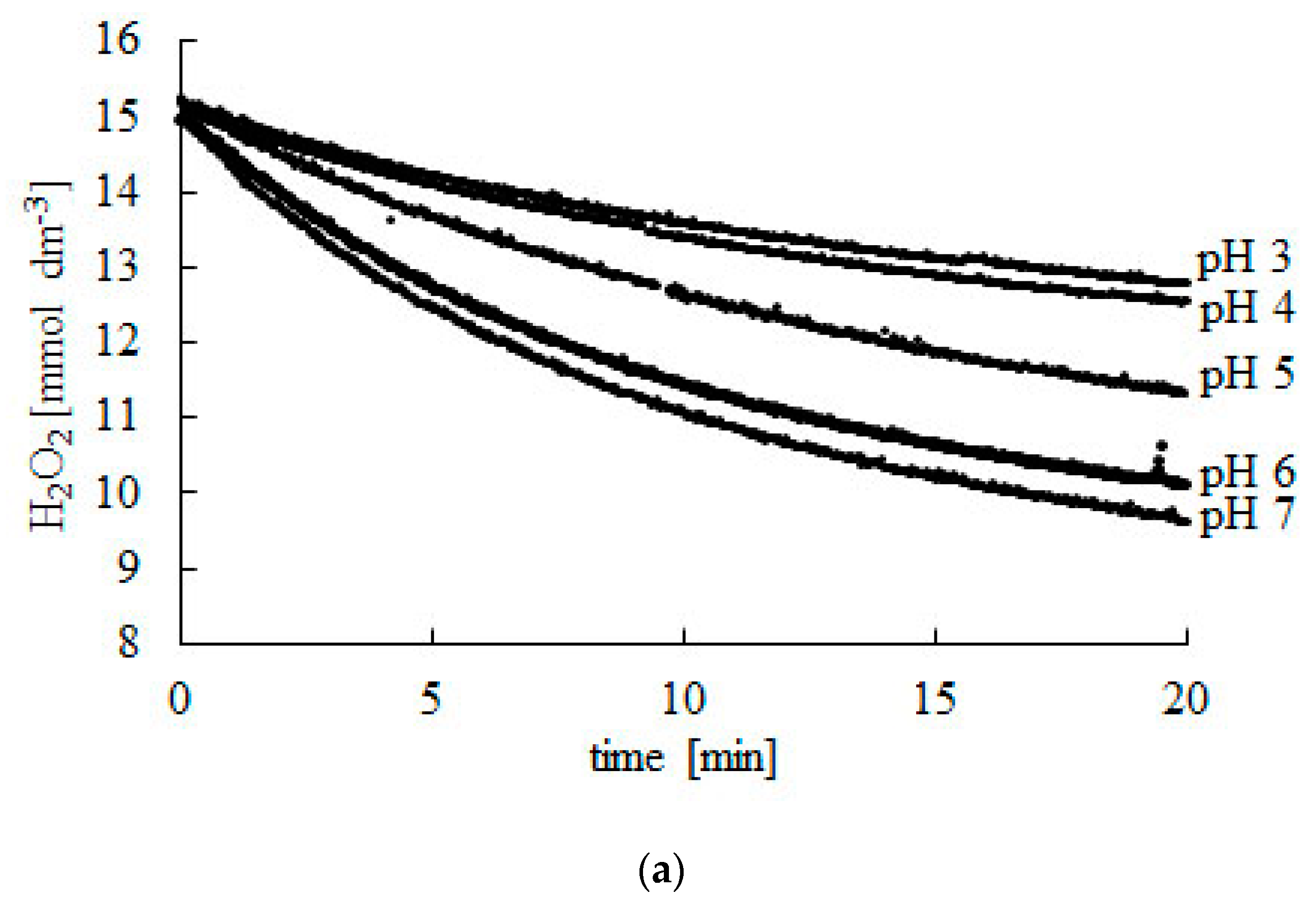
Hydrogen peroxide, also known as H2O2, is a chemical compound that is commonly used as a disinfectant and a bleaching agent. It is a pale blue liquid that is composed of two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms, and it is a powerful oxidizing agent that can be used to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
One of the most important properties of hydrogen peroxide is its pH, which refers to its acidity or basicity. pH is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic. A neutral pH is 7, which means that a substance is neither acidic nor basic.
Hydrogen peroxide has a pH of around 7, which means that it is slightly basic. This is due to the fact that hydrogen peroxide contains hydroxide ions (OH-), which are responsible for its basicity. The concentration of these ions increases as the pH increases, making hydrogen peroxide more basic as the pH increases.
The pH of hydrogen peroxide is important because it affects its ability to kill bacteria and other microorganisms. At a neutral pH, hydrogen peroxide is most effective at killing bacteria, but as the pH becomes more acidic or basic, its effectiveness decreases. This is because hydrogen peroxide relies on the presence of hydroxide ions to kill bacteria, and the concentration of these ions decreases as the pH becomes more acidic or basic.
In addition to its use as a disinfectant, hydrogen peroxide is also used in a variety of other applications, including the bleaching of textiles and the production of personal care products such as hair dyes and teeth whiteners. It is also used in the production of chemicals and in the treatment of wastewater.
Overall, hydrogen peroxide is a versatile and effective chemical compound that is used in a variety of applications. Its pH plays a critical role in its effectiveness as a disinfectant and bleaching agent, and understanding its pH is important for those who work with or use hydrogen peroxide in their daily lives. So, it's very important to know the pH of hydrogen peroxide.
What is the pH level of hydrogen peroxide?
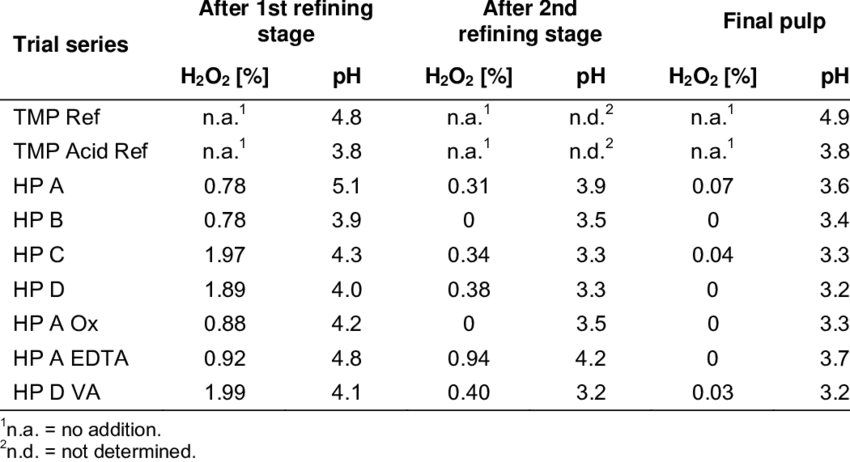
H2O2 is Widely Used Since it was first commercialized in the 1800's, hydrogen peroxide production has now grown to over a billion pounds per year as 100%. Two systems using H 2O 2 vapour are available commercially — Bioquell and Steris. Antimicrobial stewardship programs promoting judicious use of antimicrobial agents can also reduce the risk of CDAD. Retrieved 29 June 2014. Metals oxidation Oxidizes ferrous iron, manganese, arsenic, and selenium to improve their adsorption, filtration, or precipitation from process waters and wastewaters. When used properly, hydrogen peroxide is still a helpful household disinfectant and health aid. During the massive cleanup effort in the wake of the 2001 attacks, there has been increased understanding of decontamination of spores that has continued during the remainder of the decade.
Hydrogen peroxide

Removal of blood stains Hydrogen peroxide reacts with blood as a bleaching agent, and so if a blood stain is fresh, or not too old, liberal application of hydrogen peroxide, if necessary in more than single application, will bleach the stain fully out. Journal of Chemical Physics. But hydrogen peroxide and benzoyl peroxide are not the same. Or if you feel like giving this hardworking appliance a spa day, use hydrogen peroxide, baking soda, and essential oils to make a 2. Brian K Meyer, in Therapeutic Protein Drug Products, 2012 4.
Drinking Hydrogen Peroxide: Is It Safe?

Before using peroxide, check the expiration date. Check out the video having a litmus test for hydrogen peroxide. One method uses a deep vacuum to pull liquid hydrogen peroxide from a disposable cartridge through a heated vaporizer and then, following vaporization, into the sterilization chamber. One very popular peracetic acid sterilisation system for endoscopes and devices that are sensitive to moisture and radiation, Steris 1, is now under mandatory recall by the FDA Steris 1 peracetic acid sterilisation system recall 8. See: Joseph William Mellor, A Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry, vol.