In Broad Daylight by Ha Jin is a poignant and thought-provoking novel that explores the complex dynamics of power, corruption, and justice in a small Chinese village during the Cultural Revolution.
The story follows the lives of two main characters: Ning, a schoolteacher who becomes embroiled in a power struggle with the local party secretary, and Shuyu, Ning's wife, who is caught between her loyalty to her husband and her fear of the party's retribution. Through these characters, Ha Jin deftly illustrates the ways in which the Cultural Revolution's ideology of revolution and class struggle was used to justify violence and abuse of power, as well as the ways in which individuals were forced to navigate the treacherous waters of political loyalty and personal morality.
One of the key themes of the novel is the corrupting influence of power. The party secretary, Lao Li, is a ruthless and cunning man who will stop at nothing to maintain his position of authority, even if it means resorting to threats, intimidation, and violence. Ning, on the other hand, is a principled and honest man who refuses to bow to Lao Li's demands, even when it puts him and his family in danger. As the conflict between the two men escalates, it becomes clear that Lao Li's power is not derived from his leadership or moral character, but rather from his ability to manipulate the system and use fear and intimidation to silence his opponents.
Another theme that emerges in the novel is the role of justice in a society where the rule of law is subverted by those in power. Ning's struggle to bring Lao Li to justice is a poignant reminder of the importance of due process and the rule of law in upholding a just society. However, Ha Jin also highlights the ways in which the legal system can be used to protect the powerful and punish the weak, as Ning's efforts to seek justice are repeatedly thwarted by the corruption and bias of the local authorities.
Ultimately, In Broad Daylight is a powerful and poignant exploration of the ways in which power and corruption can corrupt even the most well-intentioned individuals. Ha Jin's vivid and nuanced portrayal of the characters and their struggles is a testament to his skill as a writer, and the novel serves as a thought-provoking and timely reminder of the dangers of unchecked power and the importance of upholding justice and the rule of law.
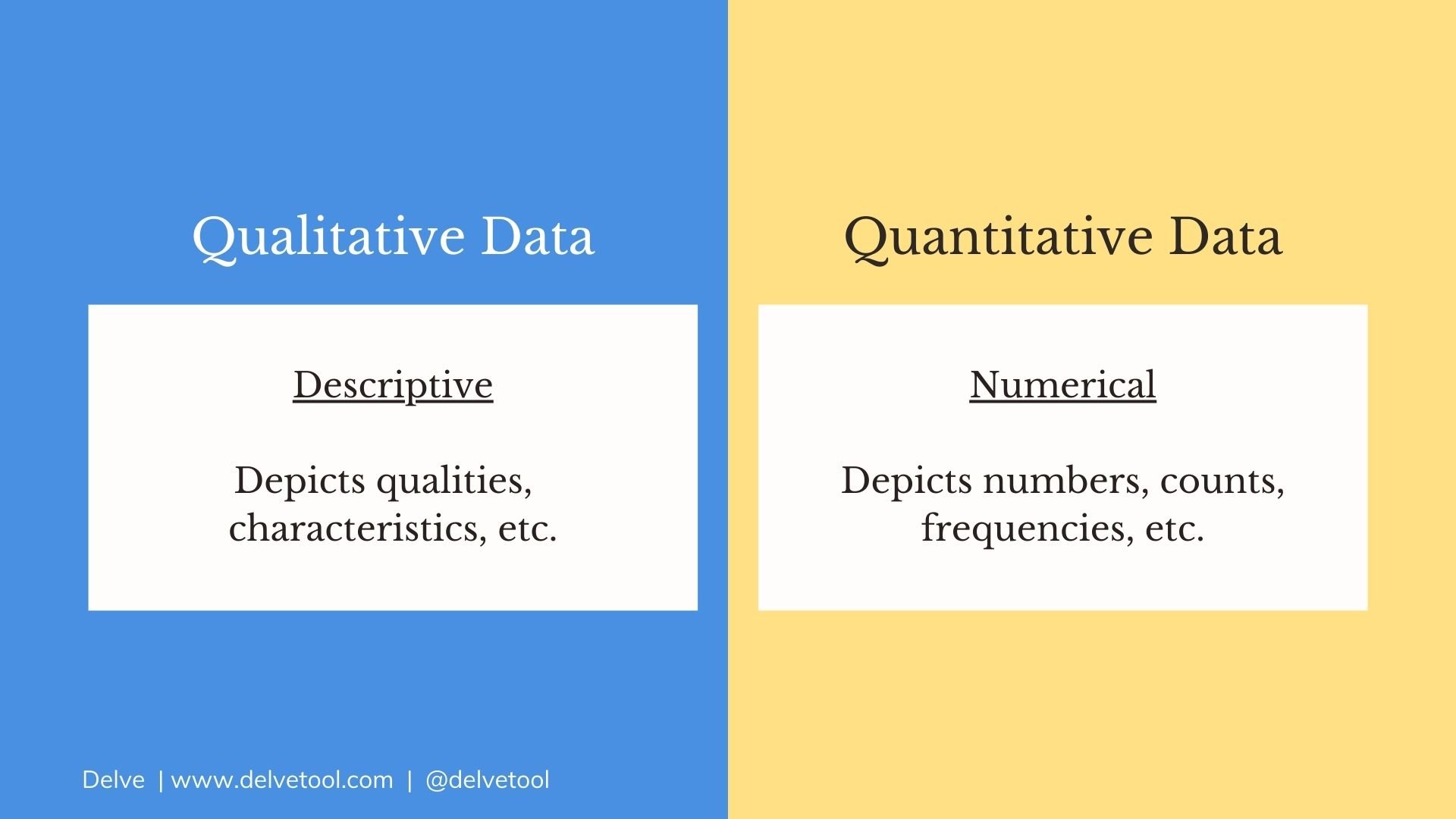
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
This suggests that qualitative method analysis of data points out the fact the two methods are not distinctive but have some areas where they merge. Qualitative and quantitative research methods have grown out of, and still represent, different paradigms. Methods used for data collection Qualitative data collection uses open-ended questions. In qualitative research it remains flexible and can be developed throughout the research process. This approach allows researchers to construct a theory based on data that is collected, analyzed, and compared to reach new discoveries. Nature Holistic Particularistic Approach Subjective Objective Research type Exploratory Conclusive Reasoning Inductive Deductive Sampling Purposive Random Data Verbal Measurable Inquiry Process-oriented Result-oriented Hypothesis Generated Tested Elements of analysis Words, pictures and objects Numerical data Objective To explore and discover ideas used in the ongoing processes. Further, statistical analysis requires a large data sample, which calls for a large pool of participants.
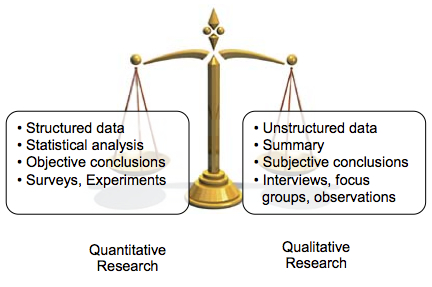
Difference between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Clinical and academic perspectives on how to develop and enhance nursing research activities. Open-ended: in-depth interviews, focus group discussions, field notes, case studies, etc. Qualitative data cannot be expressed as a number. It establishes the cause-and-effect relationship between two variables using different statistical, computational, and statistical methods. Quantitative research is a more methodical approach to solving problems by generating and using data. What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative data? The main difference between quantitative research and qualitative research is that the purpose of quantitative research is to describe ongoing processes, while the goal of quantitative research is to find cause and effect relationships. Other fields that conduct extensive research include business, economics, healthcare, marketing and education.
Difference Between Qualitative and Qualitative Research
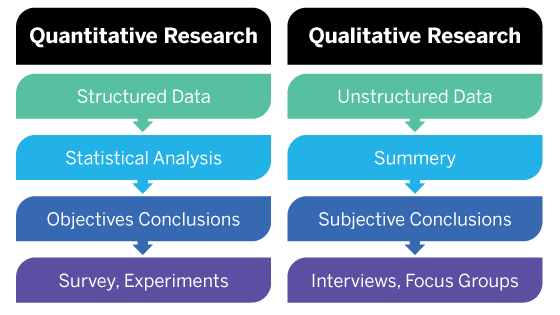
What do you mean by quantitative data? What kind of data might you gather or use to paint a vivid picture? Other courses will ask you to apply and analyze research skills. Ultimately, the researcher must determine which kind of research best serves the goals of the study. In contrast, quantitative data are analyzed numerically to develop a statistical picture of a trend or connection. Qualitative data is gathered through interviews, surveys, and observations. First, you might describe their physical attributes, such as their height, their hair style and color, what size feet they have, and how much they weigh. Moreover, the researcher must look for materials to support the research process which will be suitable from the beginning to the end Kothari, 2008.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Degree

As a rule, then, qualitative research is not generalizable cannot be applied to people outside the research participants. Qualitative Methods Quantitative Methods Text-based Number-based More in-depth information on a few cases Less in-depth but more breadth of information across a large number of cases Unstructured or semi-structured response options Fixed response options No statistical tests Statistical tests are used for analysis What is a qualitative paradigm? Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 49 3 , 263-280. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or to interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings of people to bring to them. New Delhi: New Age International. Qualitative Information — Involves a descriptive judgment using concept words instead of numbers. Understanding the difference between quantitative and qualitative data is one of the very first steps towards becoming a data expert. An example of discrete data is when you count something, such as the number of people in a room.