Kolcaba's Comfort Theory is a nursing theory that was developed by Katharine Kolcaba in the 1990s. It is based on the idea that comfort is a fundamental human need, and that nursing care should be focused on providing comfort to patients in order to promote healing and well-being.
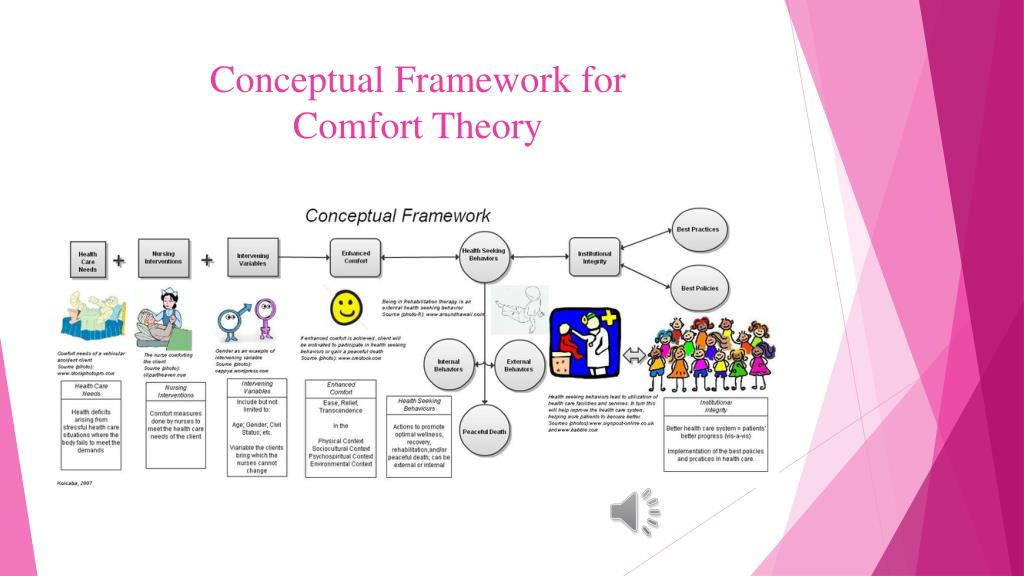
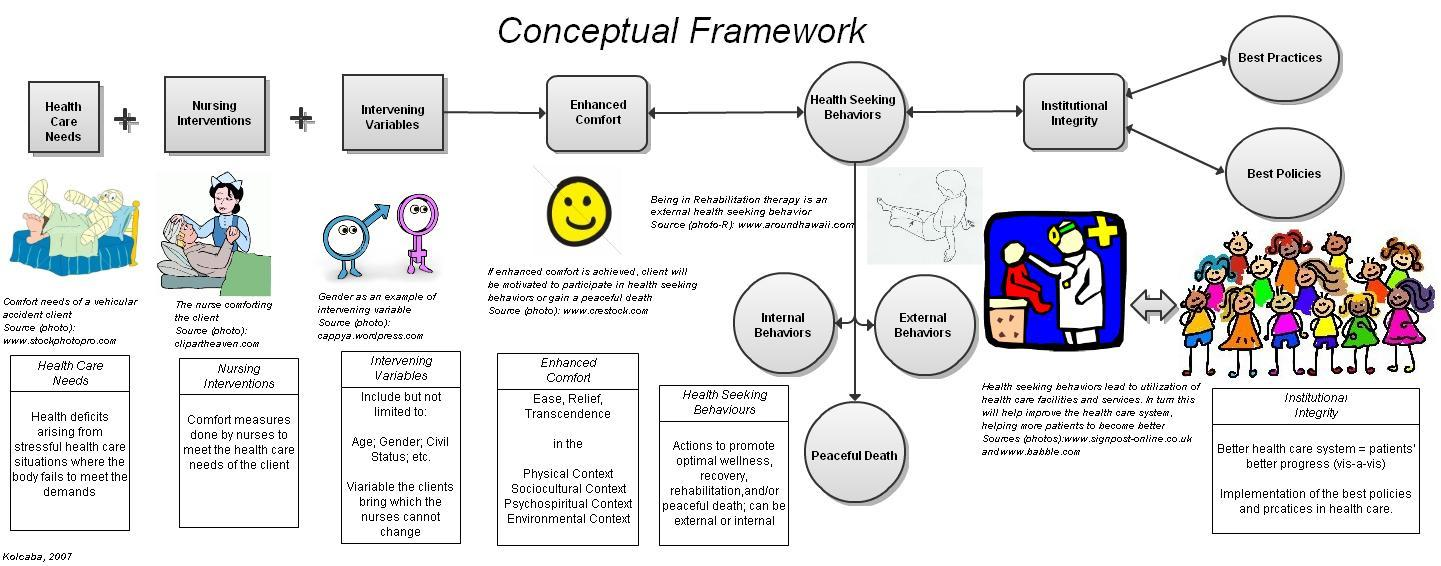
One way to understand the Comfort Theory is through the use of a diagram. This diagram represents the different elements of the theory and how they relate to one another.
At the center of the diagram is the concept of comfort. This is the ultimate goal of nursing care, and it is achieved through the provision of comfort measures. Comfort measures are activities or interventions that are designed to promote comfort and alleviate discomfort.
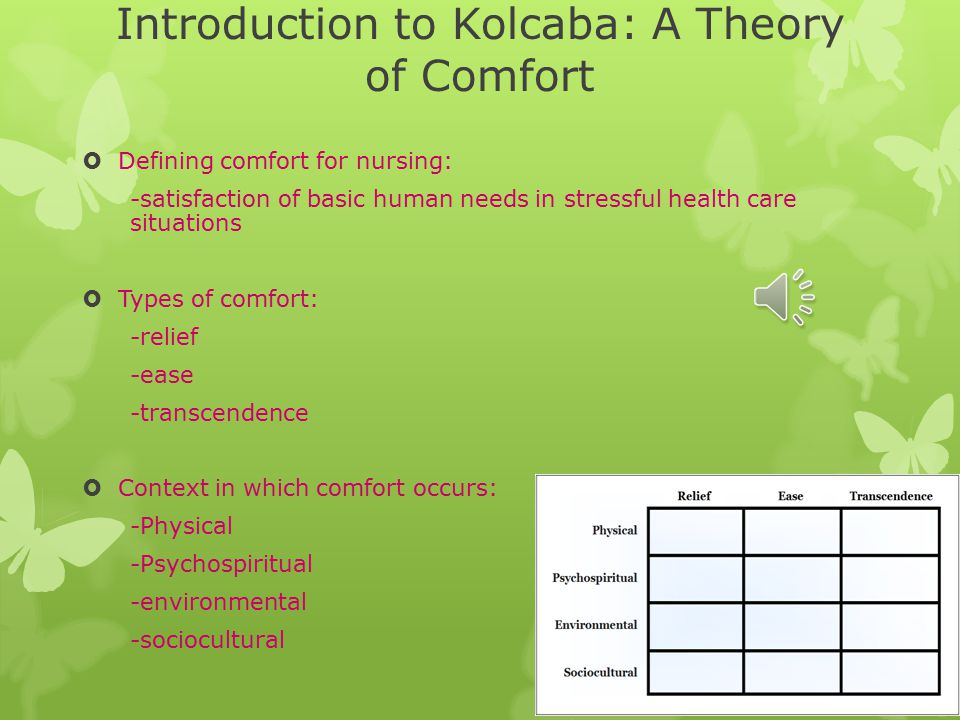
Surrounding the concept of comfort are the three comfort modes: physical, psychospiritual, and social. These modes represent the different ways in which comfort can be experienced by patients. Physical comfort refers to the relief of physical symptoms and discomfort, such as pain or fatigue. Psychospiritual comfort refers to the sense of inner peace and spiritual well-being that patients may experience. Social comfort refers to the feeling of connection and support that patients may receive from their social environment.
The next layer of the diagram represents the four contexts in which comfort can be provided. These contexts are: physiological, safety, sense of control, and social. The physiological context refers to the physical needs of the patient, such as the need for nourishment or pain relief. The safety context refers to the need for patients to feel safe and secure in their environment. The sense of control context refers to the need for patients to feel that they have some control over their own care and treatment. The social context refers to the need for patients to feel connected and supported by their social environment.
The final layer of the diagram represents the nursing actions that are necessary to provide comfort to patients. These actions include assessment, diagnosis, intervention, and evaluation. The assessment phase involves gathering information about the patient's comfort needs and preferences. The diagnosis phase involves identifying the specific comfort needs of the patient based on the assessment. The intervention phase involves implementing the appropriate comfort measures to address the identified needs. The evaluation phase involves assessing the effectiveness of the comfort measures and making any necessary adjustments.
In summary, Kolcaba's Comfort Theory is a holistic approach to nursing care that recognizes the importance of comfort in promoting healing and well-being. It is based on the idea that comfort can be experienced in multiple ways and contexts, and that nursing actions should be focused on providing comfort to patients through a variety of comfort measures. This understanding can be represented visually through the use of a diagram that shows the different elements of the theory and how they relate to one another.