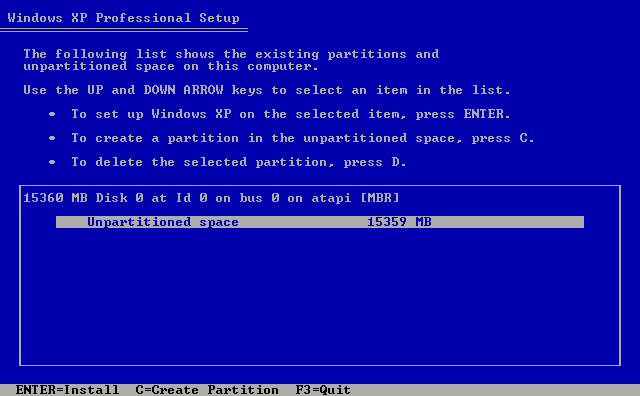
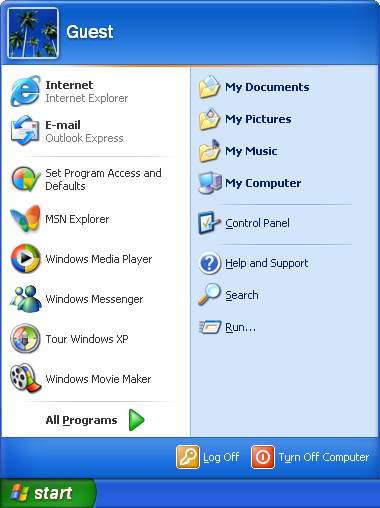
Windows XP was a popular operating system (OS) developed by Microsoft that was released in 2001. It was the successor to Windows 2000 and the predecessor to Windows Vista. Windows XP was known for its stability, user-friendly interface, and compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software.
One of the key features of Windows XP was its use of the graphical user interface (GUI). This made it easy for users to navigate and interact with their computer using visual elements like icons, windows, and menus. Windows XP also introduced the taskbar, which allowed users to easily switch between different programs and access common tasks.
Windows XP was designed to be user-friendly, with a number of built-in tools and utilities to help users manage their system. These included the System Restore tool, which allowed users to roll back their system to a previous state in case of problems, and the Disk Cleanup utility, which helped users free up space on their hard drives.
In addition to its user-friendly features, Windows XP was also known for its compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software. It was designed to work with a wide range of hardware devices, including printers, scanners, and digital cameras, and was compatible with a wide range of software applications, including productivity tools like Microsoft Office and media players like Windows Media Player.
Despite its popularity, Windows XP eventually reached the end of its life cycle and was no longer supported by Microsoft. It was replaced by newer operating systems, such as Windows Vista and Windows 7. However, many users still continue to use Windows XP today due to its stability and compatibility with older hardware and software.
Overall, Windows XP was a popular and successful operating system that introduced many features that are still used in modern operating systems today. Its user-friendly interface and wide range of compatibility made it a popular choice for both personal and professional users.