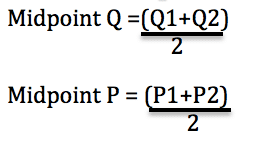Elasticity of demand is a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded of a good or service is to a change in one of its determinants, such as the price of the good or service, the price of related goods or services, or the income of the consumers. There are several methods of measuring elasticity of demand, and each has its own advantages and limitations.
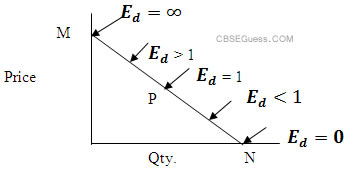
One method of measuring elasticity of demand is the percentage change method. This method calculates the elasticity of demand by dividing the percentage change in the quantity demanded by the percentage change in the determinant. For example, if the price of a good increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 20%, the elasticity of demand would be calculated as follows: (-20%)/(10%) = -2. This means that the demand for the good is elastic, as the percentage change in the quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in the price.
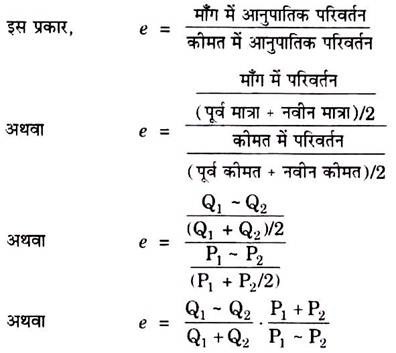
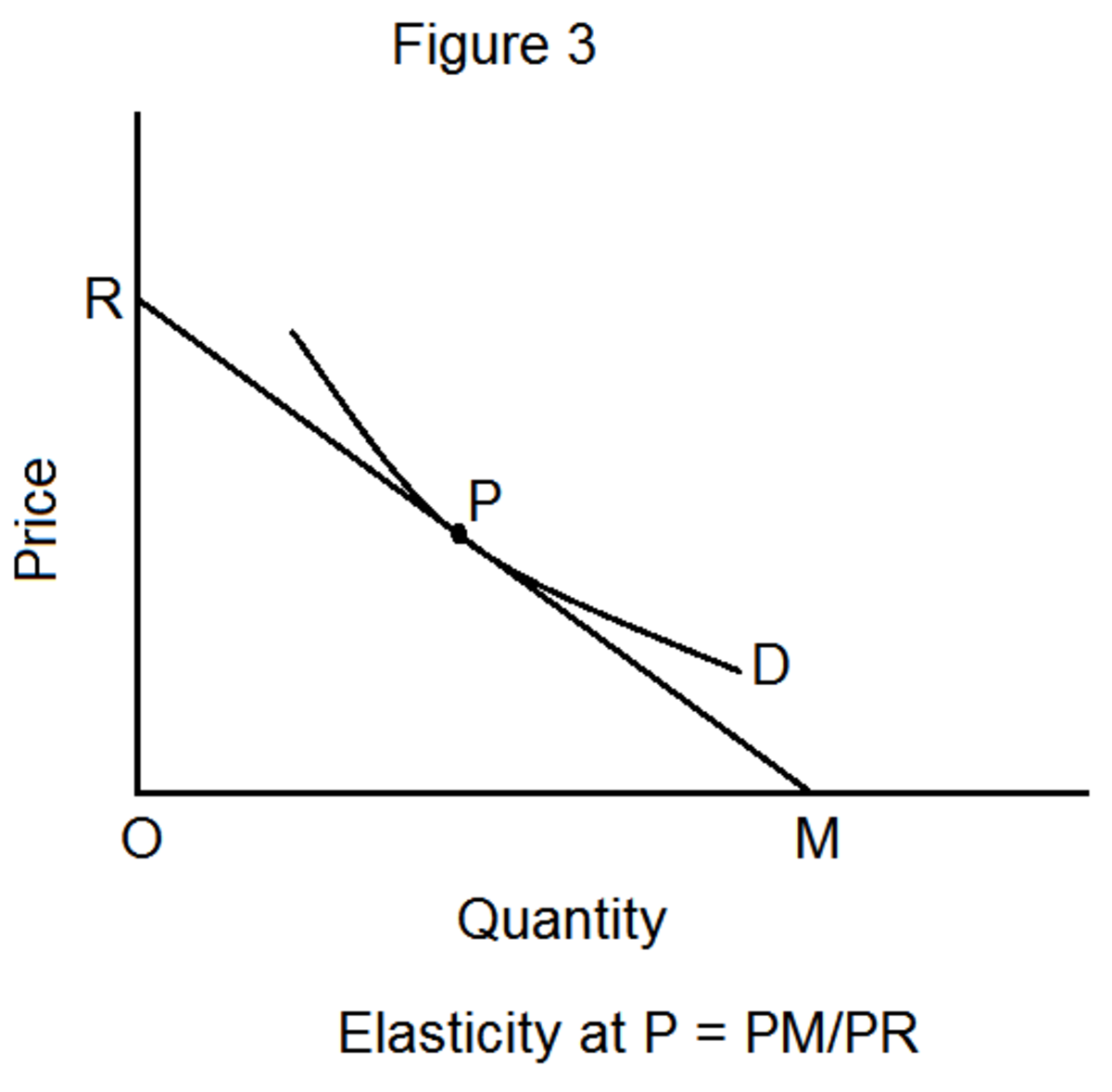
Another method of measuring elasticity of demand is the point elasticity method. This method calculates the elasticity of demand at a specific point on the demand curve. To do this, the elasticity of demand is calculated using the formula: (ΔQ/Q)/(ΔP/P), where Q is the quantity demanded, P is the price, and ΔQ and ΔP represent the changes in the quantity demanded and the price, respectively. For example, if the price of a good increases from $10 to $12 and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 units to 80 units, the elasticity of demand would be calculated as follows: (-20/80)/(2/10) = -0.5. This means that the demand for the good is relatively inelastic, as the percentage change in the quantity demanded is smaller than the percentage change in the price.
A third method of measuring elasticity of demand is the total expenditure method. This method calculates the elasticity of demand by dividing the percentage change in total expenditure on a good or service by the percentage change in the quantity demanded. Total expenditure is calculated as the quantity demanded multiplied by the price. For example, if the price of a good increases from $10 to $12 and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 units to 80 units, the total expenditure would decrease from $1000 to $960. The elasticity of demand would be calculated as follows: (-$40/$960)/(-20/80) = -0.5. This result is the same as the point elasticity method, indicating that the demand for the good is relatively inelastic.
There are several advantages and limitations to each of these methods of measuring elasticity of demand. The percentage change method is simple and easy to use, but it may not accurately reflect the elasticity of demand in all situations. The point elasticity method is more accurate, as it calculates the elasticity of demand at a specific point on the demand curve, but it requires more data and may be more difficult to calculate. The total expenditure method is useful for comparing the elasticity of demand for different goods or services, but it may not accurately reflect the elasticity of demand in all situations.
In conclusion, there are several methods of measuring elasticity of demand, including the percentage change method, the point elasticity method, and the total expenditure method. Each of these methods has its own advantages and limitations, and the appropriate method will depend on the specific situation and the data available.