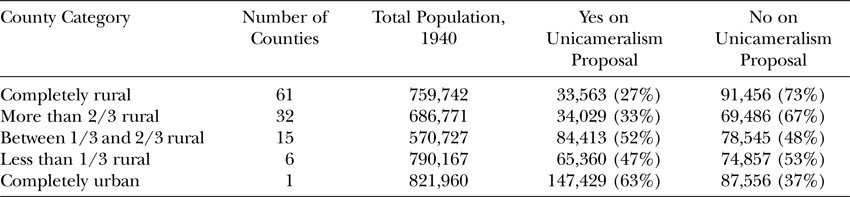
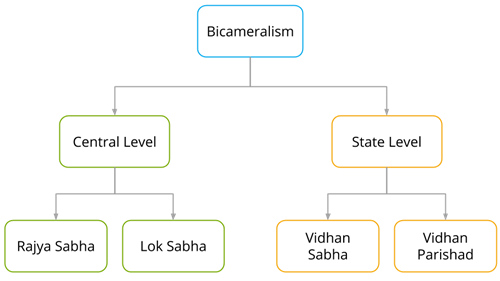
A unicameral system is a type of government in which there is only one legislative chamber or house. This is in contrast to a bicameral system, which has two legislative chambers, such as the United States Congress, which is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
The idea behind a unicameral system is that it allows for more efficient decision-making and reduces the potential for gridlock and political stalemate. In a bicameral system, both chambers must pass legislation before it can become law, which can lead to delays and disagreement. In a unicameral system, there is only one body responsible for passing laws, which means that decisions can be made more quickly and decisively.
There are several countries that operate under a unicameral system, including Denmark, Sweden, and Finland. These countries have historically had strong traditions of consensus-based decision-making and have generally been able to avoid the political polarization and gridlock that can occur in bicameral systems.
One potential downside to a unicameral system is that it can lead to a lack of checks and balances on the legislative process. In a bicameral system, the two chambers can serve as a check on each other, with one chamber serving as a more deliberative body and the other being more responsive to the needs of the public. In a unicameral system, there is no such check, which can lead to abuses of power by the legislative branch.
Despite these potential drawbacks, a unicameral system can have several benefits. It can be more efficient and cost-effective, as there is only one legislative chamber to maintain and fund. It can also be more representative of the will of the people, as there is only one body responsible for making laws.
Overall, a unicameral system can be an effective way of governing a country, particularly in cases where there is a strong tradition of consensus-based decision-making and a commitment to avoiding political polarization. While it may not be suitable for every country, it can be a useful alternative to the more traditional bicameral system.