Lean manufacturing is a production philosophy that aims to minimize waste and maximize value for the customer. It was developed by Toyota in the 1950s and has since been adopted by many companies around the world. The goal of lean manufacturing is to eliminate waste and improve efficiency by streamlining the production process and eliminating unnecessary steps.
One key aspect of lean manufacturing is the concept of "value stream mapping." This involves mapping out the entire production process, from raw materials to finished product, and identifying every step that adds value for the customer. Once these steps have been identified, the goal is to eliminate or streamline any non-value-adding steps in order to increase efficiency and reduce waste.
Another important aspect of lean manufacturing is the use of "just-in-time" (JIT) production. This means that materials and parts are only brought into the production process as they are needed, rather than being stockpiled in advance. This helps to reduce inventory costs and minimize the risk of waste due to overproduction or obsolescence.
Lean manufacturing also emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement. This means that the production process is continuously examined and refined in order to identify and eliminate waste and improve efficiency. This can be achieved through the use of tools such as root cause analysis and the 5S method, which helps to organize the production environment and improve productivity.
One of the benefits of lean manufacturing is that it can lead to significant cost savings. By streamlining the production process and reducing waste, companies can reduce their production costs and improve their bottom line. In addition, lean manufacturing can also lead to improved customer satisfaction by providing high-quality products that are delivered in a timely manner.
Overall, lean manufacturing is a valuable approach for companies looking to improve efficiency and reduce waste in their production processes. By focusing on value-adding activities and continuously seeking ways to improve, companies can improve their competitiveness and profitability.
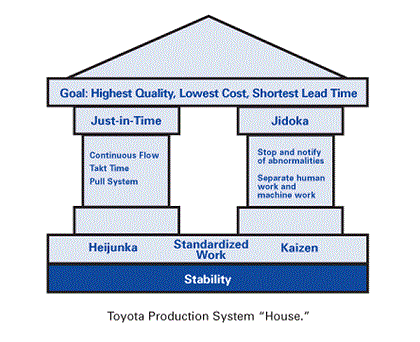
Lean manufacturing is a production approach that focuses on maximizing value and minimizing waste. It is based on the principles of the Toyota Production System, which was developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in the 1950s.
The goal of lean manufacturing is to create a smooth and efficient production process that can quickly respond to changes in customer demand. To achieve this goal, lean manufacturing relies on a number of tools and techniques, including value stream mapping, just-in-time (JIT) production, and continuous improvement.
Value stream mapping is a tool that helps companies identify the value-adding and non-value-adding steps in their production process. By identifying the non-value-adding steps, companies can eliminate them or streamline them to increase efficiency.
Just-in-time (JIT) production is another key element of lean manufacturing. This approach involves producing goods in small quantities, as close to the point of consumption as possible. This helps to minimize inventory costs and reduce the risk of waste.
Continuous improvement is an ongoing process in lean manufacturing. It involves regularly reviewing and improving the production process to increase efficiency and reduce waste. This can be achieved through techniques such as kaizen, which involves small, incremental improvements to the production process.
There are many benefits to adopting a lean manufacturing approach. It can help companies reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve quality. It can also lead to increased customer satisfaction, as companies are able to respond more quickly to changes in customer demand.
However, implementing lean manufacturing can be challenging. It requires a significant cultural shift within an organization, as well as the adoption of new tools and techniques. It also requires a strong commitment from leadership and the support of all employees.
In conclusion, lean manufacturing is a production approach that focuses on maximizing value and minimizing waste. It is based on the principles of the Toyota Production System and relies on tools such as value stream mapping, JIT production, and continuous improvement. While implementing lean manufacturing can be challenging, it can lead to significant benefits for companies in terms of cost reduction, increased productivity, and improved quality.
Lean manufacturing is a production methodology that aims to maximize value and minimize waste within a manufacturing system. It is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement and the flow of value to the customer.
The concept of lean manufacturing originated in the automotive industry in the 1950s, with the implementation of the Toyota Production System (TPS) at Toyota. TPS was developed by Taiichi Ohno, who sought to streamline production and eliminate waste in order to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
The principles of lean manufacturing are based on the idea of value stream mapping, which involves identifying all of the activities within a production process and evaluating which ones add value and which ones do not. Activities that do not add value, known as waste, are eliminated or minimized. The focus is on creating a "flow" of value through the production process, from raw materials to finished goods, with the goal of maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste.
There are several key tools and techniques used in lean manufacturing to identify and eliminate waste. These include:
Value stream mapping: This involves creating a visual representation of the production process, from raw materials to finished goods, and identifying all of the activities that take place within it. This allows manufacturers to identify areas of waste and inefficiency and to implement changes to improve the flow of value.
Kanban: This is a visual signaling system that helps to ensure that materials and parts are available when they are needed in the production process. By using kanban, manufacturers can reduce the amount of inventory they need to hold, which helps to minimize waste.
Five S: This refers to five principles that are used to create a clean and organized work environment, which can improve efficiency and reduce waste. The five S principles are sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain.
Continuous improvement: Lean manufacturing relies on the continuous improvement of production processes in order to eliminate waste and increase value. This can be achieved through techniques such as root cause analysis and the use of statistical process control to identify and fix problems in the production process.
Implementing lean manufacturing can have numerous benefits for manufacturers. It can help to reduce costs by eliminating waste, improve efficiency and productivity, and enhance the quality of products. It can also lead to increased customer satisfaction, as manufacturers are able to produce goods more quickly and with fewer defects.
Overall, lean manufacturing is a valuable approach for manufacturers looking to streamline production and increase value for their customers. By focusing on continuous improvement and the elimination of waste, manufacturers can create more efficient and effective production processes, leading to increased profitability and competitiveness.
Lean manufacturing is a production philosophy that aims to eliminate waste and increase efficiency in the manufacturing process. It was first developed by Toyota in the 1950s and has since been adopted by a number of companies around the world.
One key aspect of lean manufacturing is the concept of "flow." This refers to the smooth and uninterrupted flow of materials and information through the production process. The goal is to create a "pull" system, where each step in the process only produces what is needed for the next step, rather than producing large batches of products that may sit in inventory for long periods of time. This reduces waste and increases efficiency by minimizing the amount of time that materials spend waiting in inventory.
Another key aspect of lean manufacturing is the use of "visual management" techniques. This involves using visual cues, such as colored tags or charts, to quickly and easily communicate information about the production process. This can help identify problems and bottlenecks in the process and allow for quick corrective action.
One tool commonly used in lean manufacturing is the "5S" system, which stands for sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. This system involves organizing the work area, maintaining cleanliness and order, standardizing processes, and continuously improving the system. The goal is to create a visually organized and efficient work environment that is conducive to lean principles.
Lean manufacturing also emphasizes the importance of involving all employees in the continuous improvement process. This can involve the use of "kaizen" events, where teams come together to identify and solve problems in the production process. By involving employees in the improvement process, companies can tap into their knowledge and ideas and create a culture of continuous improvement.
In summary, lean manufacturing is a production philosophy that aims to eliminate waste and increase efficiency in the manufacturing process. It focuses on creating a smooth flow of materials and information, using visual management techniques, and involving all employees in the continuous improvement process. By implementing lean principles, companies can reduce costs, increase competitiveness, and improve customer satisfaction.