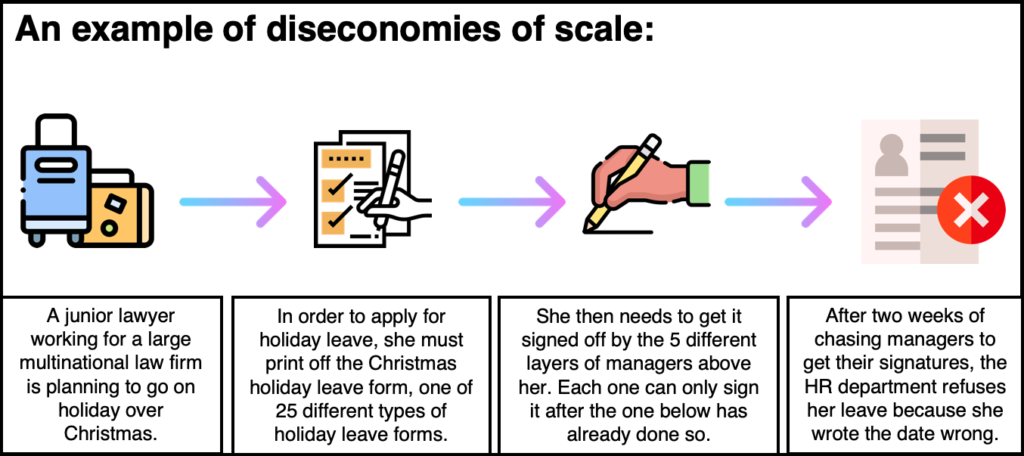
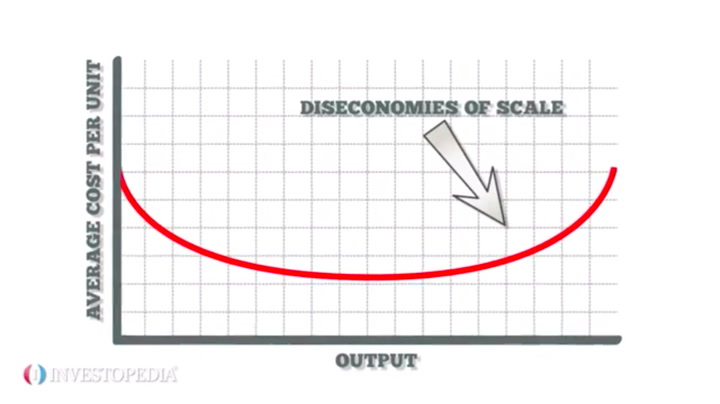
Internal diseconomies of scale refer to the negative effects that a company experiences as it expands in size. These effects can lead to decreased efficiency and increased costs, which can ultimately hinder the company's competitiveness and profitability.
There are several factors that can contribute to internal diseconomies of scale. One common factor is the complexity of the organization. As a company grows, it may become increasingly difficult to coordinate and manage all of its different parts. This can lead to problems with communication, decision-making, and resource allocation, which can all impact efficiency.
Another factor that can contribute to internal diseconomies of scale is the increased bureaucracy that often comes with growth. As a company expands, it may need to create more layers of management and bureaucracy in order to oversee and control its operations. This can lead to slower decision-making and a decrease in flexibility, as well as higher administrative costs.
A third factor that can cause internal diseconomies of scale is the loss of personal touch and individual attention. As a company grows, it may be more difficult for managers and employees to have personal relationships with each other, leading to a decrease in motivation and morale. This can also lead to a decline in the quality of customer service, as there may be less individual attention given to each customer.
There are several ways that companies can mitigate the negative effects of internal diseconomies of scale. One approach is to adopt new technologies and processes that can help streamline operations and improve efficiency. Another approach is to reorganize the company's structure in order to reduce bureaucracy and improve communication and decision-making. Finally, companies can focus on maintaining a positive company culture and keeping employees motivated and engaged, in order to maintain high levels of productivity and customer service.
In conclusion, internal diseconomies of scale refer to the negative effects that a company can experience as it grows in size. These effects can include decreased efficiency, increased bureaucracy, and a loss of personal touch, which can all impact the company's competitiveness and profitability. By adopting new technologies, reorganizing the company's structure, and maintaining a positive company culture, companies can mitigate the negative effects of internal diseconomies of scale and continue to thrive as they grow.