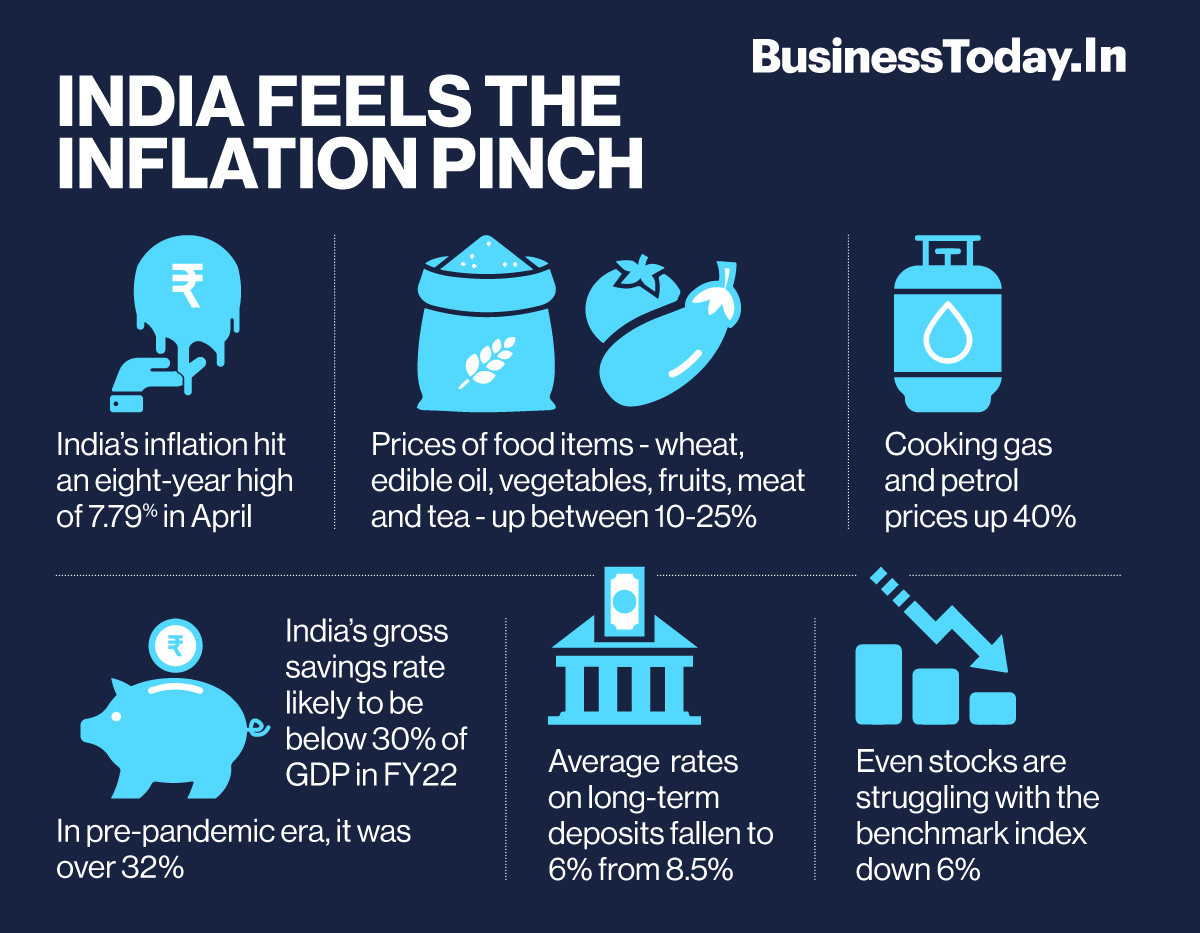
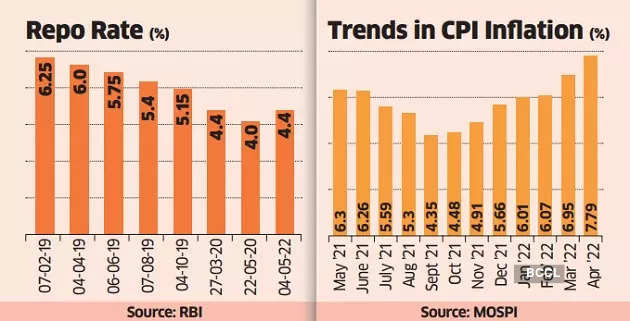
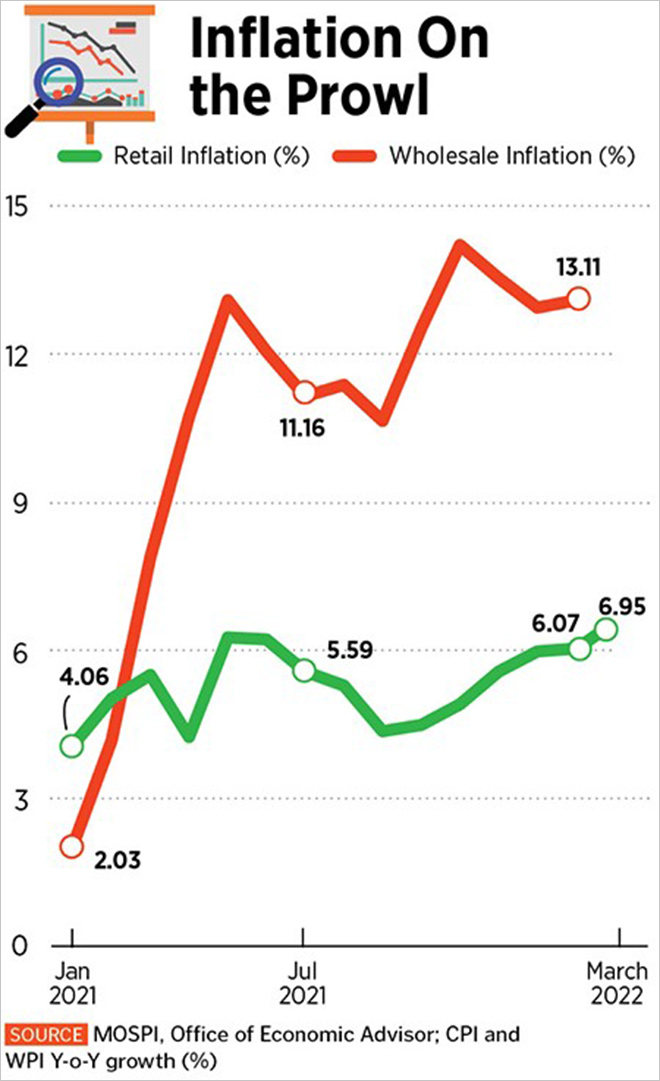
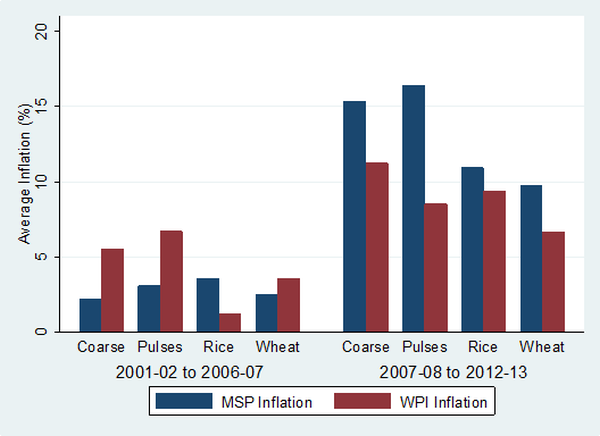
Inflation is a rise in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within an economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index (normally the consumer price index) over time.
In India, inflation has been a persistent problem for many years. It has not only affected the purchasing power of the common man, but has also had a negative impact on the country's economic growth.
One of the main causes of inflation in India is the increasing demand for goods and services. As the population of India grows and the economy expands, there is a higher demand for goods and services. However, if the supply of these goods and services does not increase at the same rate, it leads to a rise in prices.
Another factor contributing to inflation in India is the rising cost of production. The cost of raw materials, labor, and other inputs has been increasing over the years, leading to a rise in the prices of finished goods.
The government's monetary and fiscal policies also play a role in the inflationary trend in the country. If the government increases the money supply without a corresponding increase in the production of goods and services, it can lead to inflation. Similarly, if the government increases taxes or reduces spending, it can lead to a decrease in demand and a fall in prices.
The impact of inflation on the common man in India is significant. As the prices of goods and services rise, the purchasing power of the individual decreases. This means that the same amount of money that could buy a certain quantity of goods and services in the past may not be sufficient to buy the same quantity in the present. Inflation also affects the savings of individuals as the value of money decreases over time.
Inflation also has a negative impact on the country's economic growth. High inflation leads to uncertainty and instability in the economy, as businesses and consumers are unable to make long-term plans due to the constantly changing prices. This can lead to a slowdown in economic activity, as businesses may be hesitant to invest and consumers may be hesitant to spend.
To combat inflation, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has a number of tools at its disposal. It can increase the interest rates, which can reduce the demand for goods and services, leading to a fall in prices. The RBI can also sell government securities, which can reduce the money supply in the economy and lead to a fall in prices.
In conclusion, inflation has a significant impact on the common man and the economy of India. It affects the purchasing power of individuals and can have a negative impact on economic growth. The RBI has various tools at its disposal to combat inflation, but it is important for the government to adopt policies that address the root causes of inflation in the country.