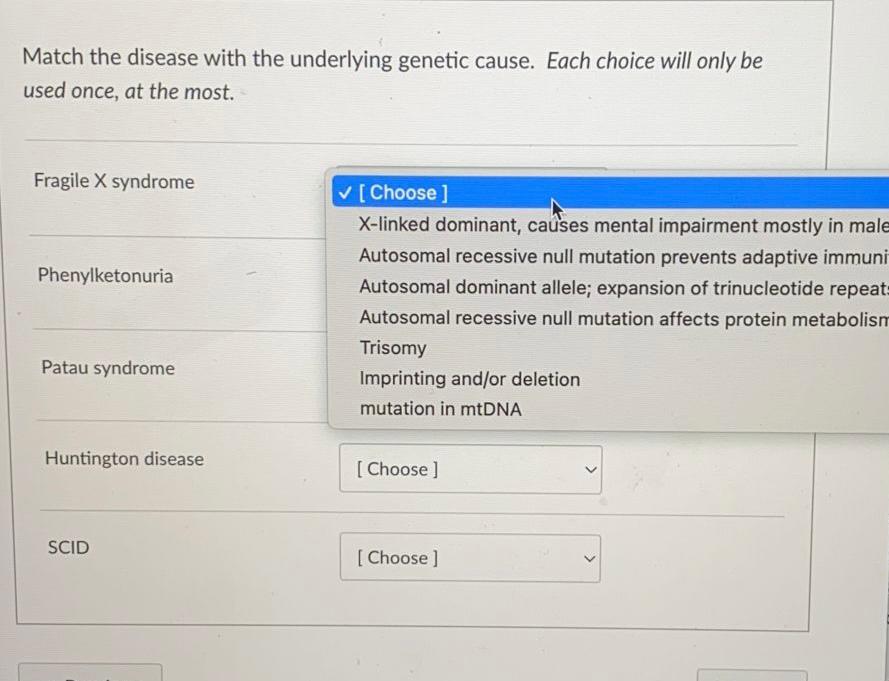
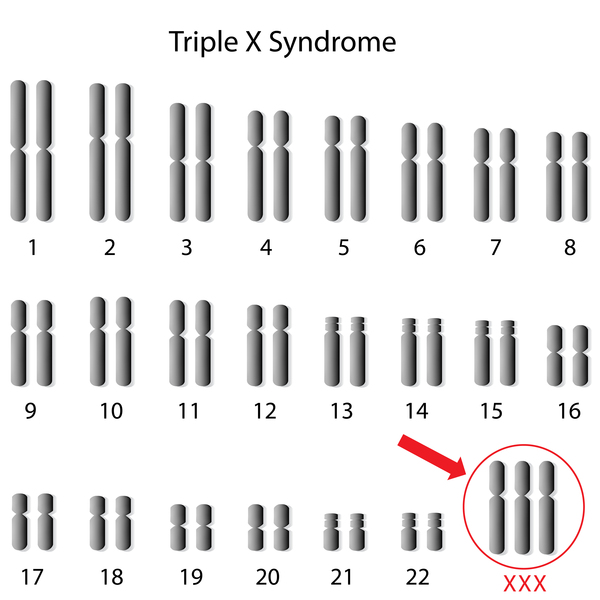
Triple X syndrome, also known as trisomy X or 47,XXX, is a chromosomal condition that occurs when a person has an extra copy of the X chromosome. This condition is caused by a chromosomal aberration during the formation of the egg or sperm cells, which results in the fertilized egg having an extra copy of the X chromosome.
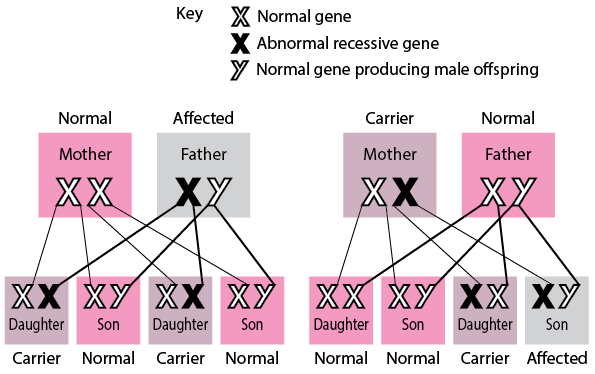
There are several different types of chromosomal conditions, including dominant and recessive conditions. Dominant conditions are caused by a single copy of a mutated gene, and the trait or condition is expressed in the individual even if only one copy of the mutated gene is present. Recessive conditions, on the other hand, require two copies of a mutated gene in order for the trait or condition to be expressed in the individual.
So, is triple X syndrome a dominant or recessive condition? It is actually neither, as it is caused by a chromosomal aberration rather than a mutated gene. This means that triple X syndrome is not inherited in the same way that dominant or recessive conditions are inherited. Instead, it is caused by a random event that occurs during the formation of the egg or sperm cells.
It is important to note that while triple X syndrome is not inherited in the same way as dominant or recessive conditions, it can still be passed down from parent to child. If a parent with triple X syndrome has a child, there is a small risk (about 1%) that the child will also have triple X syndrome. However, the majority of cases of triple X syndrome occur randomly and are not inherited from a parent.
Triple X syndrome can cause a variety of physical and developmental differences, including taller than average height, delayed development, and reproductive abnormalities. However, the severity of these differences can vary greatly from person to person, and many individuals with triple X syndrome have no physical or developmental differences at all.
In conclusion, triple X syndrome is a chromosomal condition that is caused by a chromosomal aberration rather than a mutated gene. It is not a dominant or recessive condition, but it can still be passed down from parent to child. While triple X syndrome can cause physical and developmental differences, the severity of these differences can vary greatly from person to person.