Mitosis and meiosis are both processes that involve the division of cells. However, they differ in several key ways.
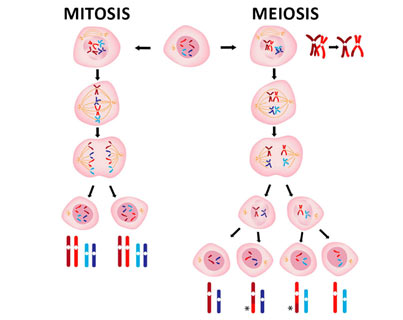
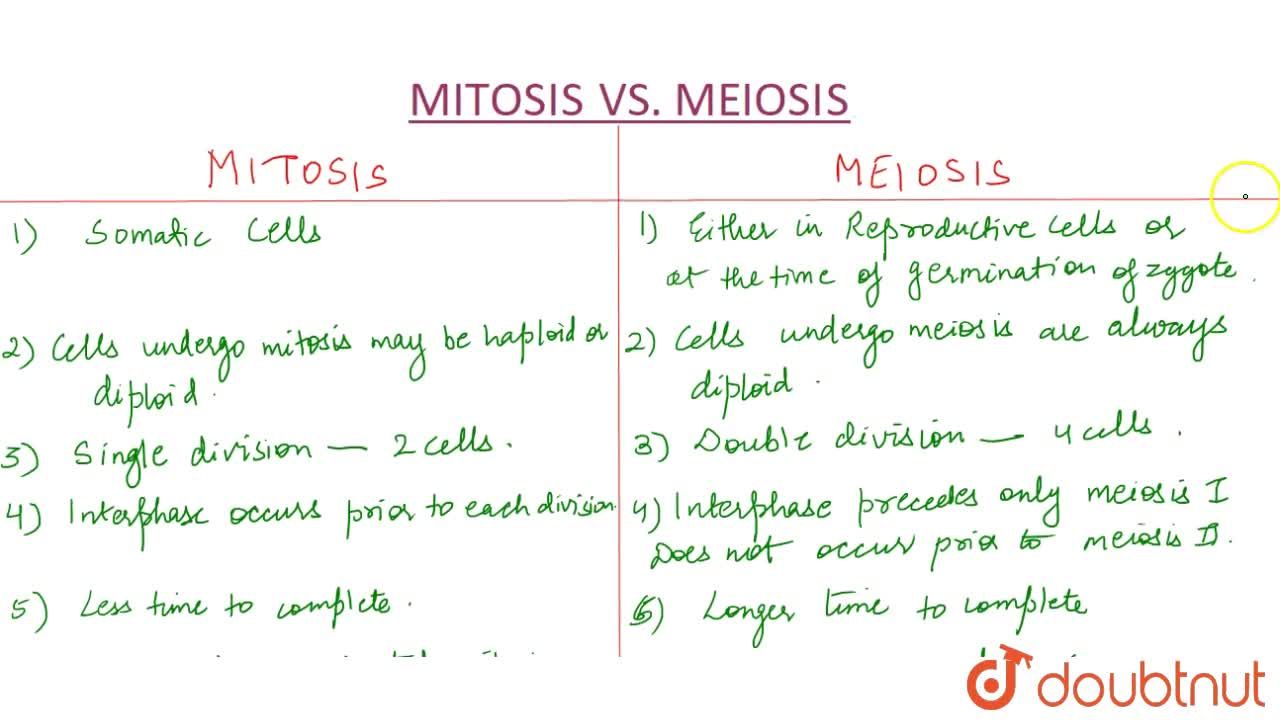
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in somatic cells, or cells that make up the body of an organism. It results in the production of two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The process of mitosis is divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell become visible. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. In anaphase, the chromosomes are separated and move to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, in telophase, the cell begins to divide, forming two new nuclei.
Meiosis, on the other hand, is a type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, such as eggs and sperm. It results in the production of four genetically diverse daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The process of meiosis is also divided into four stages: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I, followed by a second round of division known as prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. During prophase I, the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell become visible and pair up with their homologous chromosomes. In metaphase I, the pairs of chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. In anaphase I, the pairs of chromosomes are separated and move to opposite ends of the cell. Finally, in telophase I, the cell begins to divide, forming two new nuclei. The second round of division is similar to mitosis, with the chromosomes lining up in the center of the cell, separating, and moving to opposite ends of the cell, resulting in the production of four genetically diverse daughter cells.
One key difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced. Mitosis results in the production of two daughter cells, while meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells. Another difference is the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells. In mitosis, the daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while in meiosis, the daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This is because during meiosis, the chromosomes are separated into pairs and only one chromosome from each pair is passed on to each daughter cell.
In summary, mitosis and meiosis are both processes of cell division, but they differ in the number of daughter cells produced and the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells. Mitosis is responsible for the growth and repair of the body, while meiosis is responsible for the production of genetically diverse reproductive cells.