A stereotype is a widely held but fixed and oversimplified image or idea of a particular type of person or thing. Stereotypes are often based on appearances, culture, ethnicity, gender, and other characteristics, and they can be both positive and negative. While stereotypes may seem harmless, they can have serious consequences and can be harmful to those who are being stereotyped.
One of the main problems with stereotypes is that they often lead to prejudice and discrimination. When people hold stereotypes about certain groups of people, they may treat those individuals unfairly or unjustly. This can lead to negative consequences such as difficulty finding employment, housing, or even experiencing violence. Stereotypes also limit individuals by restricting their opportunities and limiting their ability to be seen as individuals rather than members of a group.
Another issue with stereotypes is that they often rely on incomplete or inaccurate information. People may base their stereotypes on a limited number of experiences or interactions with a particular group, rather than taking the time to understand the diversity and complexity of that group. This can lead to misunderstandings and further perpetuate negative stereotypes.
It is important to challenge and dismantle stereotypes in order to create a more inclusive and equitable society. This can be done by educating oneself about different cultures and groups, engaging in respectful dialogue with others, and speaking out against stereotypes when they are encountered. By actively working to combat stereotypes, we can create a more understanding and accepting world for everyone.
In conclusion, stereotypes are harmful and limiting beliefs that rely on incomplete or inaccurate information. It is important to challenge and dismantle stereotypes in order to create a more inclusive and equitable society. By educating ourselves and actively working to combat stereotypes, we can create a more understanding and accepting world for everyone.
Z
In an upper tail test, if the test statistic is greater than or equal to the critical value, reject the null hypothesis. To test the hypothesis in the critical value approach, compare the critical value to the test statistic. The researchers reported the following sample statistics. If the p-value is greater than the level of significance, do not reject the null hypothesis. We welcome all your suggestions in order to make our website better.
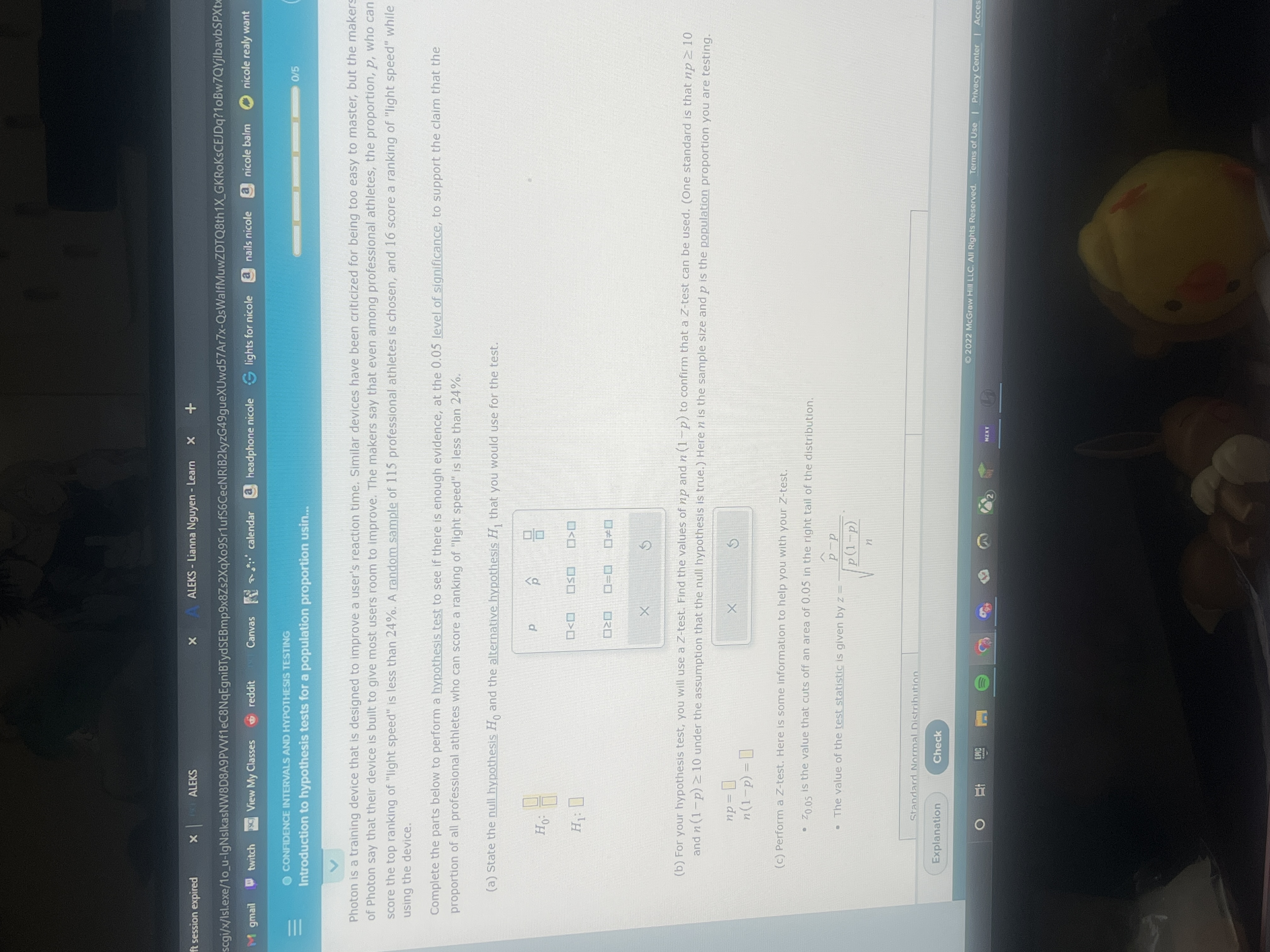
Hypothesis Test for a Population Mean (1 of 5)

Only 12 seconds on average to download a 3-minute song from iTunes! The mean pregnancy length is 266 days. However, there are certain conditions that should be satisfied by the sample to run the Z-Test. Then fill in the table below. Can we support, at the level of significance , the claim that the mean breaking strength has increased? In practice, it is often impossible to verify that the variable is normally distributed in the population. Z-test uses the sample data to test the hypothesis about the population parameters mean or proportion. If the p-value is less than or equal to the level of signifance, reject the null hypothesis. If the alternative hypothesis is not equal to, the P-value is equal to double the tail area beyond the test statistic.
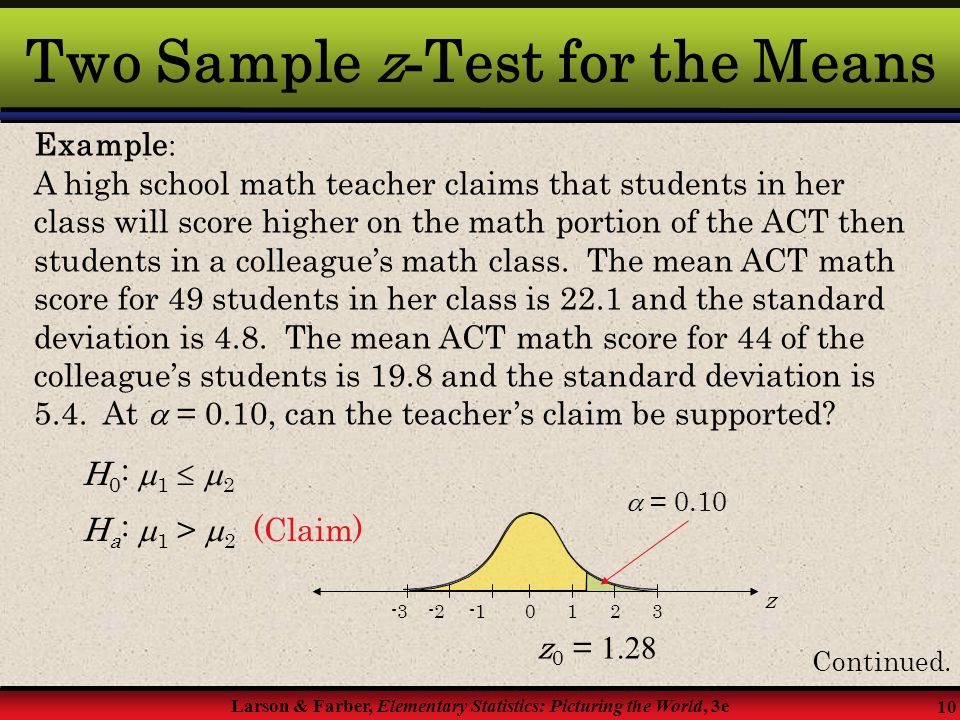
Aleks Hypothesis Test Of Difference In Population Means T Test
With a t-score this large, the P-value is very small. This means the data fits with typical results from random samples selected from the population described by the null hypothesis. With this speed, the ad claims, it takes, on average, only 12 seconds to download a typical 3-minute song from iTunes. We conclude there is significant evidence in favor of H a. We will reject the null hypothesis.
Chapter 7: Hypothesis Testing with z Tests Flashcards
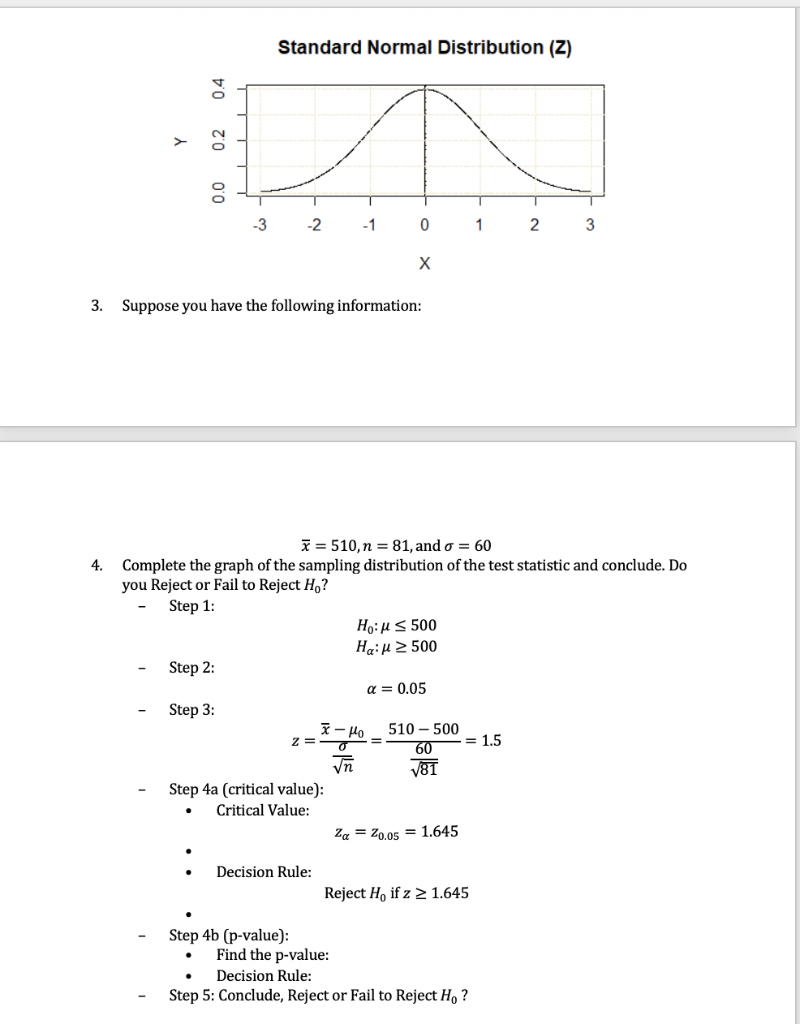
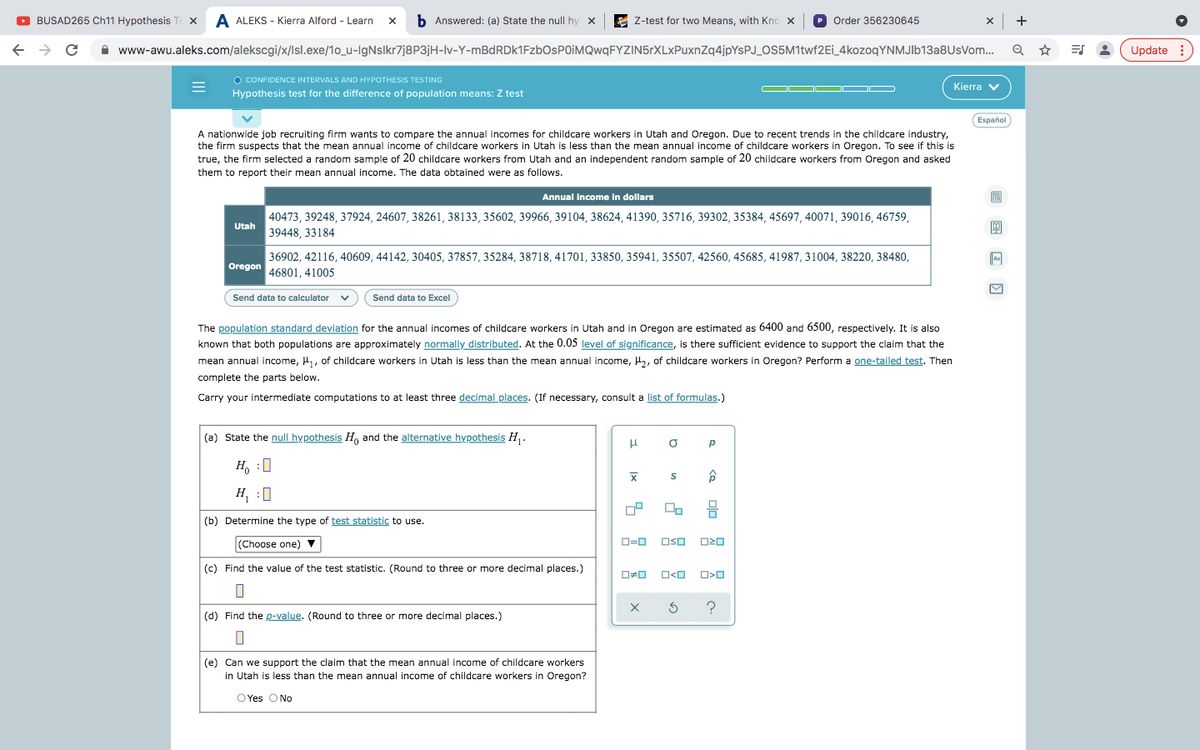
As sample data provide us a door to the entire population, it should be large enough for us to arrive at a significant inference. If she had, the logic is the same as we used for hypothesis tests in Modules 8 and 9. Hence the alpha level should be chosen in such a way that the chance of making Type I or Type II error is minimal. The authors did this, also. The mean of the sampling distribution is at 3,500 as predicted by the null hypothesis. Hypothesis test for the difference of population means: Z test Past records suggest that the mean annual income, , of teachers in state of California is less than or equal to the mean annual income, , of teachers in Oregon.
10.16: Hypothesis Test for a Population Mean (5 of 5)

The t-test statistic has a familiar form. Since the researchers conducted a t-test with this data, we will assume that the conditions are met. Step 4: State a conclusion. When the population has a large size, and the sample data is small, we will not be able to draw an accurate conclusion from the test to prove our null hypothesis is false. If there is a less than sign in the alternative hypothesis then it is a lower tail test, greater than sign is an upper tail test and inequality is a two-tailed test.
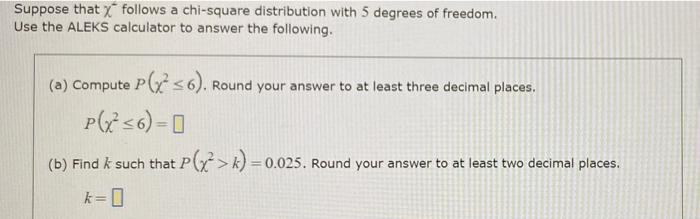
Hypothesis test for the population mean
The test statistic is larger than the critical value it falls in the rejection zone. Review of Type I and Type II Errors We know that statistical inference is based on probability, so there is always some chance of making a wrong decision. The logic of the hypothesis test is always the same. To find the area to the right of 2. If this variable is not known, samples of more than 30 will have a difference in sample means that can be modeled adequately by the t-distribution. By more extreme, we mean further from value of the parameter, in the direction of the alternative hypothesis.
20. Hypothesis test for the population mean

Ideally, we'd like to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. We can write the hypotheses in terms of µ. It is more complicated to calculate the probability of a type II error. She thinks ahead to the conditions required, which helps her collect a useful sample. There are two common types of Z-Test One-Sample Z-Test This is the most basic type of hypothesis test that is widely used. Can we conclude that the mean lifetime of light bulbs. For traditional-age, predominantly White college women, diminished meal size appears to be an attempt to assert femininity in groups that include men.