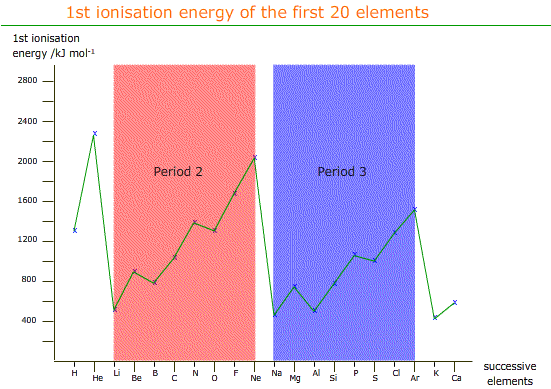
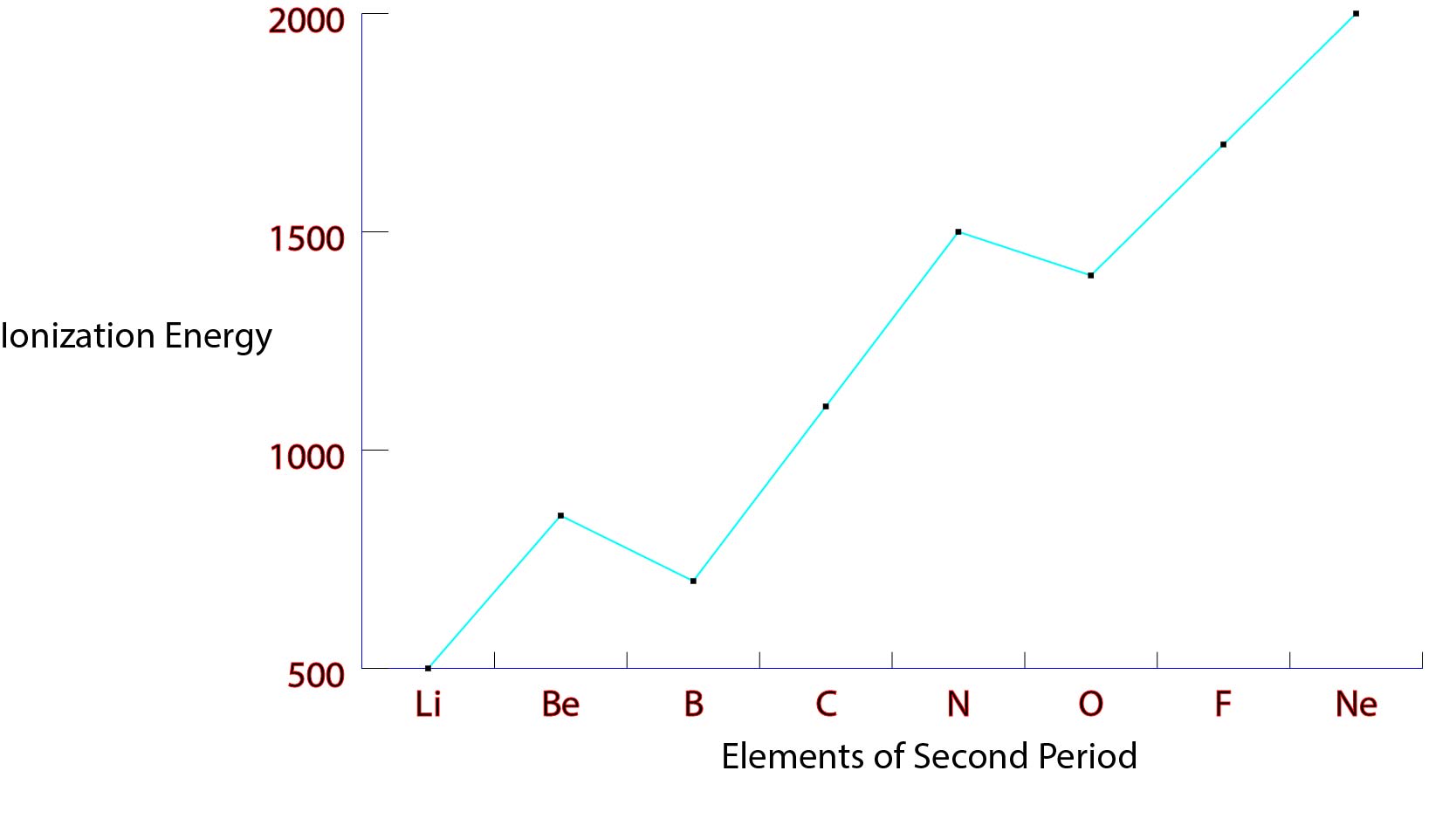
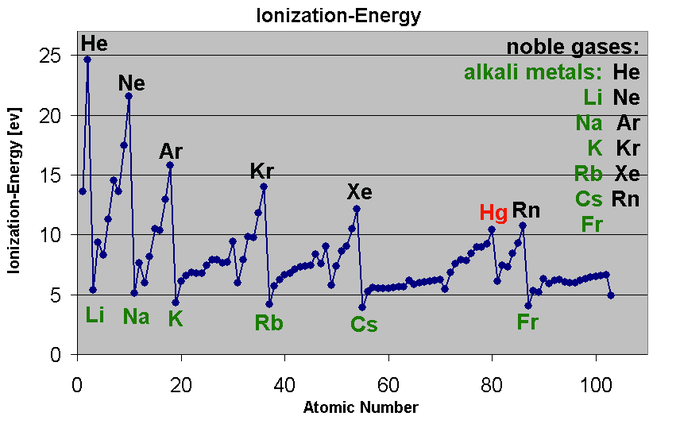
Ionization energy, also known as ionization potential, is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or a positive ion. It is a measure of the strength of the attraction between the electron and the nucleus of an atom. Ionization energy is an important concept in chemistry, as it helps to predict and understand the behavior of atoms and the way they interact with other atoms and molecules.
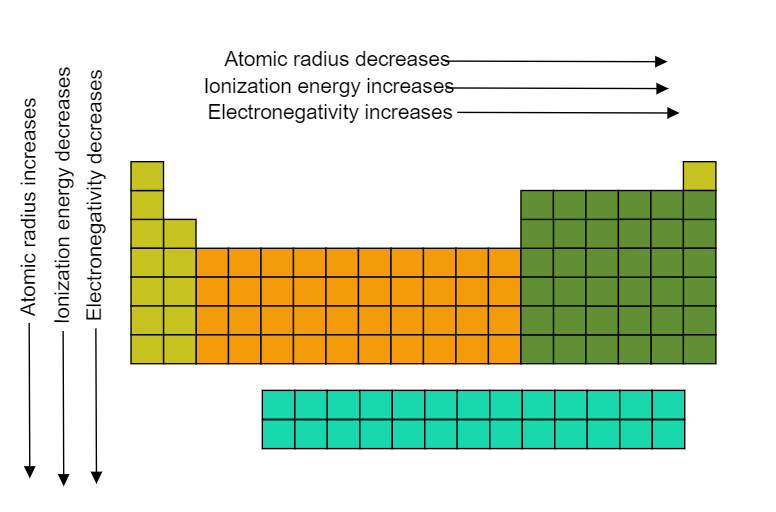
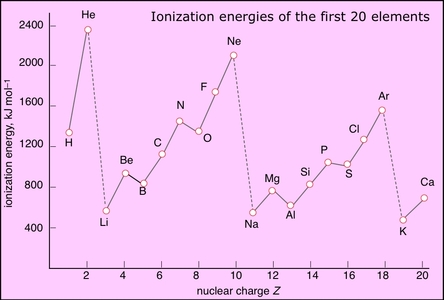
Ionization energy tends to increase as we move across a period from left to right. This is because, as we move across a period, the atomic number of the elements increases. This means that there are more protons in the nucleus, which means a stronger positive charge. As a result, the electron is attracted more strongly to the nucleus, and it requires more energy to remove it.
There are some exceptions to this trend. For example, the ionization energy of helium is much lower than that of lithium, even though helium is to the right of lithium in the periodic table. This is because helium has a full outer shell of electrons, which makes it more stable and less likely to lose an electron.
Ionization energy can also vary within a group of elements. For example, the ionization energy of oxygen is higher than that of nitrogen, even though both are in the same group (group 15). This is because oxygen has a higher atomic number, which means it has more protons in its nucleus and a stronger positive charge. As a result, it requires more energy to remove an electron from an oxygen atom.
Ionization energy has a number of practical applications in chemistry. For example, it can be used to predict the reactivity of different elements and the likelihood of them forming chemical bonds with other atoms. It can also be used to predict the melting and boiling points of elements, as well as their physical and chemical properties.
In summary, ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or positive ion. It tends to increase as we move across a period from left to right, due to the increasing atomic number and the stronger positive charge in the nucleus. However, there are some exceptions to this trend, and ionization energy can also vary within a group of elements. It is an important concept in chemistry with a number of practical applications.

.jpg)