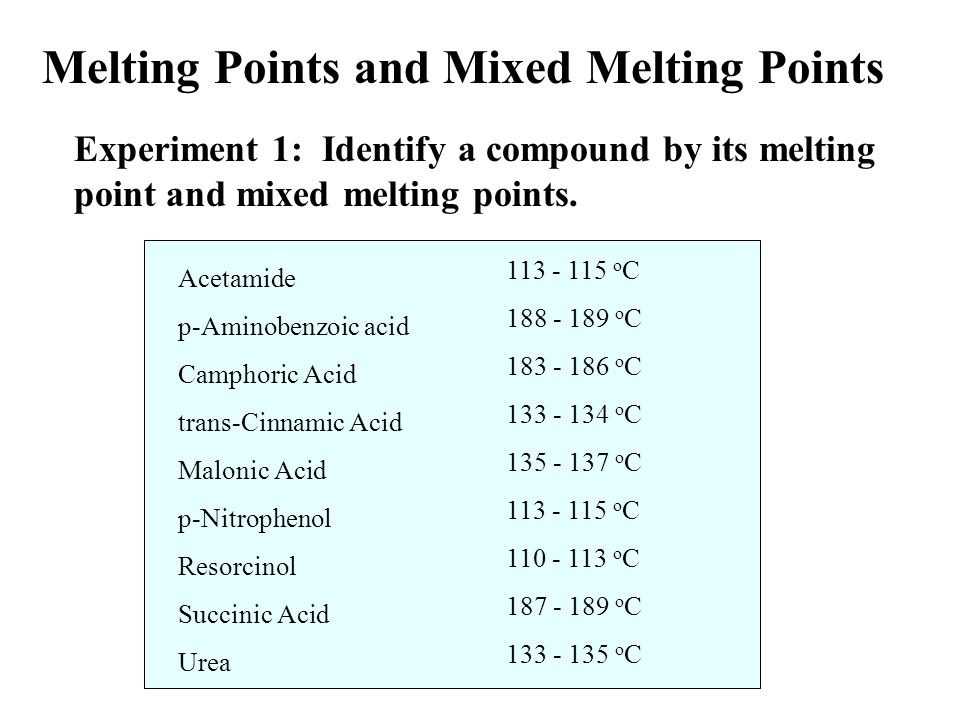
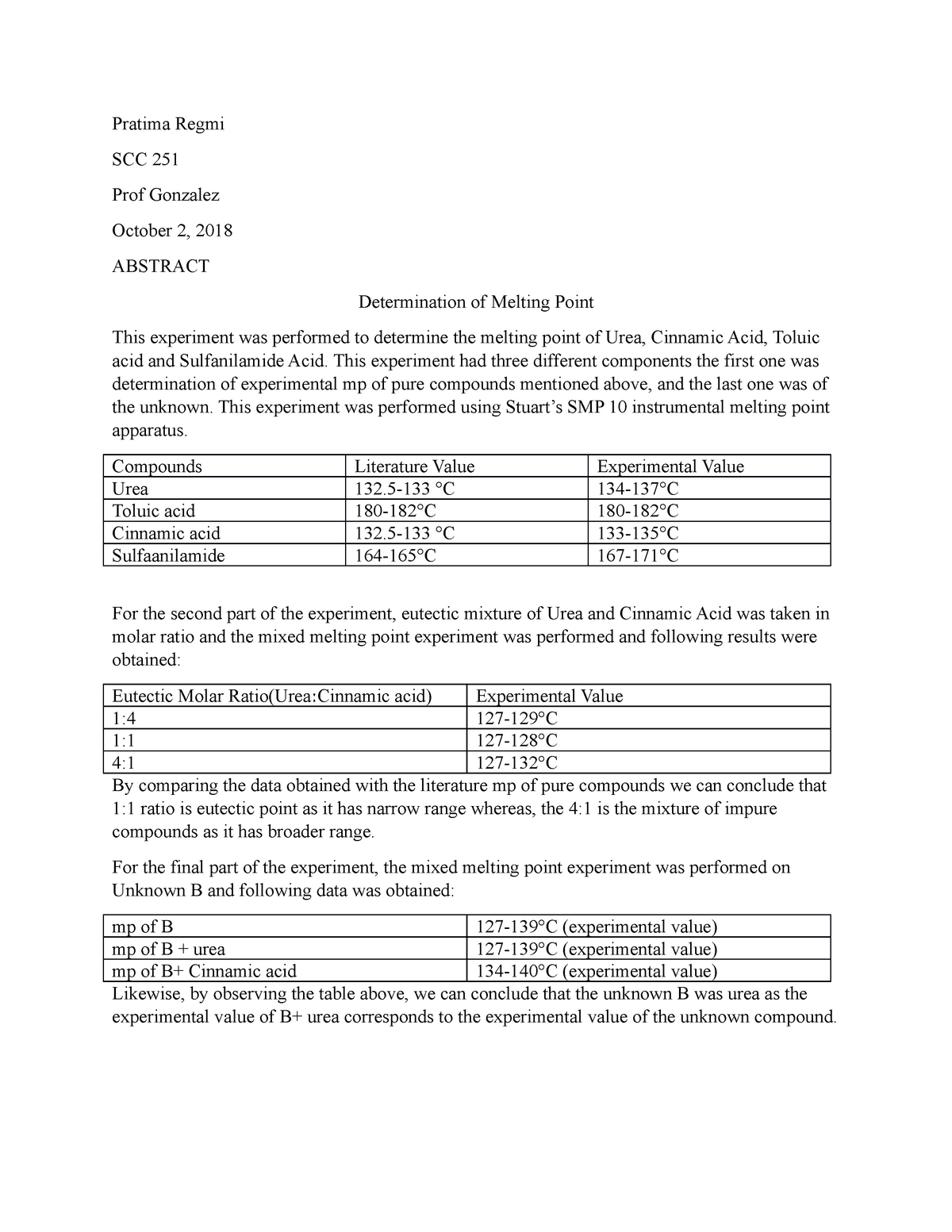
Mixed melting point determination is a technique used in chemistry to determine the purity of a compound and to identify unknown substances. It involves heating a sample of the compound until it melts and comparing the melting point to that of a known pure compound. If the melting point of the sample is the same as the pure compound, then it is likely to be pure. However, if the melting point is different, then the sample may be impure or may be a mixture of two or more compounds.
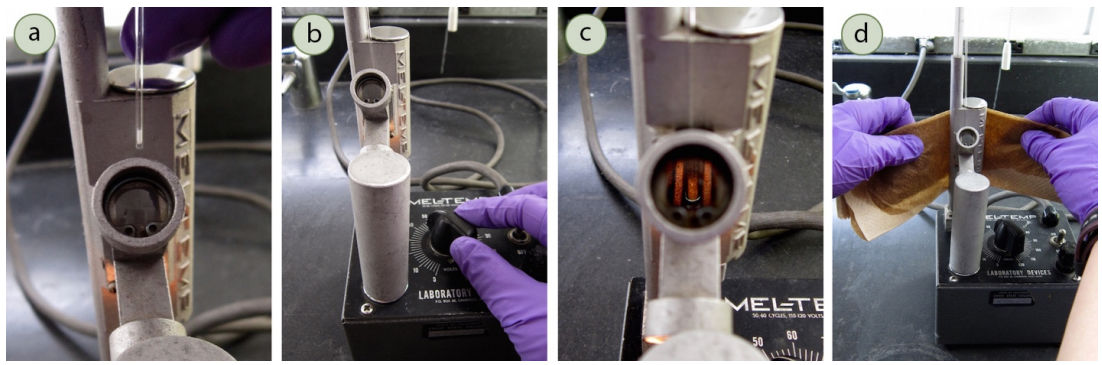
To perform a mixed melting point determination, a sample of the compound is placed in a capillary tube, which is then placed in a melting point apparatus. The apparatus consists of a heating element and a thermometer, which measures the temperature of the sample as it is heated. The sample is heated at a constant rate until it melts, and the temperature at which it melts is recorded as the melting point.
If the sample is a pure compound, its melting point will be a specific, characteristic temperature. This is because the bonds between the atoms in a pure compound are all the same, and they require a specific amount of energy to be broken in order to cause the compound to melt. However, if the sample is impure or is a mixture of two or more compounds, the melting point will be different. This is because the bonds between the atoms in the impure or mixed sample are different, and they require different amounts of energy to be broken.
There are a few factors that can affect the accuracy of a mixed melting point determination. One of these is the size of the sample. If the sample is too small, it may not melt evenly, resulting in an inaccurate melting point. Another factor is the purity of the capillary tube. If the tube is not pure, it may contaminate the sample and affect the melting point. Finally, the heating rate can also affect the accuracy of the melting point. If the sample is heated too quickly, it may not have time to reach its true melting point.
In conclusion, mixed melting point determination is a useful technique for determining the purity of a compound and identifying unknown substances. It involves heating a sample of the compound and comparing its melting point to that of a known pure compound. The accuracy of the melting point determination can be affected by factors such as the size of the sample, the purity of the capillary tube, and the heating rate.