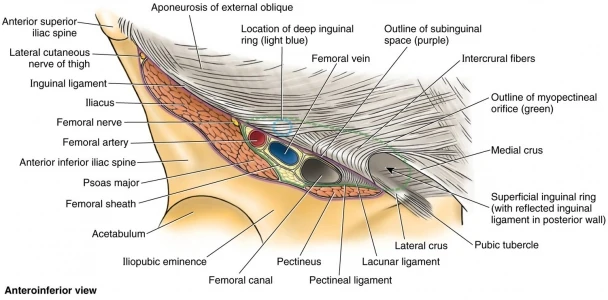
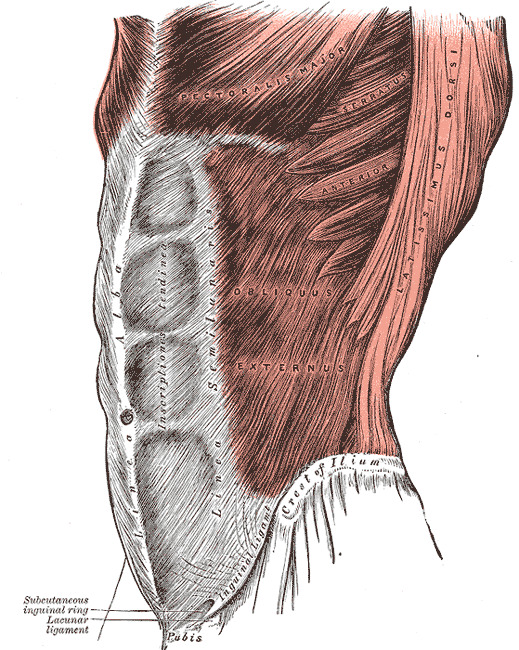
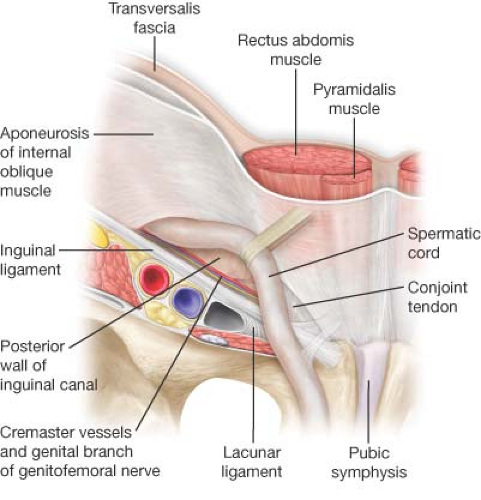
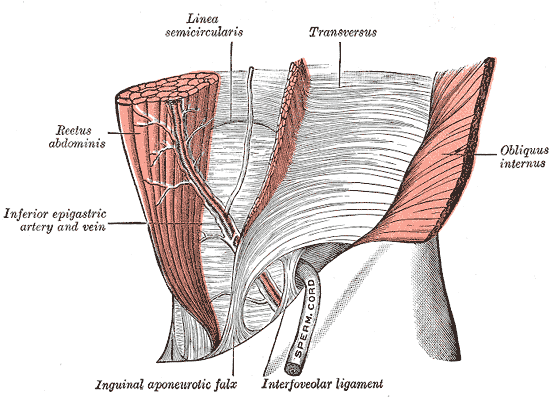
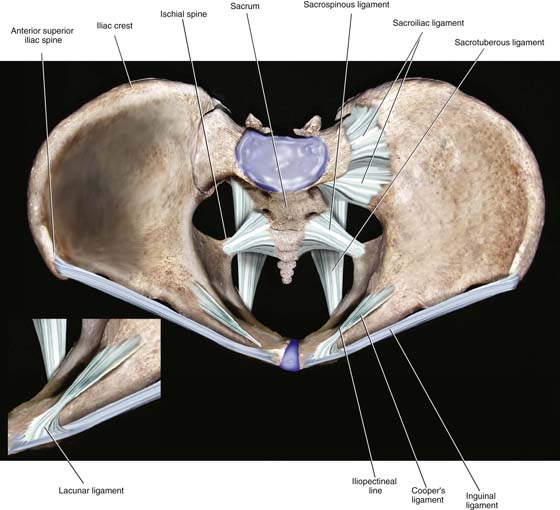
The lacunar ligament, also known as the ligamentum lacunare or ligamentum venosum, is a small, thin ligament located in the liver. It is an important anatomical structure that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the liver and its ability to filter blood and produce important enzymes and hormones.
The lacunar ligament is a long, narrow band of connective tissue that extends from the inferior vena cava (IVC) to the liver. It is located in the superior portion of the liver, just below the diaphragm. The IVC is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart. The lacunar ligament forms a vital link between the IVC and the liver, allowing blood to flow freely between these two organs.
The lacunar ligament is an important part of the hepatic venous system, which is responsible for draining blood from the liver. It is composed of several smaller veins and tributaries that converge to form the lacunar ligament. These smaller veins and tributaries are called the hepatic veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the liver back to the heart.
The lacunar ligament is also closely associated with the portal vein, which is another important blood vessel in the liver. The portal vein carries blood from the intestines, spleen, and pancreas to the liver, where it is filtered and processed. The lacunar ligament helps to regulate the flow of blood between the portal vein and the hepatic veins, ensuring that the liver receives a steady supply of oxygenated blood while also preventing the build-up of excess pressure.
In addition to its role in the hepatic venous system, the lacunar ligament also plays a crucial role in the production of enzymes and hormones. The liver is responsible for producing a variety of enzymes and hormones that are essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body. These enzymes and hormones are produced by specialized cells called hepatocytes, which are found in the liver. The lacunar ligament helps to ensure that these hepatocytes receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for their proper function.
Overall, the lacunar ligament is a small but essential structure that plays a vital role in the functioning of the liver. It helps to regulate the flow of blood between the IVC and the liver, as well as between the portal vein and the hepatic veins. It also helps to ensure that the hepatocytes receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for the production of enzymes and hormones. Without the lacunar ligament, the liver would be unable to function properly, leading to serious health problems.