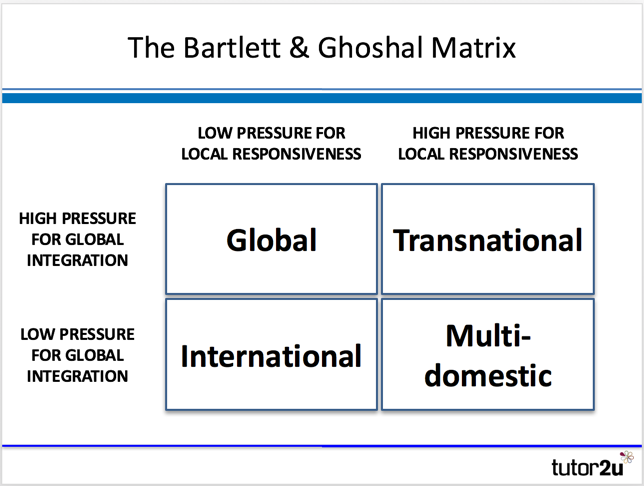
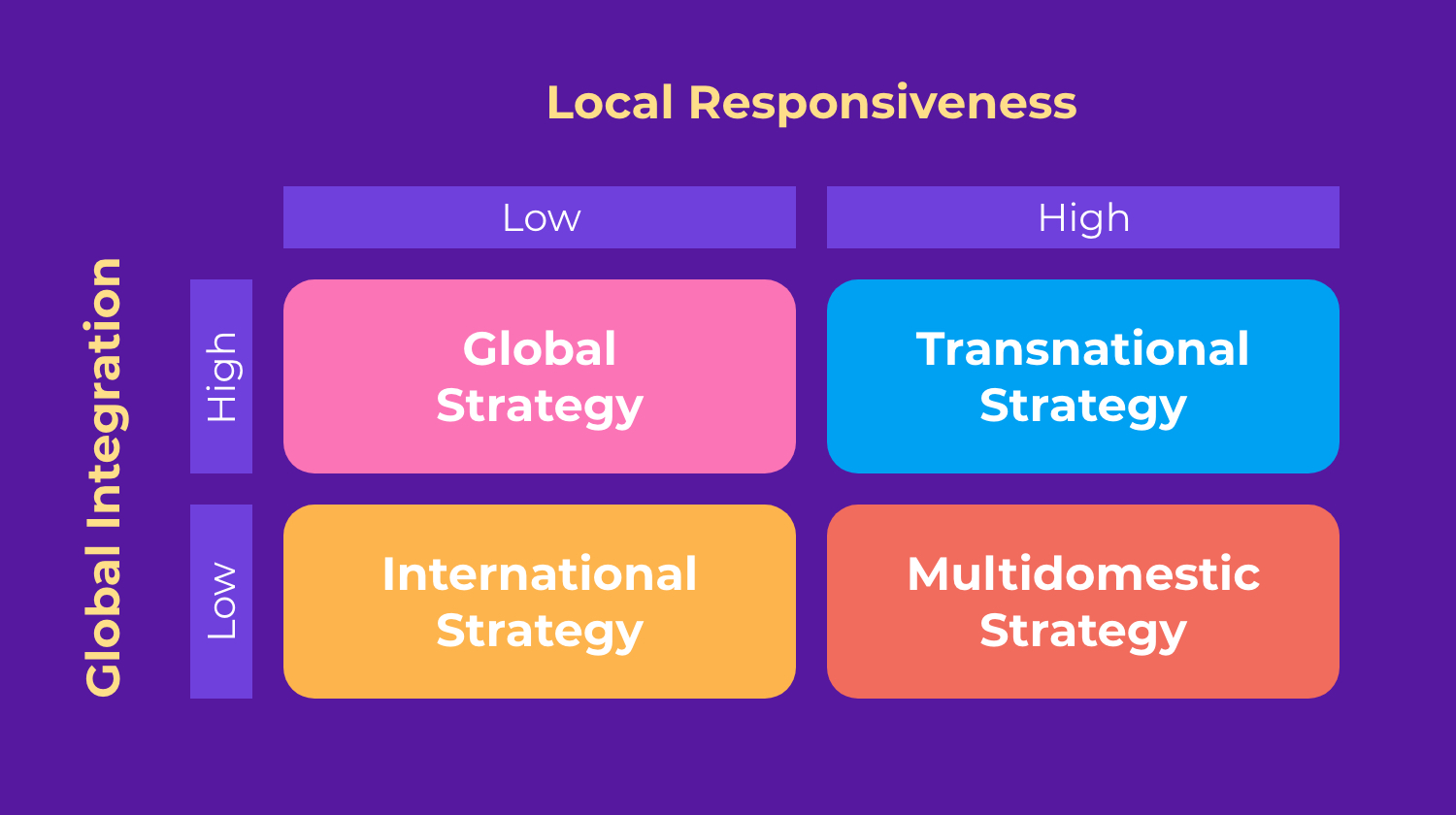
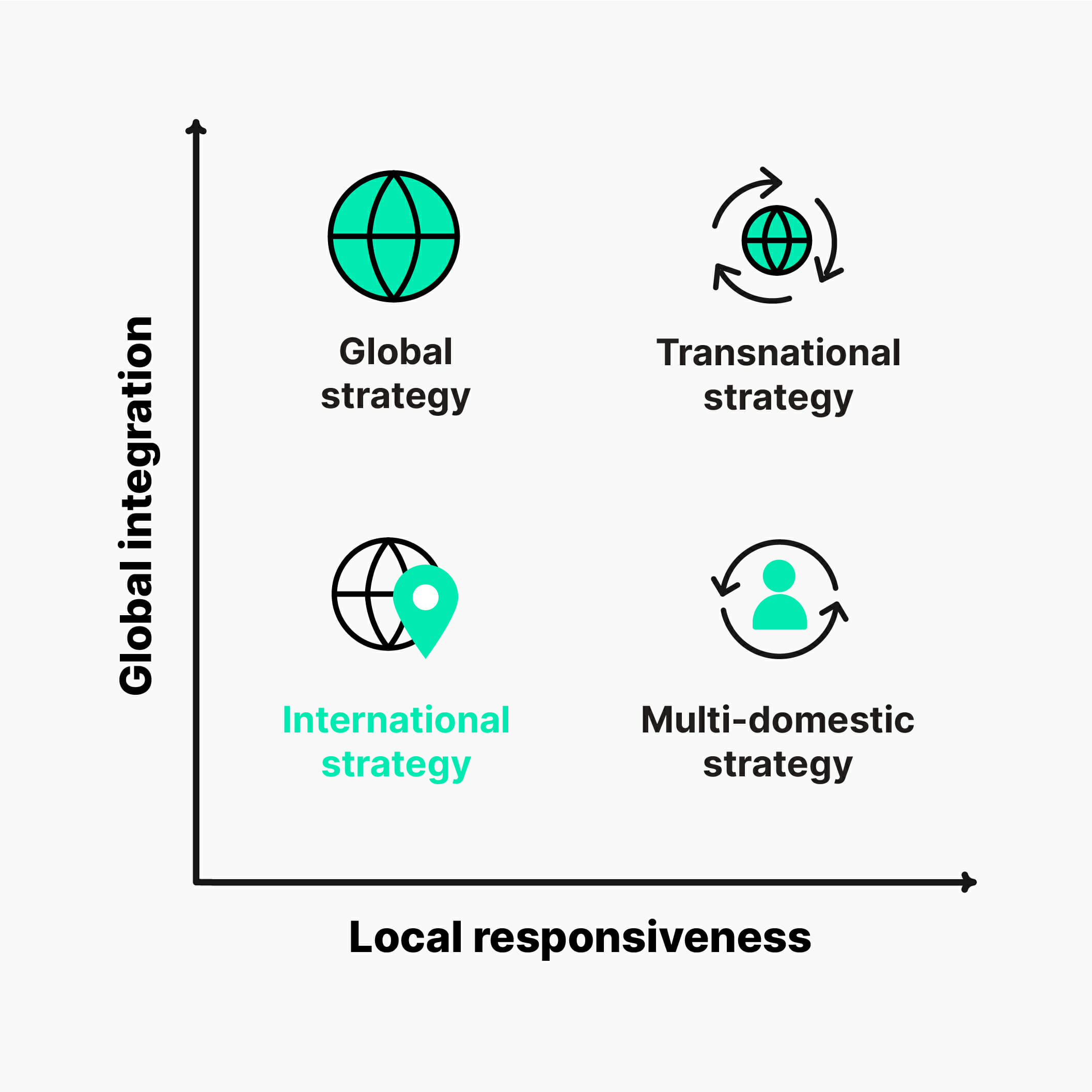
A multidomestic corporation is a type of multinational corporation that operates in multiple countries, but each country is treated as a separate market. This means that the corporation tailors its products, marketing, and operations to each individual country rather than using a standardized global strategy.
One example of a multidomestic corporation is Procter & Gamble (P&G). P&G is a consumer goods company that operates in over 180 countries around the world. In each country, P&G adapts its products and marketing to fit the local culture and tastes. For example, in India, P&G markets its products as being natural and ayurvedic, while in the United States, it focuses on innovation and technology.
Another example of a multidomestic corporation is Yum! Brands, the parent company of fast food chains such as KFC, Pizza Hut, and Taco Bell. Yum! Brands operates in over 150 countries around the world and has adapted its menu and marketing strategies to fit the local tastes and cultural preferences in each country. For example, KFC in India serves a range of vegetarian options and spicy sauces to cater to the local market, while KFC in the United States focuses on its signature fried chicken and sides.
Multidomestic corporations often face the challenge of balancing the need for local adaptation with the benefits of economies of scale. While tailoring products and operations to each country can be costly and time-consuming, it can also be necessary in order to effectively compete in the local market.
Overall, multidomestic corporations can be an effective way for companies to expand into new markets and tap into the growth potential of different countries around the world. By adapting to local cultures and preferences, they can better serve the needs of their customers and build strong relationships in each market.
A multidomestic corporation is a type of multinational corporation (MNC) that operates in multiple countries but adapts its products and business strategies to each individual market. Rather than implementing a standardized approach to global operations, a multidomestic corporation tailors its operations to the unique cultural, economic, and regulatory environments of each country in which it operates.
One example of a multidomestic corporation is Procter & Gamble (P&G). P&G is a consumer goods company that sells a wide range of products, including household cleaning products, personal care products, and health care products. P&G operates in over 180 countries and has a decentralized organizational structure, allowing it to adapt its products and marketing strategies to the specific needs and preferences of each individual market. For example, P&G markets its Tide laundry detergent differently in the United States than it does in China, where consumers have different preferences and cultural expectations.
Another example of a multidomestic corporation is Unilever. Unilever is a consumer goods company that sells a variety of products, including food, home care products, and personal care products. Like P&G, Unilever operates in multiple countries and adjusts its products and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each market. For example, Unilever sells its Dove soap brand in a variety of formulations and packaging sizes to suit different cultural preferences and price points around the world.
A third example of a multidomestic corporation is Nike. Nike is a global sports apparel and footwear company that operates in multiple countries and adapts its products and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of each market. Nike has a decentralized organizational structure, allowing it to tailor its products and marketing strategies to local cultural and sporting traditions and preferences. For example, Nike markets its soccer-specific products differently in Latin America than it does in Europe, where soccer is more popular.
In conclusion, multidomestic corporations are multinational corporations that operate in multiple countries but adapt their products and business strategies to the unique cultural, economic, and regulatory environments of each individual market. Procter & Gamble, Unilever, and Nike are all examples of multidomestic corporations that have successfully implemented this approach to global operations.