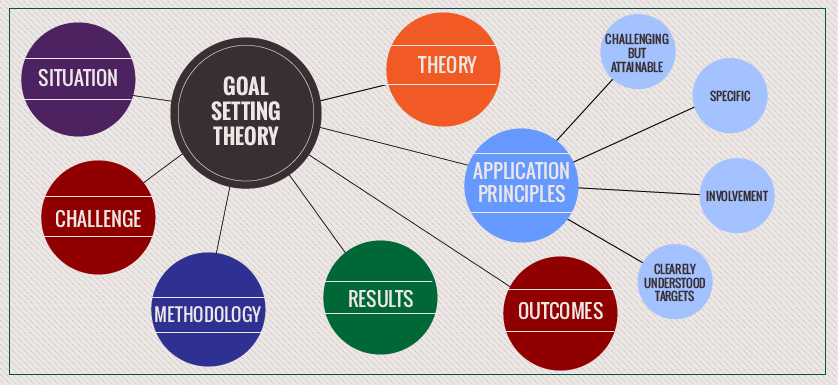
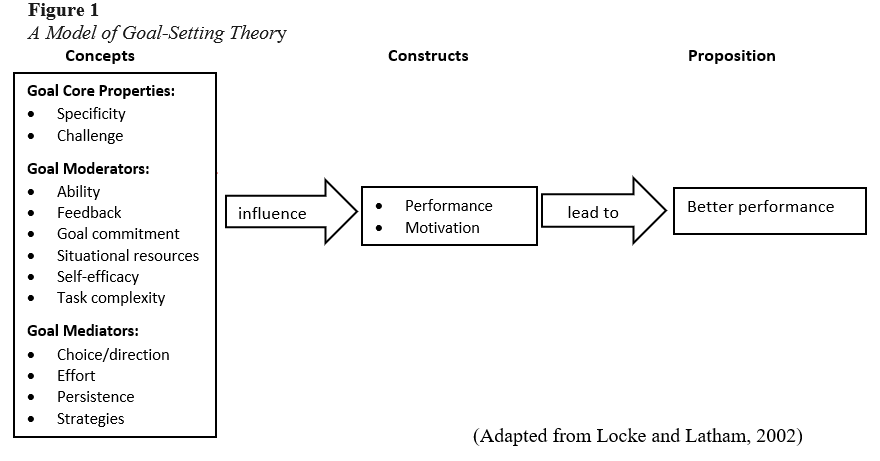
Goal setting theory is a widely accepted and widely researched theory in the field of psychology that suggests that setting specific, challenging goals can lead to higher levels of motivation and performance. However, like any theory, there are limitations to the goal setting theory that should be considered when applying it in practice.
One limitation of the goal setting theory is that it does not take into account individual differences. Different people may have different goals, values, and motivations, and these differences may influence their responses to goal setting. For example, one person may be motivated by the challenge of reaching a difficult goal, while another may be demotivated by the same goal because they do not see it as achievable. This means that the effectiveness of goal setting may vary across individuals and that it may be necessary to take individual differences into account when setting goals.
Another limitation of the goal setting theory is that it does not consider the role of other factors that may affect motivation and performance. For example, research has shown that the quality of feedback, the level of support from others, and the presence of external rewards can all affect motivation and performance. These factors may interact with goals in complex ways, and the goal setting theory does not fully account for these interactions.
Additionally, the goal setting theory does not consider the role of emotions in motivation and performance. Research has shown that emotions can have a significant impact on motivation and performance, and the goal setting theory does not fully consider the role of emotions in these processes. For example, negative emotions such as anxiety or stress can interfere with performance, while positive emotions such as excitement or enthusiasm can enhance it.
Finally, the goal setting theory assumes that goals are always beneficial, but this may not always be the case. Setting unrealistic goals or goals that are not aligned with one's values and interests can lead to demotivation and negative consequences. It is important to set goals that are challenging but also achievable and aligned with one's values and interests in order to maximize the benefits of goal setting.
In conclusion, the goal setting theory is a valuable tool for understanding and influencing motivation and performance, but it has limitations that should be taken into account when applying it in practice. It is important to consider individual differences, the role of other factors that may affect motivation and performance, the role of emotions, and the potential negative consequences of goal setting.
Contextual Limitations of Goal

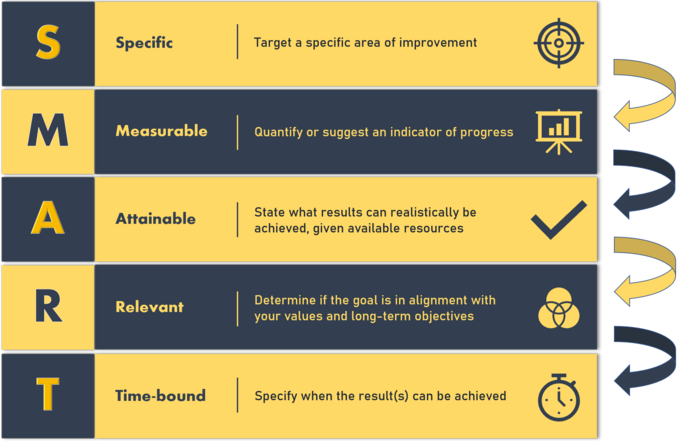
SMART goals are those that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound SMART. Setting overly aggressive goals can have negative effects on an employees performance over time, according to one study. In addition to analyzing work and business processes in order to develop better methods, Taylor popularized financial incentives for good performance. This way, the achievements are even more focused. Over the long run, this behavior can harm the organization. On one hand, they fear being laughed at if they fail. This theory states that goal setting is essentially linked to task performance.
The Negative Side of Goal
Let us take a look at some of the consequences that arise from poor goal-setting and how it impacts organizations. Goal-Setting Theory Obstacles A primary reason people avoid setting goals is that they put pressure on them to perform. The general premise of their theory was that individuals and groups produce the best output when motivated by specific, challenging, attainable and quantified goals. Goals often help people set clear and laid out plans for what they want to achieve, however it can actually add unnecessary pressure, especially if someone else has created them. He worked on a major reading system for Cambridge University Press, became an information-technology adviser and authored interactive whiteboard resources for "The Guardian. For instance, scientific management cannot explain why a successful executive will take a hefty pay cut to serve in government or a nonprofit organization. Setting goals also takes time, which causes some organizations, leaders and employees to avoid them.
DIP1BUS01

In simple words just like in the case of college students if students do not know the syllabus then they will be clueless about their course of action in the same way workers in the absence of goals will be clueless about their course of action. Therefore, other researchers have looked beyond money to discover what else motivates people. More complex and difficult goals may lead to risky behavior in an attempt to accomplish the goals in a timely manner. Without a clear target, you often struggle to find intrinsic motivation to push forward through difficulty. So, the level of motivation depends on the kind of goals that are set and the way internal and external factors affecting the process between goal identification to goal achievement are managed. Bandura 1997 proposed four sources of self-efficacy: mastery experiences, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion, and physiological and affective states. With a stated quota, you have a commitment to yourself as well as your sales manager.