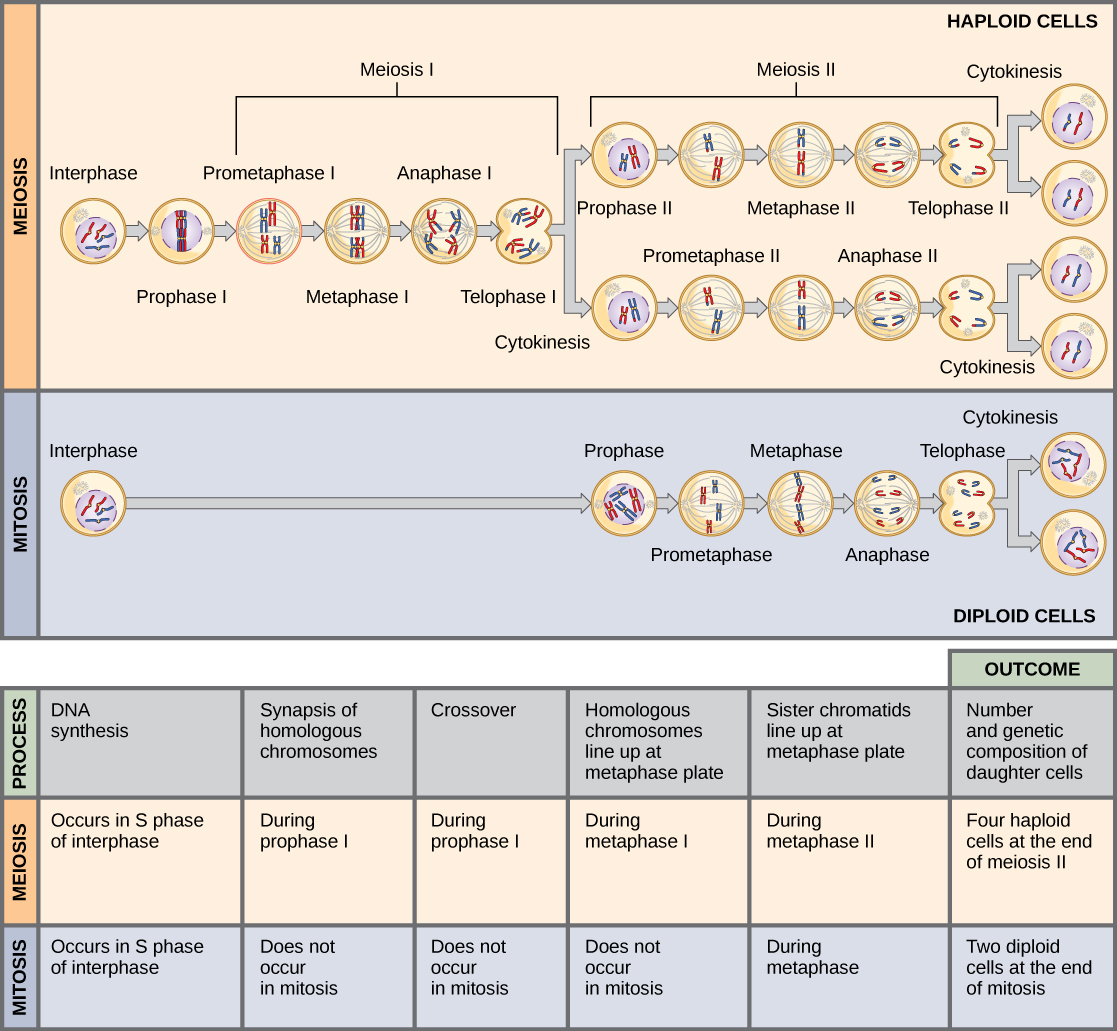
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces genetically diverse daughter cells, known as gametes, from a single parent cell. There are two stages of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. While both stages are important in the production of gametes, there are several major differences between meiosis I and meiosis II.
One of the major differences between meiosis I and meiosis II is the number of cell divisions that occur. Meiosis I involves one cell division, while meiosis II involves a second cell division. This means that meiosis I produces two daughter cells, while meiosis II produces four daughter cells.
Another significant difference between meiosis I and meiosis II is the type of cell division that occurs. Meiosis I is characterized by a process called crossing over, in which genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes. This process helps to increase genetic diversity by shuffling the genetic information present on the chromosomes. In contrast, meiosis II does not involve crossing over and is instead characterized by a more typical cell division process known as mitosis.
A third major difference between meiosis I and meiosis II is the number of chromosomes present in the daughter cells. During meiosis I, each daughter cell contains half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This reduction in chromosome number is known as reduction division. In contrast, meiosis II does not involve a reduction in chromosome number and the daughter cells contain the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Finally, meiosis I and meiosis II have different functions in the production of gametes. Meiosis I is responsible for producing cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, which is necessary for the proper development of gametes. Meiosis II, on the other hand, is responsible for dividing the cells produced in meiosis I into smaller, more mature gametes.
In summary, meiosis I and meiosis II are two distinct stages of cell division that are important in the production of gametes. Meiosis I involves one cell division, crossing over, and reduction division, while meiosis II involves a second cell division, does not involve crossing over, and does not involve a reduction in chromosome number. Each stage serves a unique function in the production of gametes and is necessary for the proper development of these cells.