New drug discovery is the process of identifying and developing new medications to treat diseases and conditions that currently have no cure or insufficient treatment options. This process involves a wide range of disciplines, including biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and clinical medicine, and often takes many years to complete.
The first step in new drug discovery is identifying a target for the drug. This could be a specific protein or enzyme involved in the disease process, a receptor on the surface of a cell, or a genetic mutation that causes the disease. Once a target has been identified, researchers must design and synthesize a compound that can bind to the target and alter its activity in a way that is beneficial to the patient. This compound is known as a lead compound, and it is the starting point for further development.
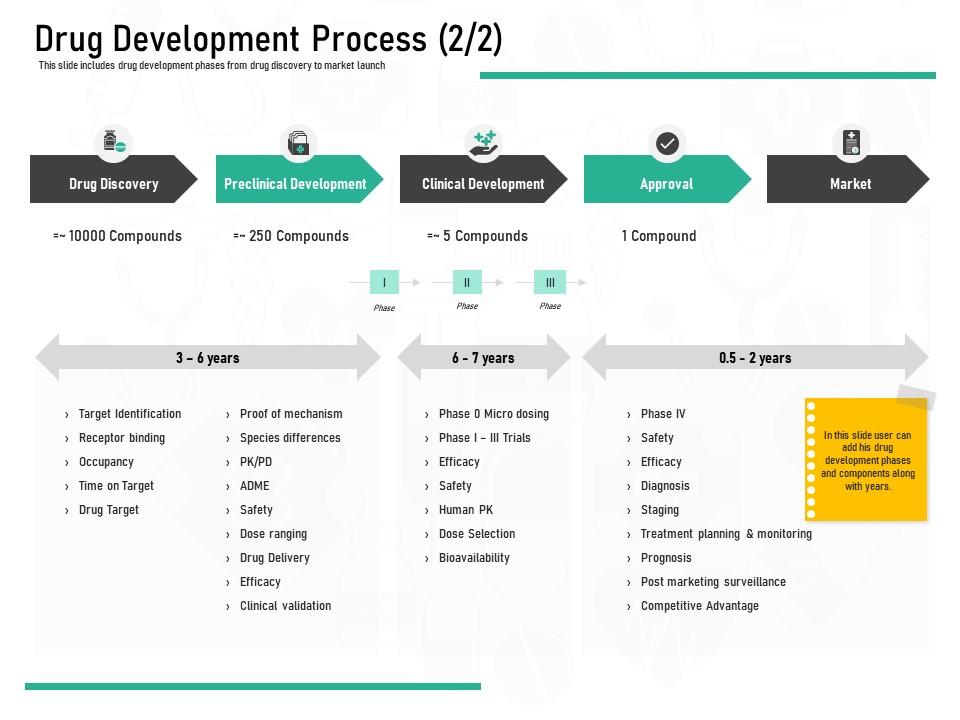
After a lead compound has been identified, it must undergo a series of tests to determine its safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. These tests typically involve animal models and cell culture systems, and may take several years to complete. If the compound shows promise in these tests, it may be tested in clinical trials on human subjects. Clinical trials are conducted in several phases, with each phase designed to answer specific questions about the drug. Phase I trials involve a small number of healthy volunteers and are designed to assess the drug's safety and dosage. Phase II trials involve a larger number of patients and are designed to evaluate the drug's effectiveness. Phase III trials involve an even larger number of patients and are designed to confirm the drug's effectiveness and monitor any side effects.
If a drug successfully completes all phases of clinical trials and receives regulatory approval, it can be marketed and prescribed to patients. However, the process of new drug discovery does not end here. Once a drug is on the market, it must be monitored for any unexpected side effects and may need to be adjusted or withdrawn if necessary. In addition, researchers continue to study the drug to identify any additional uses or to improve its effectiveness.
New drug discovery is a complex and time-consuming process, but it is also an essential part of modern medicine. By developing new drugs, researchers are able to help millions of people around the world by treating and curing diseases that were once thought to be incurable.
Drug Discovery New Drug Development Process

Synthesis and Purification 33. These studies are not necessarily conducted following regulatory statute. In clinical trials, in vivo studies can use either humans or animals as subjects,In vivo studies are able to address the major limitation of in vitro studies, they are able to demonstrate the impact of a pharmaceutical on the body as a whole, rather than how it impacted isolated cells. Clinical trials are used to determine whether new biomedical or behavioral interventions are safe, efficacious, and effective. A claim for categorical exclusion from or submission of an environmental assessment. The Process of New Drug Discovery and Development, Eds.
New drug discovery research PowerPoint (PPT) Presentations, New drug discovery research PPTs

S artichoke products are even standardized to contain a specific amount of cynarin, yet they can still be purchased here as a natural product without a prescription. Plant Based Drugs and Medicines Gaultheria procumbens Rubefacient Methyl salicylate Menthaspecies Rubefacient Menthol Lobelia inflata Smoking deterrant, respiratory stimulant a-LobelineTabebuiasp. In fact, despite the use of many new technologies, and the growing resources and funding for drug research, the number of launches of new medicines in the form of new molecular entities names has been generally decreasing for more than a decade. NDA Review Process 53. Good Laboratory Practice For Nonclinical Studies, U. Frontiers in Oncology, 8. You can view or download New drug discovery research presentations for your school assignment or business presentation.
Drug Development Process

We also focus on the molecular aspects of interactions with their recognized cellular targets, from DNA to microtubules. Related Searches for New drug discovery research Drug Discovery Process Dalla malattia al bersaglio biologico. What makes a good drug target. Journal of Health Economics, 2003; 151-185. Proteomics: It is the study of the proteome, the complete set of proteins produced by a species, using the technologies of large scale protein separation and identification. The lack of exercise due to cage systems may result in metabolic disorders which can pose a threat to the deployment of such systems in the poultry segment. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 32 10 , pp.
Drug Discovery Process

The battery-operated poultry cages are equipped with feeders that help to minimize the waste of feed thus benefiting the poultry farmers and the market positively also. S considering that the same amount of Cynarin is being delivered, dose for dose 10. For example, using X-ray crystallography and in silico computer modeling, they study how the selected molecules link themselves to the therapeutic target, for example, a protein or an enzyme. Drugs usually act on either cellular or genetic chemicals in the body, known as targets, which are believed to be associated with disease. Once the therapeutic target has been identified, scientists must then find one or more leads e.

Drug Discovery Today, 2012; 17:S24-S30. Simultaneously, the knowledge base that supports drug research has expanded considerably, increasing the challenge for chemists to understand their fields of expertise. Drug Discovery Handbook, Wiley Press, 2005; 1-10. First of all, biologists ensure that the chosen compounds have the desired therapeutic or antiviral effects on the target. However, while in vivo studies address the drawback of in vitro studies, they have their own major setback.