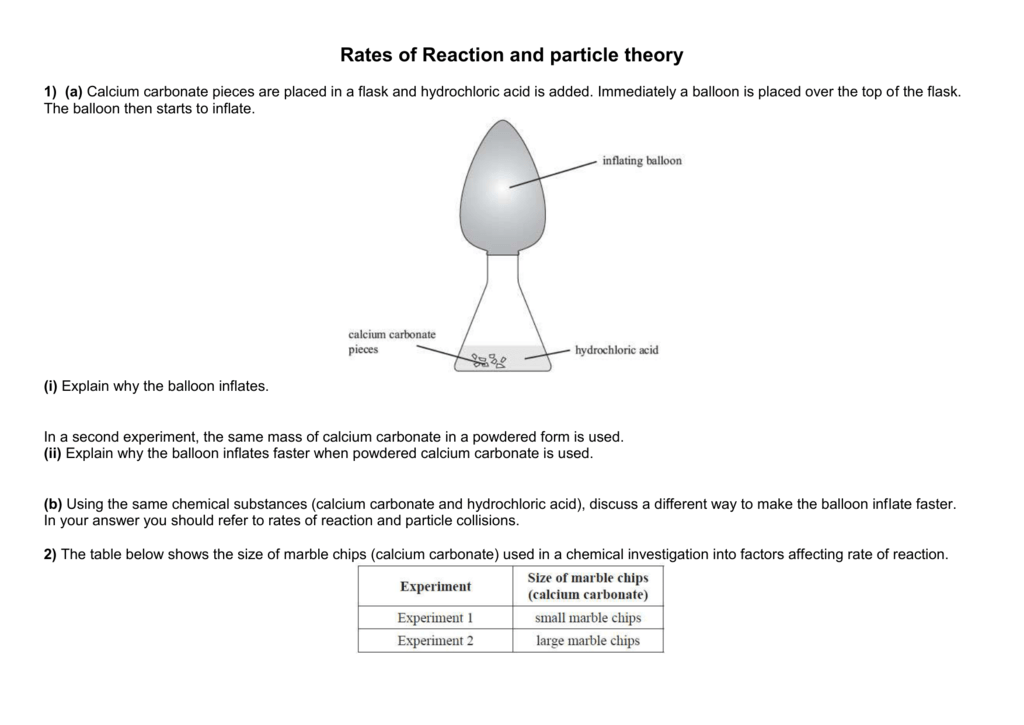
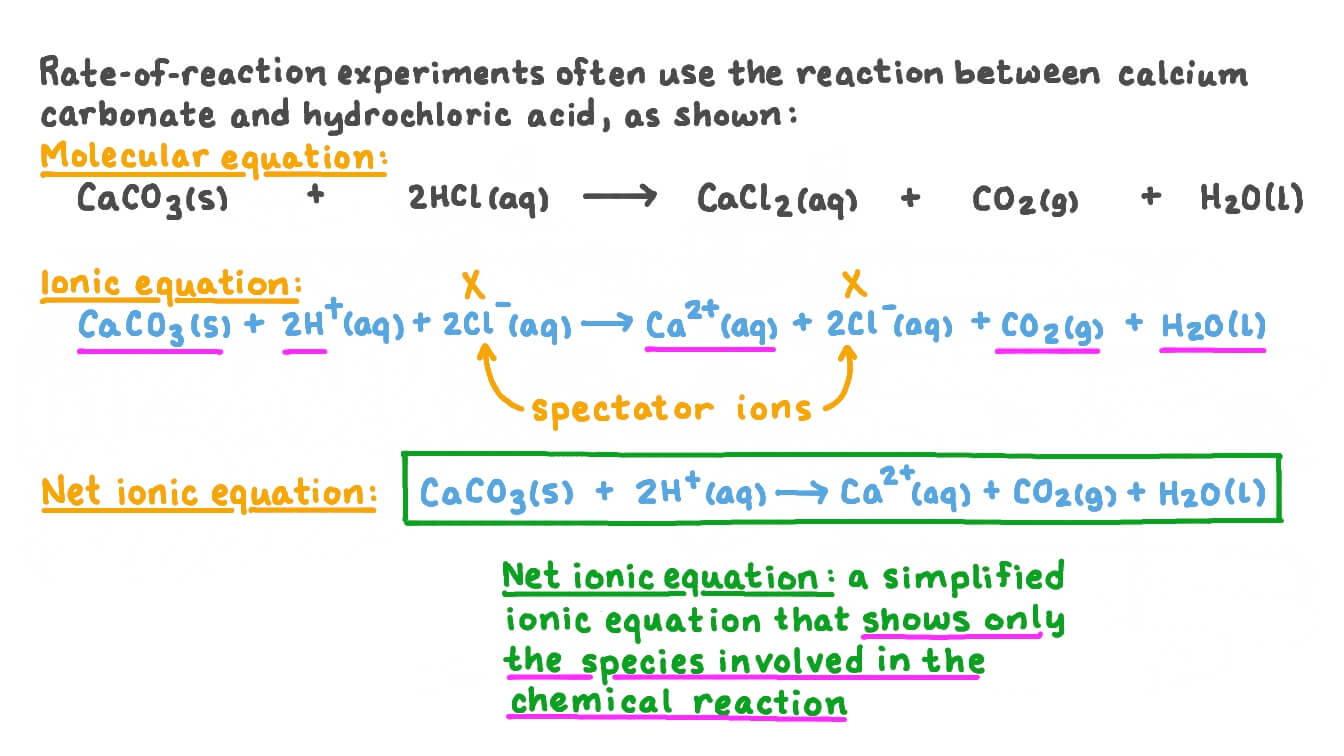
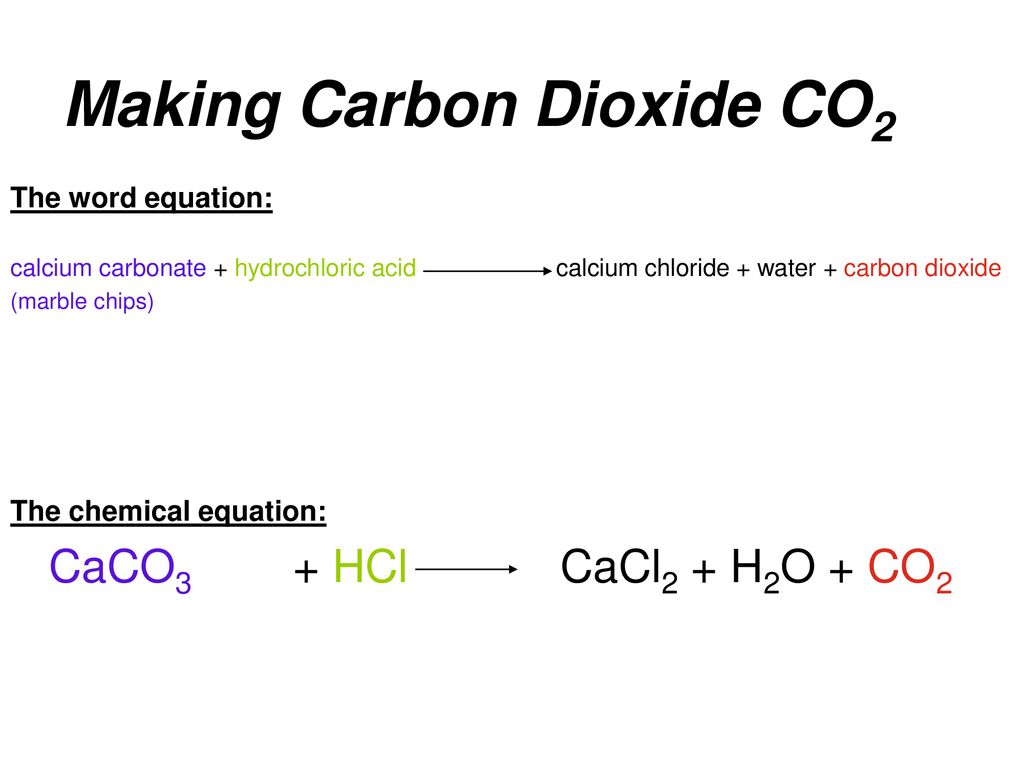
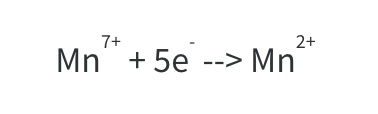Marble chips are a type of rock that is composed primarily of calcium carbonate, a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. When marble chips are placed in hydrochloric acid, a chemical reaction occurs that results in the production of several different products. The word equation for this reaction is:
Marble chips + hydrochloric acid -> calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
In this equation, the marble chips are represented by the symbol "Marble chips," and the hydrochloric acid is represented by the symbol "hydrochloric acid." The products of the reaction, which include calcium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water, are represented by the symbols "calcium chloride," "carbon dioxide," and "water," respectively.
The reaction between marble chips and hydrochloric acid is an example of a single displacement reaction, in which one element is replaced by another element. In this case, the calcium in the marble chips is replaced by the hydrogen in the hydrochloric acid, resulting in the production of calcium chloride. The carbon dioxide and water are also produced as byproducts of the reaction.
The reaction between marble chips and hydrochloric acid can be represented by the following balanced chemical equation:
CaCO3 + 2HCl -> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
In this equation, the symbols "CaCO3," "HCl," "CaCl2," "CO2," and "H2O" represent the reactants and products of the reaction, respectively. The coefficients in front of each compound indicate the relative number of atoms or molecules involved in the reaction.
Overall, the reaction between marble chips and hydrochloric acid is a simple but powerful example of how chemical reactions can produce new and useful products from simple starting materials. Understanding the principles behind this reaction can help us to better understand and predict the behavior of other chemical reactions, and to design new and more efficient processes for the production of chemicals and other materials.