Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in the cells of plants, animals, and other eukaryotic organisms. It is responsible for the production of new cells, which are needed for growth, repair, and replacement of damaged or worn-out cells. During mitosis, the genetic material of a single parent cell is replicated and then equally divided into two daughter cells. This process ensures that the daughter cells receive the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell, maintaining the genetic stability of the organism.
In plants, mitosis occurs in various tissues and organs, including the root, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruit. It is a continuous process that occurs throughout the life of the plant, and it is essential for the growth and development of the plant.
The process of mitosis can be divided into four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
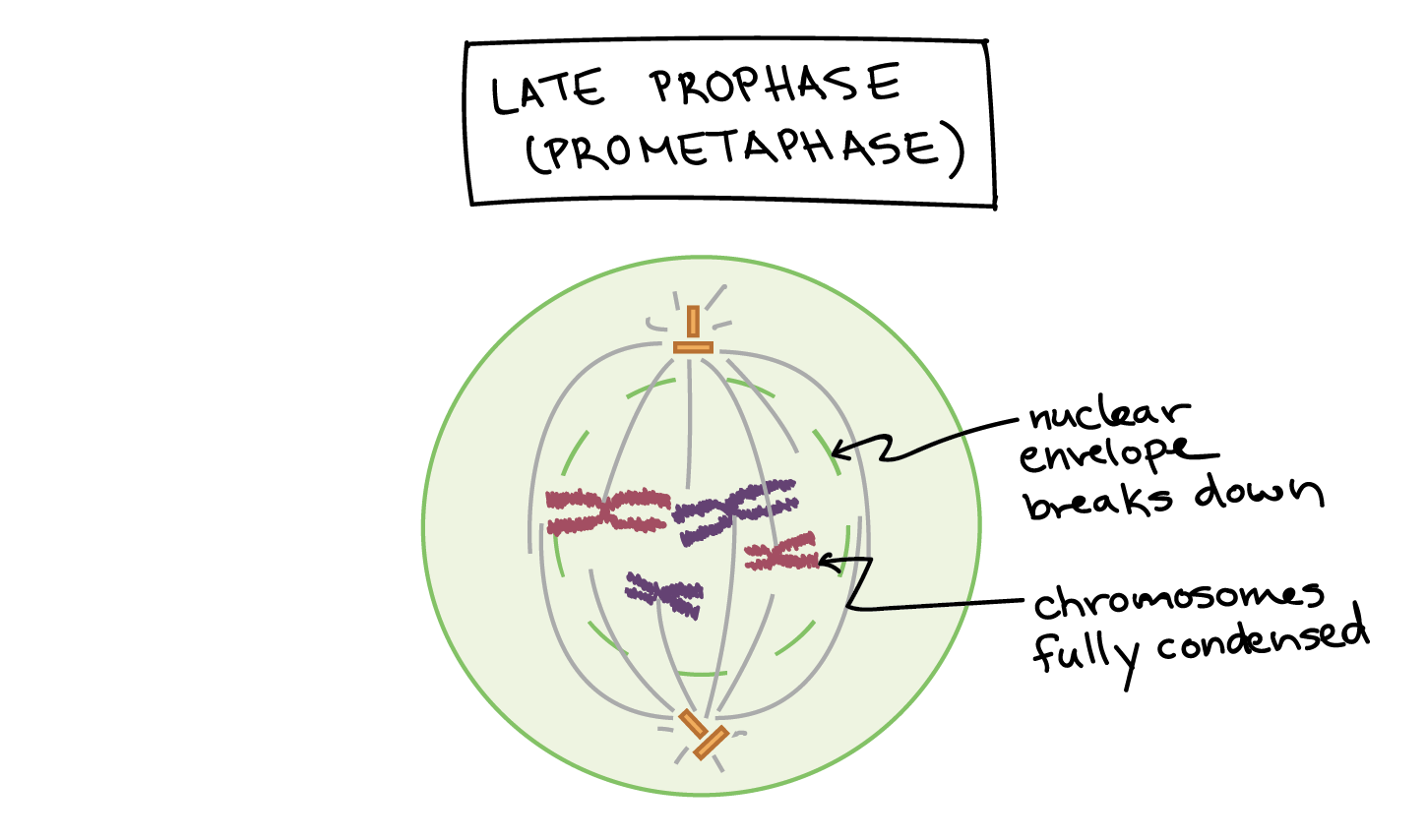
During prophase, the DNA in the nucleus of the parent cell becomes visible as chromatin, and the centrosomes, which are responsible for organizing the mitotic spindle, begin to move to opposite poles of the cell.
During metaphase, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the mitotic spindle, which is made up of microtubules, forms between the centrosomes. The chromosomes line up along the equatorial plane of the cell, with one chromosome from each pair at either pole of the cell.
In anaphase, the centromere of each chromosome splits, and the two sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the mitotic spindle.
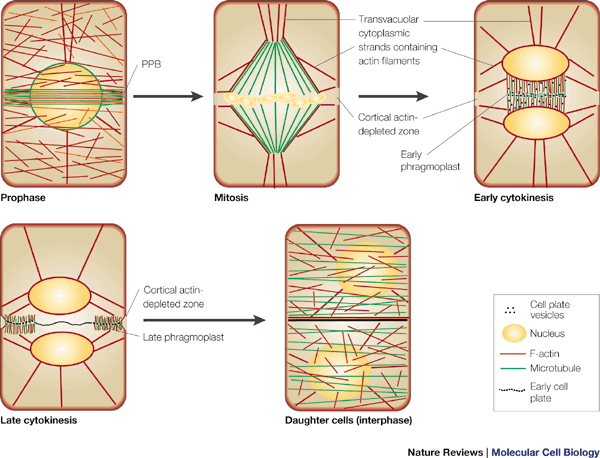
Finally, during telophase, a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells, and a new nucleus forms in each daughter cell. The process of mitosis is now complete, and two genetically identical daughter cells have been produced.
In conclusion, mitosis is a critical process in the life of plants, as it is responsible for the production of new cells and the maintenance of genetic stability. It occurs continuously throughout the life of the plant and is essential for growth and development.
Identifying Mitosis in Plant Cells (2.6.3)
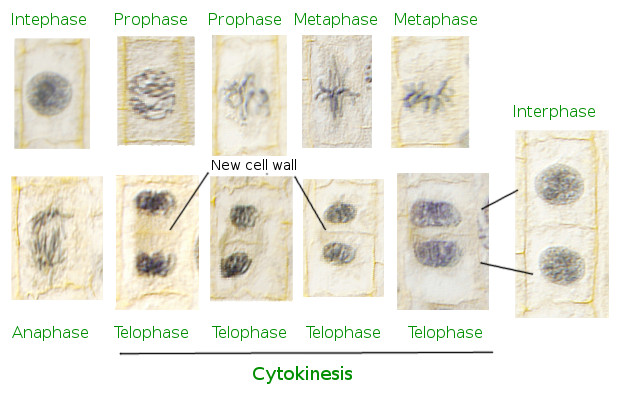
Before mitosis can take place, the parent cell must first create a duplicate of each chromosome in order to ensure that the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell. When such a material is used, all stages of cell division can be observed and studied. What is Animal cell mitosis is the process of the formation of two identical daughter nuclei from a single parent This process is followed by cytokinesis, division of cytoplasm into two identical daughter cells, ultimately resulting in the formation of two identical daughter cells. Whichever your reason is, it is valid! What happens to a plant cell during interphase? Since the growth and development of plants generally relies on a wide range of factors including, humidity, type of soil among other conditions, there is no guarantee that mitosis can always revive the health of every plant with damaged or worn out cells. In order to sustain life these cells need to reproduce from time to time, so as to keep their numbers constant. In fact, we recommend using our assignment help services for consistent results.
Plant Mitosis

Over time, cells suffer from wear and tear and old age, and eventually stop functioning, so it is extremely essential for these cells to be present in large numbers and in a healthy state in order to sustain life. Carrot cells placed in coconut milk do recover the ability to divide, and complete carrot plants with stem, root, leaves, flowers, and seeds have been Figure 3-5 Plant cell mitosis. Where is colchicine obtained from? Cell, 147 1 , 158-172. The prime location of mitosis is the meristem in plant cells, while it occurs throughout the animal body. Bur oak has 24.
Importance of Mitosis in Plants

This cellular suicide prevents cells from producing more damaged daughter cells. Comparison Table Between Mitosis in Plant Cell and Animal Cell Parameters of Comparison Mitosis in Plant Cell Mitosis in Animal Cell Meaning Process of formation of two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell of the plant cell. Though the basic premise and the process is the same, there are some fundamental differences between the two. Metaphase In metastage the spindle grows and forms attachments to the pairs of sister chromatids at the centromere that connects the sister chromatids. Wahlert and Mary Jean Holland, of Baruch College, authored this site showing. The steps are the same as in animal mitosis, but centrioles are not observed: interphase, early prophase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, new cell wall beginning to form between daughter nuclei, and return to interphase produced from isolated carrot root cells.