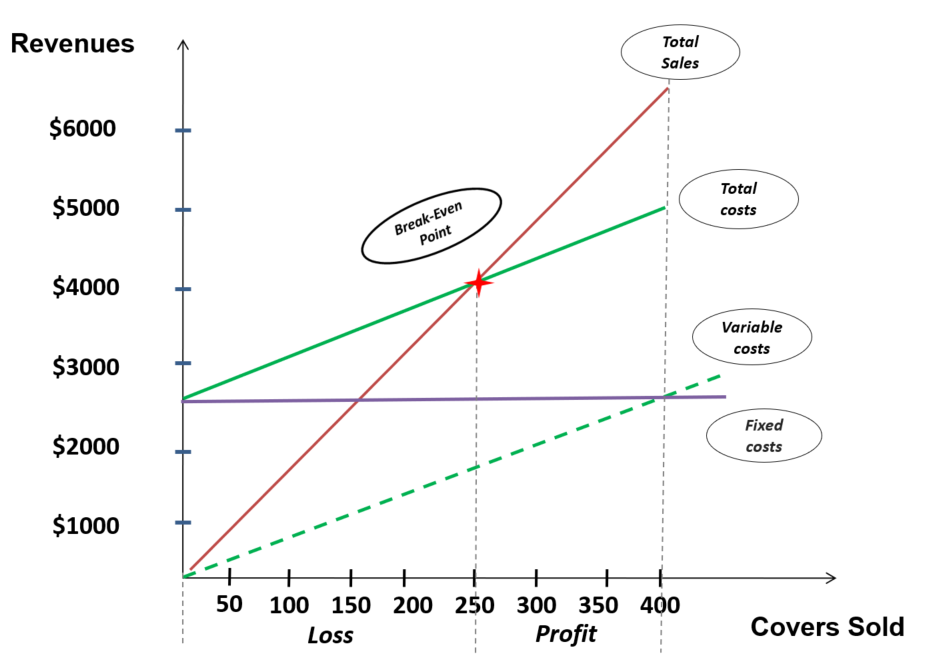
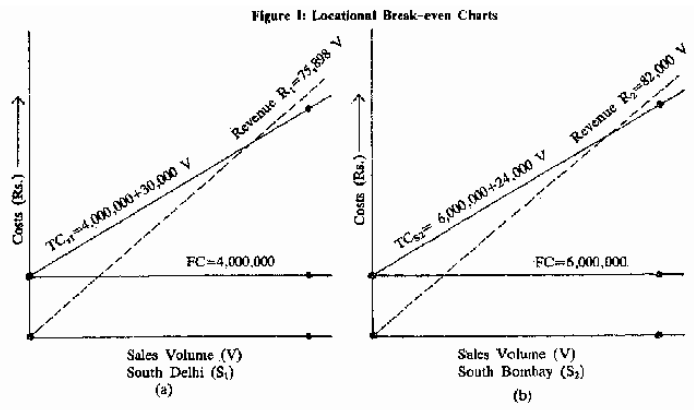
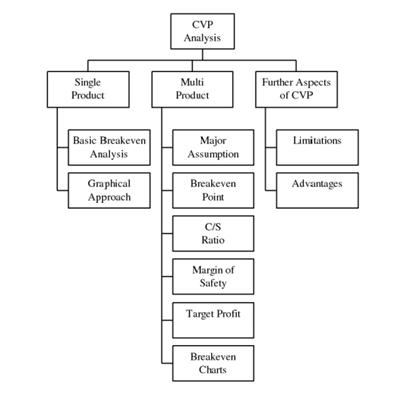
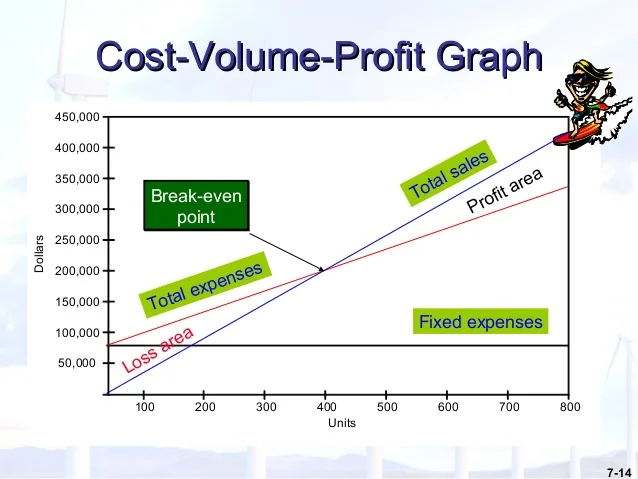
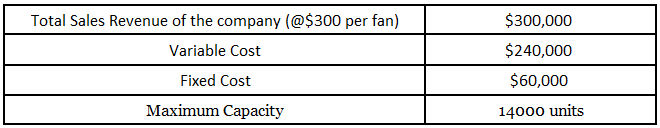Locational cost-profit-volume (CPV) analysis is a tool that businesses use to assess the feasibility of a potential project or investment. It involves analyzing the costs and revenues associated with a project, as well as the volume of sales or output that is expected to be generated. By examining these three factors together, businesses can make informed decisions about whether a project is likely to be profitable and worth pursuing.
To conduct a locational CPV analysis, businesses first need to identify all of the costs associated with the project, including fixed costs (such as rent or salaries) and variable costs (such as materials or transportation). Next, they need to estimate the volume of sales or output that is expected to be generated by the project, and calculate the expected revenue based on this volume and the projected price of the product or service.
Once the costs and revenues have been estimated, businesses can calculate the CPV ratio, which is the difference between the expected revenue and the expected costs, divided by the volume of output. This ratio can be used to determine whether a project is likely to be profitable, and can help businesses decide whether to move forward with the project or not.
There are several factors that can influence the results of a locational CPV analysis. For example, changes in the market price of a product or service can significantly impact the expected revenue and profitability of a project. In addition, changes in the cost of inputs (such as raw materials or labor) can also affect the results of the analysis.
One of the key advantages of using a locational CPV analysis is that it allows businesses to take into account the specific location of a project and how it might impact costs and revenues. For example, a business might find that a project is more profitable in one location due to lower costs or higher demand for the product or service. This information can be valuable when deciding where to locate a new facility or business venture.
Overall, locational CPV analysis is an important tool that businesses can use to assess the feasibility and profitability of a potential project or investment. By carefully analyzing costs, revenues, and volume, businesses can make informed decisions about whether a project is likely to be successful and worth pursuing.